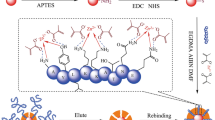
Abstract
A novel molecular-imprinted polymer (MIP)–based enzyme-free biosensor was created for the selective detection of glycoprotein transferrin (Trf). For this purpose, MIP-based biosensor for Trf was prepared by electrochemical co-polymerization of novel hybrid monomers 3-aminophenylboronic acid (M-APBA) and pyrrole on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) modified with carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes (cMWCNTs). Hybrid epitopes of Trf (C-terminal fragment and glycan) have been selected as templates. The produced sensor exhibited great selective recognition ability toward Trf under optimal preparation conditions, offering good analytical range (0.125–1.25 μM) with a detection limit of 0.024 μM. The proposed hybrid epitope in combination with hybrid monomer-mediated imprinting strategy was successfully applied to detect Trf in spiked human serum samples, with recoveries and relative standard deviations ranging from 94.7 to 106.0% and 2.64 to 5.32%, respectively. This study provided a reliable protocol for preparing hybrid epitopes and monomers-mediated MIP for the synergistic and effective determination of glycoprotein in complicated biological samples.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated in this article are included within the main texts and its supplementary information file. Data will be also available on request.
References
Chen H, Liu K, Li Z, Wang P (2019) Point of care testing for infectious diseases. Clin Chim Acta 493:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2019.03.008
Shrivastava S, Trung TQ, Lee NE (2020) Recent progress, challenges, and prospects of fully integrated mobile and wearable point-of-care testing systems for self-testing. Chem Soc Rev 49(6):1812–1866. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cs00319c
Caslavska J, Joneli J, Wanzenried U, Schiess J, Thormann W (2012) Transferrin immunoextraction for determination of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin in human serum by capillary zone electrophoresis. J Sep Sci 35(24):3521–3528. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201200712
Brandsma ME, Jevnikar AM, Ma S (2011) Recombinant human transferrin: beyond iron binding and transport. Biotechnol Adv 29(2):230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.11.007
Keenan J, Pearson D, O’Driscoll L, Gammell P, Clynes M (2006) Evaluation of recombinant human transferrin (DeltaFerrin(TM)) as an iron chelator in serum-free media for mammalian cell culture. Cytotechnology 51(1):29–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-006-9011-x
Duan R, Peng C, Sun L, Zhang L-X, Bai C-C, Dong L-Y, Wang X-H (2021) Integrating boronate affinity controllable-oriented surface imprinting nylon wire and pH-triggered allochroic-graphene oxide for ultrasensitive detection of glycoprotein. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 330:129310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129310
Rasouli Z, Ghavami R (2020) Simultaneous optical detection of human serum albumin and transferrin in body fluids. Mikrochim Acta 187(4):208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4178-y
Ma X, Li M, Tong P, Zhao C, Li J, Xu G (2020) A strategy for construction of highly sensitive glycosyl imprinted electrochemical sensor based on sandwich-like multiple signal enhancement and determination of neural cell adhesion molecule. Biosens Bioelectron 156:112150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112150
Zhao W, Li B, Xu S, Zhu Y, Liu X (2020) A fabrication strategy for protein sensors based on an electroactive molecularly imprinted polymer: cases of bovine serum albumin and trypsin sensing. Anal Chim Acta 1117:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.04.023
Kalecki J, Iskierko Z, Cieplak M, Sharma PS (2020) Oriented immobilization of protein templates: a new trend in surface imprinting. ACS Sens 5(12):3710–3720. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01634
Akiba U, Anzai JI (2016) Recent progress in electrochemical biosensors for glycoproteins. Sensors (Basel) 16 (12):2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122045
Xing R, Guo Z, Lu H, Zhang Q, Liu Z (2022) Molecular imprinting and cladding produces antibody mimics with significantly improved affinity and specificity (97–93). Science Bulletin 67(3):278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.10.006
Kumar V, Kim KH (2022) Use of molecular imprinted polymers as sensitive/selective luminescent sensing probes for pesticides/herbicides in water and food samples. Environ Pollut 299:118824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118824
