Abstract
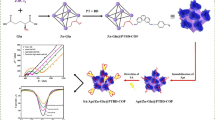
An electrochemical aptsensor for deoxynivalenol determination was successfully designed and constructed based on a defective bimetallic organic framework (denoted as ZrTi-MOF). The high porosity, large specific surface area, several structural defects, mixed metal clusters, and rich functionality of ZrTi-MOF markedly enhanced its electrochemical activity and facilitated the aptamer immobilization. As a result, the ZrTi-MOF–based aptasensor shows high sensitivity to detect deoxynivalenol via specific recognition between aptamer and deoxynivalenol, as well as the formation of aptamer-deoxynivalenol complex. On this basis, the developed ZrTi-MOF–based impedimetric aptasensor showed a low detection limit of 0.24 fg mL−1 for deoxynivalenol determination in the deoxynivalenol concentration range 1 fg mL−1– 1 ng mL−1 under optimized conditions, which also exhibited satisfactory selectivity, stability, reproducibility, and regenerability. Furthermore, determination of deoxynivalenol was achieved in bread and wheat flour samples via the developed ZrTi-MOF–based deoxynivalenol aptasensor. The result from this study showed that the ZrTi-MOF–based electrochemical aptasensor could become a promising strategy for detecting deoxynivalenol in foodstuffs in the future.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Gerez JR, Desto SS, Bracarense APFRL (2017) Deoxynivalenol induces toxic effects in the ovaries of pigs: an ex vivo approach. Theriogenology 90:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.10.023
Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuff, in: C.R. (EC) (Ed.) 1881, European Commission, Official Journal of the European Union L, 2006, pp. 5–24. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eur/2006/1881
Authority E F S (2004) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on contaminants in the food chain [CONTAM] related to deoxynivalenol (DON) as undesirable substance in animal feed. EFSA J 2(6):73. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2004.73
Guidance for Industry and FDA, in: Advisory levels for deoxynivalenol (DON) in finished wheat products for human consumption and grains and grain by-products used for animal feed, U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2010). https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-industry-and-fda-advisory-levels-deoxynivalenol-don-finished-wheat-products-human
Hickert S, Gerding J, Ncube E, Hübner F, Flett B, Cramer B, Humpf H-U (2015) A new approach using micro HPLC-MS/MS for multi-mycotoxin analysis in maize samples. Mycotoxin Res 31(2):109–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-015-0221-y
Meaney MS, McGuffin VL (2008) Luminescence-based methods for sensing and detection of explosives. Anal Bioanal Chem 391(7):2557–2576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2194-6
Stroka J, Anklam E (2000) Development of a simplified densitometer for the determination of aflatoxins by thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr A 904(2):263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00947-X
Wu H, Fan D, Cheng J (2022) Development and validation of an UHPLC–Ms/Ms method for the determination of 32 pyrrolizidine alkaloids in Chinese wild honey. J AOAC INT 106(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsac094
Liu J-M, Hu Y, Yang Y-K, Liu H, Fang G-Z, Lu X, Wang S (2018) Emerging functional nanomaterials for the detection of food contaminants. Trends Food Sci Technol 71:94–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.11.005
Deng Z, Li M, Hu Y, He Y, Tao B, Yuan Z, Wang R, Chen M, Luo Z, Cai K (2021) Injectable biomimetic hydrogels encapsulating gold/metal–organic frameworks nanocomposites for enhanced antibacterial and wound healing activity under visible light actuation. Chem Eng J 420:129668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129668
Dong J, Wen L, Yang H, Zhao J, He C, Hu Z, Peng L, Hou C, Huo D (2022) Catalytic hairpin assembly-driven ratiometric dual-signal electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA based on the ratios of Fe-MOFs and MB-GA-UiO-66-NH2. Anal Chem 94(15):5846–5855. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05293
Olcer Z, Esen E, Muhammad T, Ersoy A, Budak S, Uludag Y (2014) Fast and sensitive detection of mycotoxins in wheat using microfluidics based real-time electrochemical profiling. Biosens Bioelectron 62:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.025
Liu X, Cheng H, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Li F (2022) Portable electrochemical biosensor based on laser-induced graphene and MnO2 switch-bridged DNA signal amplification for sensitive detection of pesticide. Biosens Bioelectron 199:113906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113906
