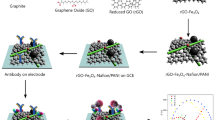
Abstract
There is an urgent need for a flexible and simple programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) dynamic measurement method enabling real-time monitoring of cancer progression and assessment of immunotherapy efficacy. In the current study, we show facile in situ synthesis of vertical alignment two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide (2D MoS2) layers on graphene-oxide-modified ITO (MoS2┴GO-ITO) using a hydrothermal approach and demonstrate the importance of the alignment of 2D in achieving high-probe capturing, enhanced electrochemical properties and target selectivity during sensing. After modification of designed PD-L1 binding peptides on the MoS2┴GO-ITO, a sensitive PD-L1 electrochemical sensor was designed using vertical alignment MoS2 to capture more probes for PD-L1 recognition and excellent in plane electron transport to accelerate electrochemical signals. The fabricated electrochemical sensor could sensitively determine PD-L1 in a wide linear range of 25–500 ng/mL and exhibit desirable accuracy and reliability in clinical samples application. This simple and sensitive method is likely to investigate further research into the exploration of the perpendicular alignment of 2D surfaces for diverse applications.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weber J (2010) Immune Checkpoint Proteins: A New Therapeutic Paradigm for Cancer—Preclinical Background: CTLA-4 and PD-1 Blockade. Semin Oncol 37:430–439
Pardoll M (2012) Drew, The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12:252–264
Yazdian-Robati R, Ramezani M, Khedri M, Ansari N, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2017) An aptamer for recognizing the transmembrane protein PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1), and its application to fluorometric single cell detection of human ovarian carcinoma cells. Microchim Acta 184:4029–4035
Wang Q, Lou W, Di W, Wu X (2017) Prognostic value of tumor PD-L1 expression combined with CD8(+) tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Int Immunopharmacol 52:7–14
Guibert N, Delaunay M, Lusque A, Boubekeur N, Rouquette I (2018) PD-L1 expression in circulating tumor cells of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab, Lung cancer: Journal of the International Association for the Study of. Lung Cancer 120:108–112
Mikami S, Mizuno R, Kondo T, Shinohara N, Oya M (2019) Clinical significance of PD and PD mm1 expression in the tumor microenvironment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci 110:1820–1828
Zhou Q, Rahimian A, Son K, Shin DS, Revzin A (2016) Development of an aptasensor for electrochemical detection of exosomes. Methods 97:88–93
Grieshaber D, Mackenzie R, Reimhult E (2008) Electrochemical Biosensors - Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 8:1400–1458
Tajik S, Orooji Y, Ghazanfari Z, Karimi F, Beitollahi H, Varma RS, Jang HW, Shokouhimehr M (2021) Nanomaterials modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of Sudan I in food. J Food Meas Charact 15:3837–3852
Beitollahi H, Shahsavari M, Sheikhshoaie I, Tajik S, Jahani PM, Mohammadi SZ, Afshar AA (2022) Amplified electrochemical sensor employing screen-printed electrode modified with Ni-ZIF-67 nanocomposite for high sensitive analysis of Sudan I in present bisphenol A. Food Chem Toxicol 161:112824
Beitollahi H, Mazloum Ardakani M, Naeimi H, Ganjipour B (2009) Electrochemical characterization of 2, 2′-[1, 2-ethanediylbis (nitriloethylidyne)]-bis-hydroquinone-carbon nanotube paste electrode and its application to simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid and uric acid. J Solid State Electrochem 13:353–363
Beitollahi H, Raoof JB, Hosseinzadeh R (2011) Electroanalysis and simultaneous determination of 6-thioguanine in the presence of uric acid and folic acid using a modified carbon nanotube paste electrode. Anal Sci 27:991
Tajik S, Beitollahi H (2019) A Sensitive Chlorpromazine Voltammetric Sensor Based on Graphene Oxide Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Anal Bioanal Chem Res 6:171–182
Pozo M, Mejías J, Hernández P, Quintana C (2014) Cucurbit[8]uril-based electrochemical sensors as detectors in flow injection analysis. Application to dopamine determination in serum samples. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 193:62–69
Tajik S, Beitollahi H, Ahmadi SA, Askari MB, Di Bartolomeo A (2021) Screen-Printed Electrode Surface Modification with NiCo2O4/RGO Nanocomposite for Hydroxylamine Detection. Nanomaterials 11:3208
Tajik S, Lohrasbi-Nejad A, MohammadzadehJahani P, Askari MB, Salarizadeh P, Beitollahi H (2022) Co-detection of carmoisine and tartrazine by carbon paste electrode modified with ionic liquid and MoO3/WO3 nanocomposite. J Food Meas Charact 16:722–730
Tajik S, Orooji Y, Karimi F, Ghazanfari Z, Beitollahi H, Shokouhimehr M, Varma RS, Jang HW (2021) High performance of screen-printed graphite electrode modified with Ni–Mo-MOF for voltammetric determination of amaranth. J Food Meas Charact 15:4617–4622
Orooji Y, Asrami PN, Beitollahi H, Tajik S, Alizadeh M, Salmanpour S, Baghayeri M, Rouhi J, Sanati AL, Karimi F (2021) An electrochemical strategy for toxic ractopamine sensing in pork samples; twofold amplified nano-based structure analytical tool. J Food Meas Charact 15:4098–4104
Ge F, Tenent RC, Wipf DO (2001) Fabricating and imaging carbon-fiber immobilized enzyme ultramicroelectrodes with scanning electrochemical microscopy. Anal Sci 17:27–35
Kumar R, Kumar J, Warnecke G (2011) Numerical methods for solving two-dimensional aggregation population balance equations. Comput Chem Eng 35:999–1009
Moncho-Jordá A, Martínez-López F, González AE, Hidalgo-álvarez R (2002) Role of long-range repulsive interactions in two-dimensional colloidal aggregation: experiments and simulations. Langmuir 18:9183–9191
Mak KF, Lee C, Hone J, Shan J, Heinz TF (2010) Atomically thin MoS2: A new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys Rev Lett 105:136805
Kim JS, Yoo HW, Choi HO, Jung HT (2014) Tunable volatile organic compounds sensor by using thiolated ligand conjugation on MoS2. Nano Lett 14:5941–5947
Alex, Smolyanitsky, Boris, I., Yakobson, Tsjerk, A., Wassenaar, Eugene, Paulechka, A MoS2-based capacitive displacement sensor for DNA sequencing, Acs Nano, 10 (2016) 9009–9016.