Lee MH, Liu KH, Thomas JL, Chen CY, Chen CY, Yang CH, Lin HY (2022) Doping of MXenes enhances the electrochemical response of peptide-imprinted conductive polymers for the recognition of C-Reactive protein. Biosens Bioelectron 200:113930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113930
Batista AD, Rajpal S, Keitel B, Dietl S, Fresco-Cala B, Dinc M, Groß R, Sobek H, Münch J, Mizaikoff B (2022) Plastic antibodies mimicking the ACE2 receptor for selective binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike. Adv Mater Interfaces 9(5):2101925. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202101925
Palladino P, Minunni M, Scarano S (2018) Cardiac Troponin T capture and detection in real-time via epitope-imprinted polymer and optical biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 106:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.068
Pirzada M, Sehit E, Altintas Z (2020) Cancer biomarker detection in human serum samples using nanoparticle decorated epitope-mediated hybrid MIP (86–11). Biosens Bioelectron 166:112464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112464
Qin YP, Wang HY, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2018) Metal chelation dual-template epitope imprinting polymer via distillation-precipitation polymerization for recognition of porcine serum albumin. Talanta 185:620–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.03.082
Matsumoto H, Sunayama H, Kitayama Y, Takano E, Takeuchi T (2019) Site-specific post-imprinting modification of molecularly imprinted polymer nanocavities with a modifiable functional monomer for prostate cancer biomarker recognition (19–31). Sci Technol Adv Mater 20(1):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2019.1583495
Turan E, Zengin A, Suludere Z, Kalkan NO, Tamer U (2022) Construction of a sensitive and selective plasmonic biosensor for prostate specific antigen by combining magnetic molecularly-imprinted polymer and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (22–1). Talanta 237:122926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122926
Drzazgowska J, Schmid B, Sussmuth RD, Altintas Z (2020) Self-assembled monolayer epitope bridges for molecular imprinting and cancer biomarker sensing (68–14). Anal Chem 92(7):4798–4806. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03813
Truta LAANA, Sales MGF (2019) Carcinoembryonic antigen imprinting by electropolymerization on a common conductive glass support and its determination in serum samples (31–26). Sens Actuators, B Chem 287:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.02.033
Tang P, Wang Y, Huo J, Lin X (2018) Love wave sensor for prostate-specific membrane antigen detection based on hydrophilic molecularly-imprinted polymer (62–35). Polymers (Basel) 10 (5):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050563
Selvolini G, Marrazza G (2017) MIP-based sensors: promising new tools for cancer biomarker determination. Sensors (Basel) 17 (4):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040718
Mehmandoust M, Erk N, Karaman C, Karaman O (2022) An electrochemical molecularly imprinted sensor based on CuBi2O4/rGO@MoS2 nanocomposite and its utilization for highly selective and sensitive for linagliptin assay. Chemosphere 291(Pt 1):132807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132807
Ahmad OS, Bedwell TS, Esen C, Garcia-Cruz A, Piletsky SA (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymers in electrochemical and optical sensors. Trends Biotechnol 37(3):294–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.08.009
Hassan SSM, A HK, Amr AEE, Hashem HM, Bary EMA (2020) Imprinted polymeric beads-based screen-printed potentiometric platforms modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) for selective recognition of fluoxetine. Nanomaterials (Basel) 10 (3):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030572
Anirudhan TS, Athira VS, Nair SS (2022) Detection of chlorpyrifos based on molecular imprinting with a conducting polythiophene copolymer loaded on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Food Chem 381:132010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.132010
Vahidifar M, Es’haghi Z, Oghaz NM, Mohammadi AA, Kazemi MS (2022) Multi-template molecularly imprinted polymer hybrid nanoparticles for selective analysis of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics in biological and pharmaceutical samples. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18308-2
Phonklam K, Wannapob R, Sriwimol W, Thavarungkul P, Phairatana T (2020) A novel molecularly imprinted polymer PMB/MWCNTs sensor for highly-sensitive cardiac troponin T detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 308:127630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127630
