Abstract
A paper-based analytical device (PAD) with an integrated composite electrode has been designed and fabricated for non-enzymatic creatinine sensing. Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) was employed to modify the PAD so that it could function as a solid-contact transducer. A new macrocyclic pyrido-hexapeptide derivative was made and used as a special ionophore in the creatinine membrane sensor. The synthesized PAD showed a detection limit of 1.0 µM (S/N = 3) and a potentiometric response towards creatinine throughout a log-linear range of 2.0 µM–10 mM (R2 = 0.9998). The sensor shows significant selectivity for a few related substances, including ephedrine, codeine, ketamine, caffeine, urea, urate, carbinoxamine, and dextromethorphan. It has been established that the testing method is appropriate for the direct potentiometric detection of creatinine in a variety of human urine sample types. When an indicating electrode and a reference electrode are put on the same flexible disposable, this lets applications with a small sample volume be done. For point-of-care creatinine measurement, the developed paper-based analytical equipment is a good choice because it is affordable, easily accessible, and self-pumping (especially when combined with potentiometric detection).
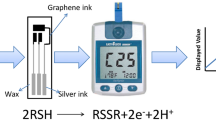
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Nagel B, Dellweg H, Gierasch LM (1992) Glossary for chemists of terms used in biotechnology (IUPAC Recommendations 1992). Pure Appl Chem 64:143–168
Randviir EP, Banks CE (2013) Analytical methods for quantifying creatinine within biological media. Sens Actuators, B Chem 183:239–252
Price CP (2001) Point of care testing Bmj 322:1285–1288
Apilux A, Dungchai W, Siangproh W et al (2010) Lab-on-paper with dual electrochemical/colorimetric detection for simultaneous determination of gold and iron. Anal Chem 82:1727–1732
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Butte MJ, Whitesides GM (2007) Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew Chem 119:1340–1342
Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2009) Electrochemical detection for paper-based microfluidics. Anal Chem 81:5821–5826
Guerreiro JRL, Kamel AH, Sales MGF (2010) FIA potentiometric system based on periodate polymeric membrane sensors for the assessment of ascorbic acid in commercial drinks. Food Chem 120:934–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.015
Yu J, Ge L, Huang J et al (2011) Microfluidic paper-based chemiluminescence biosensor for simultaneous determination of glucose and uric acid. Lab Chip 11:1286–1291
Ma L, Nilghaz A, Choi JR et al (2018) Rapid detection of clenbuterol in milk using microfluidic paper-based ELISA. Food Chem 246:437–441
Ashmawy NH, Almehizia AA, Youssef TA et al (2019) Novel carbon/PEDOT/PSS-based screen-printed biosensors for acetylcholine neurotransmitter and acetylcholinesterase detection in human serum. Molecules 24:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081539
Kamel AH, Galal HR, Awwad NS (2018) Cost-effective and handmade paper-based potentiometric sensing platform for piperidine determination. Anal Methods 10:5406–5415. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ay01811a
Abd-Rabboh HSM, El-Galil A, Amr E, Elsayed EA et al (2021) Paper-based potentiometric sensing devices modified with chemically reduced graphene oxide (CRGO) for trace level determination of pholcodine (opiate derivative drug). RSC Adv 11:12227–12234. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra00581b
Meredith NA, Quinn C, Cate DM et al (2016) Paper-based analytical devices for environmental analysis. Analyst 141:1874–1887
Abdalla NS, Youssef MA, Algarni H, et al (2019) All solid-state poly (vinyl chloride) membrane potentiometric sensor integrated with nano-beads imprinted polymers for sensitive and rapid detection of bispyribac herbicide as organic pollutant. Molecules 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040712
Amr AEGE, Kamel AH, Almehizia AA et al (2021) Paper-based potentiometric sensors for nicotine determination in smokers’ sweat. ACS Omega 6:11340–11347. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00301
Abd-Rabboh HSM, Amr AEGE, Almehizia AA, Kamel AH (2021) Paper-based potentiometric device for rapid and selective determination of salicylhydroxamate as a urinary struvite stone inhibitor. ACS Omega 6:27755–27762. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03135
Gonzalez-Gallardo CL, Arjona N, Álvarez-Contreras L, Guerra-Balcázar M (2022) Electrochemical creatinine detection for advanced point-of-care sensing devices: a review. RSC Adv 12:30785–30802
Lewińska I, Tymecki Ł, Michalec M (2019) An alternative, single-point method for creatinine determination in urine samples with optoelectronic detector. Critical comparison to Jaffé method Talanta 195:865–869
Sittiwong J, Unob F (2016) Paper-based platform for urinary creatinine detection. Anal Sci 32:639–643
Rossini EL, Milani MI, Carrilho E et al (2018) Simultaneous determination of renal function biomarkers in urine using a validated paper-based microfluidic analytical device. Anal Chim Acta 997:16–23