Peng Y, Geng L, Liu X, Liu M, Wu H, Li J (2019) A label-free small molecular hydrogel-based electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of deoxynivalenol. Anal Methods-UK 11(47):5948–5952. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AY02018G
Wei K, Sun J, Gao Q, Yang X, Ye Y, Ji J, Sun X (2021) 3D “honeycomb” cell/carbon nanofiber/gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) modified screen-printed electrode for electrochemical assessment of the combined toxicity of deoxynivalenol family mycotoxins. Bioelectrochemistry 139:107743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2021.107743
Hong F, Chen R, Lu P, Li L, Xiao R, Chen Y, Yang H (2022) A universal, portable, and ultra-sensitive pipet immunoassay platform for deoxynivalenol detection based on dopamine self-polymerization-mediated bioconjugation and signal amplification. J Hazard Mater 436:129257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129257
Zhang Z, Lou Y, Guo C, Jia Q, Song Y, Tian J-Y, Zhang S, Wang M, He L, Du M (2021) Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based chemosensors/biosensors for analysis of food contaminants. Trends Food Sci Technol 118:569–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.10.024
Song Y, Xu M, Li Z, He L, Hu M, He L, Zhang Z, Du M (2020) A bimetallic CoNi-based metal−organic framework as efficient platform for label-free impedimetric sensing toward hazardous substances. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 311:127927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127927
Zhou H-CJ, Kitagawa S (2014) Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem Soc Rev 43(16):5415–5418. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS90059F
Zhang S, Rong F, Guo C, Duan F, He L, Wang M, Zhang Z, Kang M, Du M (2021) Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based electrochemical biosensors for early cancer diagnosis in vitro. Coord Chem Rev 439:213948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213948
Wen X, Huang Q, Nie D, Zhao X, Cao H, Wu W, Han Z (2021) A multifunctional N-doped Cu–MOFs (N–Cu–MOF) nanomaterial-driven electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive detection of deoxynivalenol. Molecules 26(8):2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082243
Hu M, Zhu L, Li Z, Guo C, Wang M, Wang C, Du M (2021) CoNi bimetallic metal–organic framework as an efficient biosensing platform for miRNA 126 detection. Appl Surf Sci 542:148586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148586
Rezki M, Septiani NLW, Iqbal M, Adhika DR, Wenten IG, Yuliarto B (2021) Review—recent advance in multi-metallic metal organic frameworks (mm-mof) and their derivatives for electrochemical biosensor application. J Electrochem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ac3713
Guo C, Su F, Song Y, Hu B, Wang M, He L, Peng D, Zhang Z (2017) Aptamer-templated silver nanoclusters embedded in zirconium metal–organic framework for bifunctional electrochemical and spr aptasensors toward carcinoembryonic antigen. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(47):41188–41199. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b14952
Wang K, He B, Xie L, Li L, Yang J, Liu R, Wei M, Jin H, Ren W (2021) Exonuclease III-assisted triple-amplified electrochemical aptasensor based on PtPd NPs/PEI-rGO for deoxynivalenol detection. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 349:130767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130767
Ru J, Wang X, Cui X, Wang F, Ji H, Du X, Lu X (2021) GaOOH-modified metal-organic frameworks UiO-66-NH2: selective and sensitive sensing four heavy-metal ions in real wastewater by electrochemical method. Talanta 234:122679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122679
Li W, Zhang X, Hu X, Shi Y, Liang N, Huang X, Wang X, Shen T, Zou X, Shi J (2022) Simple design concept for dual-channel detection of ochratoxin a based on bifunctional metal–organic framework. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14(4):5615–5623. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c22809
Song H, Sun Z, Xu Y, Han Y, Xu J, Wu J, Sun T, Meng H, Zhang X (2019) Fabrication of NH2-MIL-125(Ti) incorporated TiO2 nanotube arrays composite anodes for highly efficient PEC water splitting. Sep Purif Technol 228:115764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115764
Xu Z, Zhao G, Ullah L, Wang M, Wang A, Zhang Y, Zhang S (2018) Acidic ionic liquid based UiO-67 type MOFs: a stable and efficient heterogeneous catalyst for esterification. RSC Adv 8(18):10009–10016. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01119B