Balciunas D, Plausinaitis D, Ratautaite V, Ramanaviciene A, Ramanavicius A (2022) Towards electrochemical surface plasmon resonance sensor based on the molecularly imprinted polypyrrole for glyphosate sensing. Talanta 241:123252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123252
Ratautaite V, Boguzaite R, Brazys E, Ramanaviciene A, Ciplys E, Juozapaitis M, Slibinskas R, Bechelany M, Ramanavicius A (2022) Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole based sensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Electrochim Acta 403:139581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139581
Wang M, Ceto X, Del Valle M (2022) A novel electronic tongue using electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers for the simultaneous determination of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Biosens Bioelectron 198:113807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113807
Zhong M, Teng Y, Pang S, Yan L, Kan X (2015) Pyrrole-phenylboronic acid: a novel monomer for dopamine recognition and detection based on imprinted electrochemical sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 64:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.08.083
Jesadabundit W, Jampasa S, Patarakul K, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O (2021) Enzyme-free impedimetric biosensor-based molecularly imprinted polymer for selective determination of L-hydroxyproline. Biosens Bioelectron 191:113387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113387
Aytaç S, Kuralay F, Boyacı İH, Unaleroglu C (2011) A novel polypyrrole–phenylboronic acid based electrochemical saccharide sensor. Sens Actuators, B Chem 160(1):405–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2011.07.069
Mao H, Liu M, Cao Z, Ji C, Sun Y, Liu D, Wu S, Zhang Y, Song X-M (2017) Poly(4-vinylphenylboronic acid) functionalized polypyrrole/graphene oxide nanosheets for simultaneous electrochemical determination of catechol and hydroquinone. Appl Surf Sci 420:594–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.05.188
Qi S, Saad Al-mashriqi H, Salah A, Zhai H (2022) Glutathione capped gold nanoclusters-based fluorescence probe for highly sensitive and selective detection of transferrin in serum. Microchemical Journal 175:107163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.107163
Das A, Choi N, Moon JI, Choo J (2020) Determination of total iron-binding capacity of transferrin using metal organic framework-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. J Raman Spectrosc 52(2):506–515. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.6002
Rodriguez-Hidalgo G, Sierra T, Dortez S, Marcos A, Ambrosio E, Crevillen AG, Escarpa A (2022) Transferrin analysis in wistar rats plasma: Towards an electrochemical point-of-care approach for the screening of alcohol abuse. Microchemical Journal 181:107738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107738
Lv Y, Qin Y, Svec F, Tan T (2016) Molecularly imprinted plasmonic nanosensor for selective SERS detection of protein biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 80:433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.01.092
Srivastava J, Kushwaha A, Srivastava M, Srivastava A, Singh M (2019) Glycoprotein imprinted RGO-starch nanocomposite modified EQCM sensor for sensitive and specific detection of transferrin. J Electroanal Chem 835:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.01.033
Miao Y, Sun X, Lv J, Yan G (2019) Phosphorescent mesoporous surface imprinting microspheres: preparation and application for transferrin recognition from biological fluids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(2):2264–2272. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b17772
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81973451), Fundamental and Frontier Research Fund of Chongqing (No. cstc2018jcyjAX0661, No.cstc2019jsyj-yzysbAX0020), Graduate Research and Innovation Project of Chongqing, 2022 (CYB22041), the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. KJZD-K201800103), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2019CDYGYB027, 2022CDJXY-003), Graduate Research and Innovation Foundation of Chongqing (No. CYS18033), Venture & Innovation Support Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees, and Tang Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, JY., Xu, HX., Li, Q. et al. Specific capture and determination of glycoprotein using a hybrid epitopes and monomers-mediated molecular-imprinted polymer enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor. Microchim Acta 190, 118 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05651-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05651-z