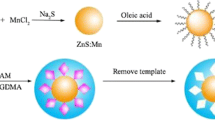
Abstract
A microplate-based assay is described for the sensitive and selective fluorometric determination of the pesticide dimethoate. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) are used as the molecular recognition probe. The MIP-coated QDs were synthesized using one-step reversed-phase microemulsion in the presence of hydrophobic CdSe/ZnS QDs. Copolymerization was performed by using 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane as the functional monomer, tetraethoxysilane as the cross-linker, and dimethoate as the template. The fluorescence of the coated QDs is quenched by dimethoate when dimethoate becomes rebound on the imprinting sites of the MIP. Under the optimal conditions, fluorescence (best measured at excitation/emisison wavelengths of 380/620 nm) drops linearly in the 5.0–150 μg L−1 dimethoate concentration range, and the limit of detection is 2.1 μg L−1 (at S/N = 3). The assay was utilized for dimethoate determination in spiked real samples. Satisfactory recoveries (89.8%–98.0%) with relatively standard deviations of <4.9% are obtained. The method is rapid, cost-effective, sensitive, and selective. The use of microplate allows for the quantitation of a large number of samples simultaneously.

Schematic representation of sensitive and selective fluorometric microplate-based assay for the high-throughput determination of dimethoate (DM) based on recognition of molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs). DM exerts a quenching effect on the fluorescence of the QDs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Hassoun EA, Stohs SJ (1995) In vitro and in vivo generation of reactive oxygen species, DNA damage and lactate dehydrogenase leakage by selected pesticides. Toxicology 104(1–3):129–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483X(95)03156-A
Liang Y, Wang W, Shen Y, Liu Y, Liu XJ (2012) Effects of home preparation on organophosphorus pesticide residues in raw cucumber. Food Chem 133(3):636–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.016
Kaewsuya P, Brewer WE, Wong J, Morgan SL (2013) Automated QuEChERS Tips for Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Fruits and Vegetables by GC-MS. J Agric Food Chem 61(10):2299–2314. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf304648h
Capoferri D, Del CM, Ntshongontshi N, Iwuoha EI, Sergi M, Di OF, Compagnone D (2017) MIP-MEPS based sensing strategy for the selective assay of dimethoate. Application to wheat flour samples. Talanta 174:599–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.06.062
Li S, Luo J, Yin G, Xu Z, Le Y, Wu X, Wu N, Zhang Q (2015) Selective determination of dimethoate via fluorescence resonance energy transfer between carbon dots and a dye-doped molecularly imprinted polymer. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 206:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.038
Panagiotopoulou M, Salinas Y, Beyazit S, Kunath S, Duma L, Prost E, Mayes AG, Resmini M, Tse SBB, Haupt K (2016) Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coated Quantum Dots for Multiplexed Cell Targeting and Imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 55(29):8244–8248. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201601122
Liu X, Zhang W, Yang C, Yao Y, Huang L, Li S, Wang J, Ji Y (2019) Rapid and selective fluorometric determination of tannic acid using MoO3-x quantum dots. Microchim Acta 186(4):247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3311-2
Xiao SJ, Chu ZJ, Zhao XJ, Zhang ZB, Liu YH (2017) Off-on-off detection of the activity of acetylcholine esterase and its inhibitors using MoOx quantum dots as a photoluminescent probe. Microchim Acta 184(12):4853–4860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2519-2
Nsibande SA, Forbes PB (2016) Fluorescence detection of pesticides using quantum dot materials - A review. Anal Chim Acta 945:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.10.002
Chen L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2922. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00084a
Haupt K (2013) Microchimica Acta special issue MIP2012 on Molecularly imprinted;polymers - science and technology. Microchim Acta 180(15–16):1357–1358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1097-1
Chen L, Wang X, Lu W, Wu X, Li J (2016) Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev 45(8):2137–2211. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CS00061D
Sun XY, Ma RT, Chen J, Shi YP (2018) Magnetic boronate modified molecularly imprinted polymers on magnetite microspheres modified with porous TiO2 (Fe3O4@pTiO2@MIP) with enhanced adsorption capacity for glycoproteins and with wide operational pH range. Microchim Acta 185(565). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3092-z
Niu M, PhamHuy C, He H (2016) Core-shell nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: a review. Microchim Acta 183(10):2677–2695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1930-4