Wang M, Yang L, Hu B, Liu Y, Song Y, He L, Zhang Z, Fang S (2018) A novel electrochemical sensor based on Cu3P@NH2-MIL-125(Ti) nanocomposite for efficient electrocatalytic oxidation and sensitive detection of hydrazine. Appl Surf Sci 445:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.144
Thévenot DR, Toth K, Durst RA, Wilson GS (2001) Electrochemical biosensors: recommended definitions and classification 1 International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Physical Chemistry Division, Commission I.7 (Biophysical Chemistry); Analytical Chemistry Division, Commission V.5 (Electroanalytical Chemistry). Biosens Bioelectron 16(1):121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-5663(01)00115-4
Kim S-N, Kim J, Kim H-Y, Cho H-Y, Ahn W-S (2013) Adsorption/catalytic properties of MIL-125 and NH2-MIL-125. Catal Today 204:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.08.014
Mahapatro A, Johnson DM, Patel DN, Feldman MD, Ayon AA, Agrawal CM (2006) Surface modification of functional self-assembled monolayers on 316l stainless steel via lipase catalysis. Langmuir 22(3):901–905. https://doi.org/10.1021/la052817h
Pauliukaite R, Ghica ME, Fatibello-Filho O, Brett CMA (2010) Electrochemical impedance studies of chitosan-modified electrodes for application in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Electrochim Acta 55(21):6239–6247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.09.055
Lu J, Do I, Drzal LT, Worden RM, Lee I (2008) Nanometal-decorated exfoliated graphite nanoplatelet based glucose biosensors with high sensitivity and fast response. ACS Nano 2(9):1825–1832. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn800244k
Yuan K, Ni Y, Zhang L (2012) Facile hydrothermal synthesis of polyhedral Fe3O4 nanocrystals, influencing factors and application in the electrochemical detection of H2O2. J Alloy Compd 532:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.04.007
Yang H, Liu Y, Luo S, Zhao Z, Wang X, Luo Y, Wang Z, Jin J, Ma J (2017) Lateral-size-mediated efficient oxygen evolution reaction: insights into the atomically thin quantum dot structure of NiFe2O4. ACS Catal 7(8):5557–5567. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b00007
Sarabaegi M, Roushani M, Hosseini H, Hoseini SJ, Bahrami M (2020) Facile synthesis of a covalent organic framework (COF) based on the reaction of melamine and trimesic acid incorporated electrospun nanofiber and its application as an electrochemical tyrosinamide aptasensor. New J Chem 44(35):14922–14927. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ02837A
Wang M, Hu M, Liu J, Guo C, Peng D, Jia Q, He L, Zhang Z, Du M (2019) Covalent organic framework-based electrochemical aptasensors for the ultrasensitive detection of antibiotics. Biosens Bioelectron 132:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.040
Zhang K, Lu L, Liu Z, Cao X, Lv L, Xia J, Wang Z (2022) Metal-organic frameworks-derived bimetallic oxide composite nanozyme fiber membrane and the application to colorimetric detection of phenol. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects 650:129662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129662
Zhang Z-H, Duan F-H, Tian J-Y, He J-Y, Yang L-Y, Zhao H, Zhang S, Liu C-S, He L-H, Chen M, Chen D-M, Du M (2017) Aptamer-embedded zirconium-based metal–organic framework composites prepared by de novo bio-inspired approach with enhanced biosensing for detecting trace analytes. ACS Sensors 2(7):982–989. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00236
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project, China (Nos. 212102210203 and 222102310153) and Xinxiang City Science and Technology Research Project, China (No. GG2021002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mengmeng Kang: Investigation, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, funding acquisition, data collection and analysis. Shunjiang Huang: Investigation, data collection and analysis. Mengfei Wang: Investigation, data collection and analysis. Olayinka Oderinde: Writing — review and editing. Minghua Wang: Formal analysis, writing — review and editing, funding acquisition. Zhihong Zhang: Investigation, methodology, formal analysis; supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, M., Huang, S., Wang, M. et al. Defective zirconium/titanium bimetallic metal–organic framework as a highly selective and sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for deoxynivalenol determination in foodstuffs. Microchim Acta 190, 358 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05935-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05935-4