Abstract
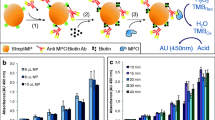
Electrochemical sandwich immunoassay strategies involving the use of carboxyl-functionalized magnetic microbeads (cMBs) and magnetic nanoparticles (cMNPs) have been evaluated and compared. The proteolytically cleaved soluble tyrosine kinase receptor sAXL was used as the target analyte. Antibodies against AXL were covalently immobilized on cMBs or cMNPs. Immunobinding of AXL was detected by means of a secondary biotinylated antibody and a streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate. The electrochemical transduction was accomplished by capturing the cMBs or cMNPs bearing the immunoconjugates onto screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) by using a small magnet. The amperometric response was measured at −0.20 V (vs the silver pseudo-reference electrode of the SPCE) upon the addition of H2O2 in the presence of hydroquinone as the redox mediator. The calibration plots for AXL extended up to 7.5 ng mL−1 when cMBs were used for the preparation of the immunosensor and up to 40 ng mL−1 in the case of using cMNPs. The respective slope values were 158 (cMBs) and 43 nA mL ng−1 (cMNPs), while the achieved LODs were 74 (cMBs) and 75 pg mL−1 (cMNPs). Although the immunosensors prepared with cMBs provided a shorter range of linearity, they exhibited a 3.7-times larger sensitivity than those constructed with cMNPs. The successful application of the new strategies was demonstrated for the determination of the endogenous content of sAXL in real human serum samples (a cut-off value of 71 ng mL−1 have been established for patients with risk of heart failure). The immunosensors constructed using cMBs or cMNPs can be advanta geously compared, in terms of sensitivity and fabrication time, with the only immunosensor for AXL previously reported. In addition, these new immunosensors took approximately half time than ELISA to perform the assay.

Comparative evaluation of the performance of amperometric immunosensors for tyrosine kinase receptor AXL determination using carboxyl-modified magnetic microparticles (cMBs) and nanoparticles (cMNPs) and application to the determination of the endogeneous concentration in real human serum samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Centi S, Laschi S, Frànek M, Mascini M (2005) A disposable immunomagnetic electrochemical sensor based on functionalised magnetic beads and carbon-based screen-printed electrodes (SPCEs) for the detection of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Anal Chim Acta 538:205–212
Zacco E, Adrian J, Galve R, Marco MP, Alegret S, Pividori MI (2007) Electrochemical magneto immunosensing of antibiotic residues in milk. Biosens Bioelectron 22:2184–2191
Ricci F, Volpe G, Micheli L, Palleschi G (2007) A review on novel developments and applications of immunosensors in food analysis. Anal Chim Acta 605:111–129
Xu Y, Wang E (2012) Electrochemical biosensors based on magnetic micro/nano particles. Electrochim Acta 84:62–73
Yáñez-Sedeño P, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM (2016) Magnetic particles coupled to disposable screen printed transducers for electrochemical biosensing. Sensors 16:1585. doi:10.3390/s16101585
de Souza CM, Laube T, Yamanaka H, Alegret S, Pividori MI (2011) Magneto immunoassays for Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 related to malaria based on magnetic nanoparticles. Anal Chem 83:5570–5577
Brandão D, Liébana S, Campoy S, Alegret S, Pividori MI (2015) Immunomagnetic separation of Salmonella with tailored magnetic micro and nanocarriers. A comparative study. Talanta 143:198–204
O’Bryan JP, Frye RA, Cogswell PC, Neubauer A, Kitch B, Prokop C, Espinosa R 3rd, Le Beau MM, Earp HS, Liu ET (1991) Axl, a transforming gene isolated from primary human myeloid leukemia cells, encodes a novel receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 11:5016–5031
Neubauer A, Fiebeler A, Graham DK, O’Bryan JP, Schmidt CA, Barckow P, Serke S, Siegert W, Snodgrass HR, Huhn D (1994) Expression of AXL, a transforming receptor tyrosine kinase, in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood 84:1931–1941
Paccez JD, Vogelsang M, Parker MI, Zerbin LF (2014) The receptor tyrosine kinase Axl in cancer: biological functions and therapeutic implications. Int J Cancer 134:1024–1033
Batchu SN, Hughson A, Gerloff J, Fowell DJ, Korshunov VA (2013) Role of Axl in early kidney inflammation and progression of salt-dependent hypertension. Hypertension 62:302–309
Batlle M, Recarte-Pelz P, Roig E, Castel MA, Cardona M, Farrero M, Campos B, Pulgarín MJ, Ramírez J, Pérez-Villa F, García de Frutos P (2014) AXL receptor tyrosine kinase is increased in patients with heart failure. Int J Cardiol 173:402–409
Liu YW, Yang QF, Zuo PY, Xiao CL, Chen XL, Liu CY (2015) Elevated serum levels of soluble Axl in acute coronary syndrome. Am J Med Sci 349:124–129
Batlle M, Campos B, Farrero M, Cardona M, González B, Castel MA, Ortiz J, Roig E, Pulgarín MJ, Ramírez J, Bedini JL, Sabaté M, García de Frutos P, Pérez-Villa F (2016) Use of serum levels of high sensitivity troponin T, galectin-3 and C-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen at long term follow-up in heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction: comparison with soluble AXL and BNP. Int J Cardiol 225:113–119
Martínez-Mancera FD, García-López P, Hernández-López JL (2015) Pre-clinical validation study of a miniaturized electrochemical immunoassay based on square wave voltammetry for early detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in human serum. Clin Chim Acta 444:199–205
Serafín V, Torrente-Rodríguez RM, Batlle M, García de Frutos P, Campuzano S, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Pingarrón JM (2017) Electrochemical immunosensor for receptor tyrosine kinase AXL using poly(pyrrolepropionic acid)-modified disposable electrodes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:1251–1256
Eguílaz M, Moreno-Guzmán M, Campuzano S, González-Cortés A, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Pingarrón JM (2010) An electrochemical immunosensor for testosterone using functionalized magnetic beads and screen-printed carbon electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 26:517–522
Arican O, Aral M, Sasmaz S, Ciragil P (2005) Serum levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-18 in patients with active psoriasis and correlation with disease severity. Mediat Inflamm 5:273–279
Esteban-Fernández de Ávila B, Escamilla-Gómez V, Campuzano S, Pedrero M, Salvador JP, Marco MP, Pingarrón JM (2013) Ultrasensitive amperometric magnetoimmunosensor for humanC-reactive protein quantification in serum. Sensors Actuators B Chem 188:212–220
Acknowledgements
The financial support of projects: Retos Colaboración RTC-2015-4184-1 (cofinanced by the Ministry of Economy and Competitivity and FEDER “una manera de hacer Europa”), CTQ2015-70023-R and CTQ2015-64402-C2-1-R (Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitivity Research Projects) and S2013/MT-3029 (NANOAVANSENS Program from the Comunidad de Madrid) are gratefully acknowledged. R.M. Torrente-Rodríguez acknowledges a predoctoral contract from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitivity.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 156 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serafín, V., Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M., Batlle, M. et al. Comparative evaluation of the performance of electrochemical immunosensors using magnetic microparticles and nanoparticles. Application to the determination of tyrosine kinase receptor AXL. Microchim Acta 184, 4251–4258 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2455-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2455-1