Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is connected to aggregation of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide and formation of insoluble plaques in the brain. Aβ level can be monitored as an AD early diagnosis route. In this study, an irregular shaped microporous gold nanostructure with a typical size of 150 × 250 nm was electrodeposited on a polycrystalline gold surface at 0 mV (vs. AgCl) using sodium alendronate. The nanostructure was then characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscopy. An electrochemical peptide-based biosensor was fabricated by immobilizing an Aβ(1–42)-binding peptide on the gold nanostructure. Binding of Aβ(1–42) by the peptide was followed electrochemically using ferro/ferricyanide as a redox probe. Differential pulse voltammograms in a potential range of 0–500 mV (vs. AgCl) with typical peak potentials at 224 mV are linear in the 3–7000 pg mL−1 Aβ(1–42) concentration range, with a 0.2 pg mL−1 detection limit. The biosensor is free of interferences and was applied to the quantitation of Aβ(1–42) in artificial cerebrospinal fluid and spiked serum samples.

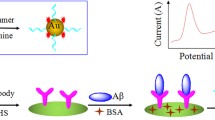
Schematic presentation of an immobilized amyloid-β(1-42)-specific peptide on the surface of a microporous gold nanostructure to fabricate an electrochemical biosensor for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Aβ(1-42) capturing by the peptide led to repulsion of ferrocyanide/ferricyanide redox couple.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubois B, Hampel H, Feldman HH, Scheltens P, Aisen P, Andrieu S, Bakardjian H, Benali H, Bertram L, Blennow K (2016) Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: definition, natural history, and diagnostic criteria. Alzheimers Dement 12(3):292–323
Almdahl IS, Lauridsen C, Selnes P, Kalheim LF, Coello C, Gajdzik B, Moller I, Wettergreen M, Grambaite R, Bjornerud A, Brathen G, Sando SB, White LR, Fladby T (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid beta 1-43 mirror 1-42 in relation to imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 9:9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00009
Englund H, Sehlin D, Johansson AS, Nilsson LN, Gellerfors P, Paulie S, Lannfelt L, Pettersson FE (2007) Sensitive ELISA detection of amyloid-β protofibrils in biological samples. J Neurochem 103(1):334–345
Song X, Li X, Wei D, Feng R, Yan T, Wang Y, Ren X, Du B, Ma H, Wei Q (2019) CuS as co-reaction accelerator in PTCA-K2S2O8 system for enhancing electrochemiluminescence behavior of PTCA and its application in detection of amyloid-β protein. Biosens Bioelectron 126:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.068
Yu X, Hayden EY, Xia M, Liang O, Cheah L, Teplow DB, Xie YH (2018) Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy distinguishes amyloid Beta-protein isoforms and conformational states. Protein Sci 27(8):1427–1438. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3434
Zhou Y, Zhang H, Liu L, Li C, Chang Z, Zhu X, Ye B, Xu M (2016) Fabrication of an antibody-aptamer sandwich assay for electrochemical evaluation of levels of beta-amyloid oligomers. Sci Rep 6:35186. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35186
Han X, Man Z, Xu S, Cong L, Wang Y, Wang X, Du Y, Zhang Q, Tang S, Liu Z, Li W (2019) A gold nanocluster chemical tongue sensor array for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 173:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.10.020
Haes AJ, Hall WP, Chang L, Klein WL, Van Duyne RP (2004) A localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor: first steps toward an assay for Alzheimer’s disease. Nano Lett 4(6):1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl049670j
Hu T, Chen C, Huang G, Yang X (2016) Antibody modified-silver nanoparticles for colorimetric immuno sensing of Aβ(1–40/1–42) based on the interaction between β-amyloid and Cu2+. Sensors Actuators B Chem 234:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.04.159
Rahi A, Sattarahmady N, Heli H (2015) Zepto-molar electrochemical detection of Brucella genome based on gold nanoribbons covered by gold nanoblooms. Sci Rep 5:18060
Negahdary M, Behjati-Ardakani M, Sattarahmady N, Yadegari H, Heli H (2017) Electrochemical aptasensing of human cardiac troponin I based on an array of gold nanodumbbells-applied to early detection of myocardial infarction. Sensors Actuators B Chem 252:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.149
Tondro GH, Dehdari Vais R, Sattarahmady N (2018) An optical genosensor for enterococcus faecalis using conjugated gold nanoparticles-rRNA oligonucleotide. Sensors Actuators B Chem 263:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.097
Altintas Z (ed) (2017) Biosensors and nanotechnology: applications in health care diagnostics. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Hayat A, Marty JL (2014) Aptamer based electrochemical sensors for emerging environmental pollutants. Front Chem 2:41
Rozenblum GT, Lopez VG, Vitullo AD, Radrizzani M (2016) Aptamers: current challenges and future prospects. Expert Opin Drug Discovery 11(2):127–135
