Abstract
For the first time, boronate affinity chromatography and metal oxide affinity chromatography mechanisms for cis-diol-compounds extraction are simultaneously realized on a single material, termed borated zirconia. This material was prepared by hydrolyzing zirconium butoxide with boric acid under non-aqueous environment. The diameter of formed particles is around 200 nm. By extracting catechol under different pH conditions or with phosphate ion competition, the dual affinity mechanisms of borated zirconia are confirmed. Benefiting from such unique feature, borated zirconia can function well under neutral condition. By using borated zirconia for dispersive solid phase extraction, specific capture of cis-diol-containing catecholamines, including epinephrine (E), norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine (DA), was achieved. A reliable LC-MS/MS method was established and validated for quantification of these target analytes in plasma samples after derivatisation with benzoyl chloride. The linear ranges are 0.010–0.200 ng·mL−1 for E and DA, and 0.050–1.000 ng·mL−1 for NE. The limits of quantification are 0.008, 0.020 and 0.004 ng·mL−1 for E, NE and DA respectively. By analyzing samples from healthy volunteers and schizophrenia patients, the plasma concentrations of E, NE and DA were found to be higher for the latter.

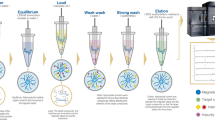
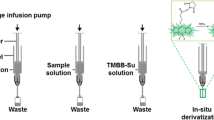
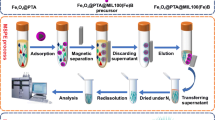
Schematic representation of boronate combined metal oxide affinity chromatography (BMOAC) extraction of cis-diol catecholamines from human plasma by borated zirconia following with benzoyl chloride derivatization and LC-MS determination.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grouzmann E, Lamine F (2013) Determination of catecholamines in plasma and urine. Best Pract Res Cl En 27:713–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2013.06.004
Young WF, Calhoun DA, Lenders JWM, Stowasser M, Textor SC (2017) Screening for Endocrine Hypertension: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr Rev 38:103–122. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2017-00054
Pedrini M, Cao B, Nani JVS, Cerqueira RO, Mansur RB, Tasic L, Hayashi MAF, McIntyre RS, Brietzke E (2019) Advances and challenges in development of precision psychiatry through clinical metabolomics on mood and psychotic disorders. Prog Neuro-Psychoph 93:182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.03.010
Bicker J, Fortuna A, Alves G, Falcão A (2013) Liquid chromatographic methods for the quantification of catecholamines and their metabolites in several biological samples—A review. Anal Chim Acta 768:12–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.12.030
Lee W, Park NH, Lee YC, Kim K-H, Hong J (2018) Advances and challenges in neurochemical profiling of biological samples using mass spectrometry coupled with separation methods. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 106:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.07.006
Ji CJ, Walton J, Su Y, Tella M (2010) Simultaneous determination of plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine using an integrated strategy of a fully automated protein precipitation technique, reductive ethylation labeling and UPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chim Acta 670:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.04.051
Ma J-B, Qiu H-W, Rui Q-H, Liao Y-F, Chen Y-M, Xu J, Zhan P-P, Zhao Y-G (2016) Fast determination of catecholamines in human plasma using carboxyl-functionalized magnetic-carbon nanotube molecularly imprinted polymer followed by liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1429:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.12.030
Zhang GD, Zhang YZ, Ji CJ, McDonald T, Walton J, Groeber EA, Steenwyk RC, Lin ZS (2012) Ultra sensitive measurement of endogenous epinephrine and norepinephrine in human plasma by semi-automated SPE-LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 895:186–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.03.026
Dunand M, Gubian D, Stauffer M, Abid K, Grouzmann E (2013) High-throughput and sensitive quantitation of plasma catecholamines by ultraperformance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry using a solid phase microwell extraction plate. Anal Chem 85:3539–3544. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4004584
Zheng J, Mandal R, Wishart DS (2018) A sensitive, high-throughput LC-MS/MS method for measuring catecholamines in low volume serum. Anal Chim Acta 1037:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.01.021
Martin AR, Vasseur JJ, Smietana M (2013) Boron and nucleic acid chemistries: merging the best of both worlds. Chem Soc Rev 42:5684–5713. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60038f
Xu J, Wu P, Ye EC, Yuan BF, Feng YQ (2016) Metal oxides in sample pretreatment. Trac-Trends in Anal Chem 80:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.02.027
He M, Wei Y, Wang R, Wang C, Zhang B, Han L (2019) Boronate affinity magnetic nanoparticles with hyperbranched polymer brushes for the adsorption of cis-diol biomolecules. Microchim Acta 186:683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3785-y
Wu J, Li Z, Jia L (2019) Solid phase extraction and capillary electrophoretic separation of racemic catecholamines by using magnetic particles coated with a copolymer prepared from poly(3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) and polyethyleneimine. Microchim Acta 186:627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3731-z
Li H, Liu Z (2012) Recent advances in monolithic column-based boronate-affinity chromatography. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 37:148–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.03.010
Wang ST, Chen D, Ding J, Yuan BF, Feng YQ (2013) Borated titania, a new option for the selective enrichment of cis-diol biomolecules. Chem-Eur J 19:605–611. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201203109
Wang S-T, Huang W, Lu W, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q (2013) TiO2-based solid phase extraction strategy for highly effective elimination of normal ribonucleosides before detection of 2′-deoxynucleosides/low-abundance 2′-O-modified ribonucleosides. Anal Chem 85:10512–10518. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4025297
Wang S-T, Huang W, Deng Y-F, Gao Q, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q (2014) “Old” metal oxide affinity chromatography as “novel” strategy for specific capture of cis-diol-containing compounds. J Chromatogr A 1361:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.07.091