Balendhran S, Ou JZ, Bhaskaran M, Sriram S, Ippolito S, Vasic Z, Kats E, Bhargava S, Zhuiykov S, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2012) Atomically thin layers of MoS2 via a two step thermal evaporation-exfoliation method. Nanoscale 4:461–466
Bang GS, Nam KW, Kim JY, Shin J, Choi JW, Choi SY (2014) Effective liquid-phase exfoliation and sodium ion battery application of MoS2 nanosheets. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 6:7084–7089
Vallés C, Núnez J, Benito AM, Maser WK (2012) Flexible conductive graphene paper obtained by direct and gentle annealing of graphene oxide paper. Carbon 50:835–844
Huang ZD, Liang R, Zhang B, He YB, Kim JK (2013) Evolution of flexible 3D graphene oxide/carbon nanotube/polyaniline composite papers and their supercapacitive performance. Compos Sci Technol 88:126–133
Zhu S, Cen Y, Yang M, Guo J, Chen C, Wang J, Fan W (2017) Probing the intrinsic active sites of modified graphene oxide for aerobic benzylic alcohol oxidation. Appl Catal B 211:89–97
Choi M, Hwang J, Setiadi H, Chang W, Kim J (2017) One-pot synthesis of molybdenum disulfide–reduced graphene oxide (MoS2-RGO) composites and their high electrochemical performance as an anode in lithium ion batteries. J Supercrit Fluids 127:81–89
Sun Y, Alimohammadi F, Zhang D, Guo G (2017) Enabling colloidal synthesis of edge-oriented MoS2 with expanded interlayer spacing for enhanced HER catalysis. Nano Lett 17:1963–1969
Fenghe, Duan, Shuai, Zhang, Longyu, Yang, Zhihong, Linghao, Minghua, Wang, Bifunctional aptasensor based on novel two-dimensional nanocomposite of MoS2 quantum dots and g-C3N4 nanosheets decorated with chitosan-stabilized Au nanoparticles for selectively detecting prostate specific antigen, Analytica chimica acta, (2018).
Mao Z, Chen H, Chen J, Chu X (2021) A simple and direct SPR platform combining three-in-one multifunctional peptides for ultra-sensitive detection of PD-L1 exosomes. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 346:130496
Casellas H, Massera C, Buda F, Gamez P, Reedijk J (2006) Crystallographic evidence of theoretically novel anion–π interactions. New J Chem 30:1561–1566
Gang W, Jian Z, Sheng Y, Wang F, Feng X (2018) Vertically aligned MoS2 nanosheets patterned on electrochemically exfoliated graphene for high-performance lithium and sodium storage. Adv Energy Mater 8:1702254
Chatterjee S, Lesniak WG, Miller MS et al (2017) Rapid PD-L1 detection in tumors with PET using a highly specific peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483:258–263
Hu Z, Wang L, Zhang K, Wang J, Cheng F, Tao Z, Chen J (2015) MoS2 nanoflowers with expanded interlayers as high-performance anodes for sodium-ion batteries. Angew Chem 53:12794–12798
Liang L, Meunier V (2014) First-principles Raman spectra of MoS2, WS2 and their heterostructures. Nanoscale 6:5394–5401
Hu L, Ren Y, Yang H, Xu Q (2014) Fabrication of 3D Hierarchical MoS2/Polyaniline and MoS2/C Architectures for Lithium-Ion Battery Applications. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 6:14644–14652
Nikam RD, Lu AY, Sonawane PA, Kumar UR, Yadav K, Li LJ, Chen YT (2015) Three-Dimensional heterostructures of MoS2 nanosheets on conducting MoO2 as an efficient electrocatalyst to enhance hydrogen evolution reaction, Acs Appl Mater Interfaces, 23328.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61875114 and 62005156).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial interests or personal relationships that could inappropriately influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Z., Zhu, H., Peng, X. et al. In situ vertical alignment of 2D MoS2 layers on GO film: enhanced electrochemical properties for PD-L1 sensing. Microchim Acta 189, 155 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05269-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05269-7