Chen J-L (2017) Determination of tetracycline using imprinted polymethacrylates along with fluorescent CdTe quantum dots on plastic substrates. Microchim Acta 184(5):1335–1343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2118-2
Zhang C, Cui H, Cai J, Duan Y, Liu Y (2015) Development of fluorescence sensing material based on cdse/zns quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer for the detection of carbaryl in rice and chinese cabbage. J Agric Food Chem 63(20):4966–4972. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01072
Li Q, Kamra T, Ye L (2016) A modular approach for assembling turn-on fluorescence sensors using molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Chem Commun 52(82):12237–12240. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC06628C
Wagner S, Bell J, Biyikal M, Gawlitza K, Rurack K (2017) Integrating fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) sensor particles with a modular microfluidic platform for nanomolar small-molecule detection directly in aqueous samples. Biosens Bioelectron 99:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.053
Liu H, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Zheng F, Huang M, Sun J, Sun X, Li H, Wang J, Sun B (2019) A fluorescent nanoprobe for 4-ethylguaiacol based on the use of a molecularly imprinted polymer doped with a covalent organic framework grafted onto carbon nanodots. Microchim Acta 186(3):182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3306-z
Alizadeh T, Zare M, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Tavana B (2010) A new molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based electrochemical sensor for monitoring 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) in natural waters and soil samples. Biosens Bioelectron 25(5):1166–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.10.003
Yang Y, Fang G, Liu G, Pan M, Wang X, Kong L, He X, Wang S (2013) Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer film via sol-gel technology and multi-walled carbon nanotubes-chitosan functional layer for sensitive determination of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid. Biosens Bioelectron 47(18):475–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.03.054
Yang Y, Fang G, Wang X, Liu G, Wang S (2016) Imprinting of molecular recognition sites combined with π-donor-acceptor interactions using bis-aniline-crosslinked Au-CdSe/ZnS nanoparticles array on electrodes: development of electrochemiluminescence sensor for the ultrasensitive and selective detection of 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid. Biosens Bioelectron 77:1134–1143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.006
Yang Y, Fang G, Wang X, Zhang F, Liu J, Zheng W, Wang S (2017) Electrochemiluminescent graphene quantum dots enhanced by MoS2 as sensing platform: a novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor for 2-methyl-4- chlorophenoxyacetic acid assay. Electrochim Acta 228:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.043
Cennamo N, D’Agostino G, Pesavento M, Zeni L (2014) High selectivity and sensitivity sensor based on MIP and SPR in tapered plastic optical fibers for the detection of l -nicotine. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 191(2):529–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.10.067
Dong J, Gao N, Peng Y, Guo C, Lv Z, Wang Y, Zhou C, Ning B, Liu M, Gao Z (2012) Surface plasmon resonance sensor for profenofos detection using molecularly imprinted thin film as recognition element. Food Control 25(2):543–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.11.015
Fang G, Liu G, Yang Y, Wang S (2016) Quartz crystal microbalance sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer membrane and three-dimensional Au nanoparticles@mesoporous carbon CMK-3 functional composite for ultrasensitive and specific determination of citrinin. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 230:272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.02.053
Fang G, Yang Y, Zhu H, Qi Y, Liu J, Liu H, Wang S (2017) Development and application of molecularly imprinted quartz crystal microbalance sensor for rapid detection of metolcarb in foods. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 251:720–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.094
Zhang D, Wang Y, Geng W, Liu H (2019) Rapid detection of tryptamine by optosensor with molecularly imprinted polymers based on carbon dots-embedded covalent-organic frameworks. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 285:546–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.092
Liu H, Ni T, Mu L, Zhang D, Wang J, Wang S, Sun B (2018) Sensitive detection of pyrraline with a molecularly imprinted sensor based on metal-organic frameworks and quantum dots. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 256:1038–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.048