Tseng C-C, Yang R-J, Ju W-J, Fu L-M (2018) Microfluidic paper-based platform for whole blood creatinine detection. Chem Eng J 348:117–124
Chang T-H, Tung K-H, Gu P-W et al (2018) Rapid simultaneous determination of paraquat and creatinine in human serum using a piece of paper. Micromachines 9:586
Talalak K, Noiphung J, Songjaroen T et al (2015) A facile low-cost enzymatic paper-based assay for the determination of urine creatinine. Talanta 144:915–921
Baek SH, Park C, Jeon J, Park S (2020) Three-dimensional paper-based microfluidic analysis device for simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers with a smartphone. Biosensors 10:187
Cincotto FH, Fava EL, Moraes FC et al (2019) A new disposable microfluidic electrochemical paper-based device for the simultaneous determination of clinical biomarkers. Talanta 195:62–68
Fava EL, Martimiano do Prado T, Almeida Silva T, et al (2020) New disposable electrochemical paper-based microfluidic device with multiplexed electrodes for biomarkers determination in urine sample. Electroanalysis 32:1075–1083
Boobphahom S, Ruecha N, Rodthongkum N et al (2019) A copper oxide-ionic liquid/reduced graphene oxide composite sensor enabled by digital dispensing: non-enzymatic paper-based microfluidic determination of creatinine in human blood serum. Anal Chim Acta 1083:110–118
Amr A, Abo-Ghalia M, Moustafa G et al (2018) Design, synthesis and docking studies of novel macrocyclic pentapeptides as anticancer multi-targeted kinase inhibitors. Molecules 23:2416. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102416
Hu L, Choi JW, Yang Y et al (2009) Highly conductive paper for energy-storage devices. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:21490–21494
Bakker E (1996) Determination of improved selectivity coefficients of polymer membrane ion-selective electrodes by conditioning with a discriminated ion. J Electrochem Soc 143:L83–L85. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1836608
Bobacka J (1999) Potential stability of all-solid-state ion-selective electrodes using conducting polymers as ion-to-electron transducers. Anal Chem 71:4932–4937
Fibbioli M, Morf WE, Badertscher M et al (2000) Potential drifts of solid-contacted ion-selective electrodes due to zero-current ion fluxes through the sensor membrane. Electroanalysis: Int J Devoted to Fundamental and Practical Aspects of Electroanalysis 12:1286–1292
Cram DJ (1988) The design of molecular hosts, guests, and their complexes (Nobel lecture). Angew Chem, Int Ed Engl 27:1009–1020
Kelly TR, Maguire MP (1987) A receptor for the oriented binding of uric acid type molecules. J Am Chem Soc 109:6549–6551
Chang SK, Van Engen D, Fan E, Hamilton AD (1991) Hydrogen bonding and molecular recognition: synthetic, complexation, and structural studies on barbiturate binding to an artificial receptor. J Am Chem Soc 113:7640–7645
Hegde V, Madhukar P, Madura JD, Thummel RP (1990) Fischer route to pyrido [3, 2-g] indoles. A novel receptor for urea derivatives. J Am Chem Soc 112:4549–4550
Rebek J Jr, Askew B, Killoran M et al (1987) Convergent functional groups. 3. A molecular cleft recognizes substrates of complementary size, shape, and functionality. J Am Chem Soc 109:2426–2431
Gbinigie O, Thompson M, Price CP, et al (2014) Point-of-care creatinine testing for the detection and monitoring of chronic kidney disease. National Institute for Health Research, Horizon Scan Rep 38
Dal Dosso F, Decrop D, Pérez-Ruiz E et al (2018) Creasensor: SIMPLE technology for creatinine detection in plasma. Anal Chim Acta 1000:191–198
Guinovart T, Hernández-Alonso D, Adriaenssens L et al (2017) Characterization of a new ionophore-based ion-selective electrode for the potentiometric determination of creatinine in urine. Biosens Bioelectron 87:587–592
Hassan SSM, Elnemma EM, Mohamed AHK (2005) Novel biomedical sensors for flow injection potentiometric determination of creatinine in human serum. Electroanalysis 17:2246–2253. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200503363
Acknowledgements
The authors present their deep thanks for prof. A.E.G.E. Amr for supporting the ionophores used in this work.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, through the project number KKU-IFP2-P-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The listed authors contributed to this work as follows: A.H.K. provided the concepts of the work; A.H.K. and H.S.M.A. interpreted the results. A. H. K. and M. A. B. performed the experimental part. A. H. K. and H. S. M. A. prepared the manuscript; A.H.K. performed the revision before submission; H.S., M.A., and M. A. B. obtained the financial support for the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kamel, A.H., Abd-Rabboh, H.S.M. & Bajaber, M.A. Non-enzymatic paper-based analytical device for direct potentiometric detection of urine creatinine. Microchim Acta 191, 128 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06203-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06203-9