Zhang Q, Lu Y, Li S, Wu J, Liu Q (2018) Peptide-based biosensors. In: Koutsopoulos S. Peptide applications in biomedicine, biotechnology and bioengineering, 1st edn. Elsevier, pp 565-601
Dehdari Vais R, Sattarahmady N, Heli H (2016) Green electrodeposition of gold nanostructures by diverse size, shape, and electrochemical activity. Gold Bull 49(3–4):95–102
Sattarahmady N, Firoozabadi V, Nazari-Vanani R, Azarpira N (2018) Investigation of amyloid formation inhibition of chemically and biogenically from Citrus aurantium L. blossoms and Rose damascena oils of gold nanoparticles: toxicity evaluation in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Int J Biol Macromol 112:703–711
Rahimi-Moghaddam F, Azarpira N, Sattarahmady N (2018) Evaluation of a nanocomposite of PEG-curcumin-gold nanoparticles as a near-infrared photothermal agent: an in vitro and animal model investigation. Lasers Med Sci 33(8):1769–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2538-1
Sattarahmady N, Heidari M, Zare T, Lotfi M, Heli H (2016) Zinc-nickel ferrite nanoparticles as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging. Appl Magn Reson 47(8):925–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-016-0801-9
Rushworth JV, Ahmed A, Griffiths HH, Pollock NM, Hooper NM, Millner PA (2014) A label-free electrical impedimetric biosensor for the specific detection of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta oligomers. Biosens Bioelectron 56:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.12.036
Wang J, Duan G, Li Y, Liu G, Dai Z, Zhang H, Cai W (2013) An invisible template method toward gold regular arrays of nanoflowers by electrodeposition. Langmuir 29(11):3512–3517. https://doi.org/10.1021/la400433z
Kumar A, Mandal S, Selvakannan PR, Pasricha R, Mandale AB, Sastry M (2003) Investigation into the interaction between surface-bound alkylamines and gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 19(15):6277–6282. https://doi.org/10.1021/la034209c
Ross RD, Roeder RK (2011) Binding affinity of surface functionalized gold nanoparticles to hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res A 99A(1):58–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.33165
Kozlowski LP (2016) IPC - Isoelectric Point Calculator. Biol Direct 11:55. http://isoelectric.org/calculate.php. Accessed 02 Oct 2019
Innovagen AB (2015) PepCalc.com - Peptide property calculator. https://pepcalc.com. Accessed 02 Oct 2019
GenScript (2002) Peptide Molecular Weight Calculator. https://www.genscript.com/tools/peptide-property-calculator. Accessed 02 Oct 2019
Kang Y, Feng K-J, Chen J-W, Jiang J-H, Shen G-L, Yu R-Q (2008) Electrochemical detection of thrombin by sandwich approach using antibody and aptamer. Bioelectrochemistry 73(1):76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2008.04.024
Huang Y, Nie X-M, Gan S-L, Jiang J-H, Shen G-L, Yu R-Q (2008) Electrochemical immunosensor of platelet-derived growth factor with aptamer-primed polymerase amplification. Anal Biochem 382(1):16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2008.07.008
Li L, Zhao H, Chen Z, Mu X, Guo L (2010) Aptamer-based electrochemical approach to the detection of thrombin by modification of gold nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 398(1):563–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3922-2
Rahi A, Sattarahmady N, Heli H (2016) Label-free electrochemical aptasensing of the human prostate-specific antigen using gold nanospears. Talanta 156-157:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.05.029
Hortschansky P, Schroeckh V, Christopeit T, Zandomeneghi G, Fändrich M (2005) The aggregation kinetics of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid peptide is controlled by stochastic nucleation. Protein Sci 14(7):1753–1759. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.041266605
Zecca C, Tortelli R, Panza F, Arcuti S, Piccininni M, Capozzo R, Barulli MR, Barone R, Cardinali R, Abbrescia D (2018) Plasma β-amyloid1–42 reference values in cognitively normal subjects. J Neurol Sci 391:120–126
Pesaresi M, Lovati C, Bertora P, Mailland E, Galimberti D, Scarpini E, Quadri P, Forloni G, Mariani C (2006) Plasma levels of beta-amyloid (1–42) in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 27(6):904–905
Andreasen N, Hesse C, Davidsson P, Minthon L, Wallin A, Winblad B, Vanderstichele H, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K (1999) Cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid (1-42) in Alzheimer disease: differences between early-and late-onset Alzheimer disease and stability during the course of disease. Arch Neurol 56(6):673–680
Acknowledgments
The financial support of the Iran National Science Foundation Grant NO. 96005985 is gratefully acknowledged. We would also like to thank the Research Councils of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 464 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Negahdary, M., Heli, H. An electrochemical peptide-based biosensor for the Alzheimer biomarker amyloid-β(1–42) using a microporous gold nanostructure. Microchim Acta 186, 766 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3903-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3903-x