Zhang L, Chen L (2018) Visual detection of melamine by using a ratiometric fluorescent probe consisting of a red emitting CdTe core and a green emitting CdTe shell coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta 185(2):135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2664-7
Liu H, Fang G, Wang S (2014) Molecularly imprinted optosensing material based on hydrophobic CdSe quantum dots via a reverse microemulsion for specific recognition of ractopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 55:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.064
Liu H, Wu D, Zhou K, Wang J, Sun B (2016) Development and applications of molecularly imprinted polymers based on hydrophobic CdSe/ZnS quantum dots for optosensing of Nε-carboxymethyllysine in foods. Food Chem 211:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.038
Kong W, Yang X, Yang M, Zhou H, Ouyang Z, Zhao M (2016) Photoluminescent nanosensors capped with quantum dots for high-throughput determination of trace contaminants: Strategies for enhancing analytical performance. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 78:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.07.013
Liu B, Zhang D, Ni H, Wang D, Jiang L, Fu D, Han X, Zhang C, Chen H, Gu Z (2017) Multiplex analysis on a single porous hydrogel bead with encoded SERS nanotags. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(1):21–26. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b14942
Li H, Li Y, Cheng J (2010) Molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded CdSe quantum dots for highly selective and sensitive optosensing of pyrethroids. Chem Mater 22(8):2451–2457. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm902856y
Wu L, Lin ZZ, Zhong HP, Peng AH, Chen XM, Huang ZY (2017) Rapid detection of malachite green in fish based on CdTe quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted silica. Food Chem 229:847–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.144
Tan TT, Selvan ST, Zhao L, Shujun Gao A, Ying JY (2007) Size control, shape evolution, and silica coating of near-infrared-emitting PbSe quantum dots. Chem Mater 19(13):3112–3117. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm061974e
Koole R, Schooneveld MMV, Hilhorst J, Donegá CDM, Hart DC’, Blaaderen AV, Vanmaekelbergh D, Meijerink A (2008) On the incorporation mechanism of hydrophobic quantum dots in silica spheres by a reverse microemulsion method. Chem Mater 20(7):2503–2512. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm703348y
Liu H, Zhou K, Wu D, Wang J, Sun B (2016) A novel quantum dots-labeled on the surface of molecularly imprinted polymer for turn-off optosensing of dicyandiamide in dairy products. Biosens Bioelectron 77:512–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.10.007
Sadeghi S, Jahani M, Belador F (2016) The development of a new optical sensor based on the Mn doped ZnS quantum dots modified with the molecularly imprinted polymers for sensitive recognition of florfenicol. Spectrochimi Acta A 159:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.01.043
Huang S, Guo M, Tan J, Geng Y, Wu J, Tang Y, Su C, Lin CC, Liang Y (2018) Novel fluorescence sensor based on all-inorganic Perovskite quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymers for highly selective and sensitive detection of Omethoate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(45):39056–39063. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b14472
Simões M, Martins N, Cabrita MJ, Burke AJ, Garcia R (2014) Tailor-made molecularly imprinted polymers for dimethoate and deltamethrin recognition: synthesis, characterization and chromatographic evaluation. J Polym Res 21(3):368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0368-9
Amjadi M, Jalili R, Manzoori JL (2016) A sensitive fluorescent nanosensor for chloramphenicol based on molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Luminescence 31(3):633–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3003
Vahid B (2017) Specific fluorescence probe for direct recognition of dimethoate using molecularly imprinting polymer on ZnO quantum dots. J Fluoresc 27(4):1339–1347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-017-2068-4
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the Scientific Instrument Centre (Shanxi University), Wei Zhou and Zhiqiang Guo for the convenience of the characterization experiment. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project No. 31701686, 31801670); the Young Technology Research Fund of Shanxi, China (project No. 201701D221180); Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (project No. 201802016); the fund of the Beijing Laboratory for Food Quality and Safety, Beijing Technology and Business University (project No. FQS-201803).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 248 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Chang, Y., Guo, Y. et al. Fluorometric microplate-based dimethoate assay using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta 186, 589 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3649-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3649-5