Wu Q, Wu D, Guan Y (2014) Hybrid titania–zirconia nanoparticles coated adsorbent for highly selective capture of nucleosides from human urine in physiological condition. Anal Chem 86:10122–10130. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac502876u
Fan H, Chen P, Wang C, Wei Y (2016) Zirconium-doped magnetic microspheres for the selective enrichment of cis-diol-containing ribonucleosides. J Chromatogr A 1448:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.04.048
Jiang H-P, Chu J-M, Lan M-D, Liu P, Yang N, Zheng F, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q (2016) Comprehensive profiling of ribonucleosides modification by affinity zirconium oxide-silica composite monolithic column online solid-phase microextraction--Mass spectrometry analysis. J Chromatogr A 1462:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.07.086
Jiang M-Y, Huang Y-Q, Chu J-M, Zhu Q-F, Ding J, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q (2016) A magnetic ZrO2 based solid-phase extraction strategy for selective enrichment and profiling of glycosylated compounds in rice. Anal Methods-UK 8:6436–6443. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY01383J
Chu J-M, Yin T-L, Zheng S-J, Yang J, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q (2017) Metal oxide-based dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled with mass spectrometry analysis for determination of ribose conjugates in human follicular fluid. Talanta 167:506–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.02.062
Wan L, Zhu H, Guan Y, Huang G (2017) Nanocoating cellulose paper based microextraction combined with nanospray mass spectrometry for rapid and facile quantitation of ribonucleosides in human urine. Talanta 169:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.03.085
Jin S, Liu L, Zhou P (2018) Amorphous titania modified with boric acid for selective capture of glycoproteins. Microchim Acta 185:308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2824-4
Xu Y, Yang Y, Xue A, Chen H, Li S (2018) In situ precipitation of hydrous titanium dioxide for dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of nucleosides and their separation. New J Chem 42:4909–4914. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ04590E
Mohyuddin A, Hussain D, Fatima B, Athar M, Ashiq MN, Najam-ul-Haq M (2019) Gallic acid functionalized UiO-66 for the recovery of ribosylated metabolites from human urine samples. Talanta 201:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.072
Creutz C, Chou MH (2008) Binding of catechols to mononuclear titanium(IV) and to 1- and 5-nm TiO2 nanoparticles. Inorg Chem 47:3509–3514. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic701687k
Chen D, Caruso RA (2012) Recent progress in the synthesis of spherical titania nanostructures and their applications. Adv Func Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201201880
van de Merbel NC, Hendriks G, Imbos R, Tuunainen J, Rouru J, Nikkanen H (2011) Quantitative determination of free and total dopamine in human plasma by LC–MS/MS: the importance of sample preparation. Bioanalysis 3:1949–1961. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.11.170
Song P, Mabrouk OS, Hershey ND, Kennedy RT (2012) In vivo neurochemical monitoring using benzoyl chloride derivatization and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 84:412–419. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac202794q
Yuan T-F, Huang H-Q, Gao L, Wang S-T, Li Y (2018) A novel and reliable method for tetrahydrobiopterin quantification: benzoyl chloride derivatization coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Free Radical Bio Med 118:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.02.035
Farzin L, Shamsipur M, Samandari L, Sheibani S (2018) Advances in the design of nanomaterial-based electrochemical affinity and enzymatic biosensors for metabolic biomarkers: A review. Microchim Acta 185:276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2820-8
Hou XY, Huang W, Tong YK, Tian MM (2019) Hollow dummy template imprinted boronate-modified polymers for extraction of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine prior to quantitation by HPLC. Microchim Acta 186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3801-2
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Marcu A, Guo AC, Liang K, Vazquez-Fresno R, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li CR, Karu N, Sayeeda Z, Lo E, Assempour N, Berjanskii M, Singhal S, Arndt D, Liang YJ, Badran H, Grant J, Serra-Cayuela A, Liu YF, Mandal R, Neveu V, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M, Manach C, Scalbert A (2018) HMDB 4.0: the human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D608–D617. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1089
Yao J, Lu H, Wang Z, Wang T, Fang F, Wang J, Yu J, Gao R (2018) A sensitive method for the determination of the gender difference of neuroactive metabolites in tryptophan and dopamine pathways in mouse serum and brain by UHPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 1093-1094:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.06.054
Eisenhofer G, Peitzsch M, McWhinney BC (2016) Impact of LC-MS/MS on the laboratory diagnosis of catecholamine-producing tumors. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 84:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.01.027
Erjavec GN, Konjevod M, Perkovic MN, Strac DS, Tudor L, Barbas C, Grune T, Zarkovic N, Pivac N (2018) Short overview on metabolomic approach and redox changes in psychiatric disorders. Redox Biol 14:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.002
Lozupone M, La Montagna M, D’Urso F, Daniele A, Greco A, Seripa D, Logroscino G, Bellomo A, Panza F (2019) The role of biomarkers in psychiatry. In: Guest PC (ed) Reviews on Biomarker Studies in Psychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 135–162
Wang S-T, Li Y (2017) Development of a UPLC-MS/MS method for routine therapeutic drug monitoring of aripiprazole, amisulpride, olanzapine, paliperidone and ziprasidone with a discussion of their therapeutic reference ranges for Chinese patients. Biomed Chromatogr 31:e3928–e3n/a. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3928
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China support (21705121, 81572069, 81501815).
Funding
The authors declare no competing financial interest. And no color should be used for any figures in print.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that can have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2144 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, J., Sun, T., Peng, R. et al. LC-MS/MS determination of plasma catecholamines after selective extraction by borated zirconia. Microchim Acta 187, 165 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4145-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4145-7