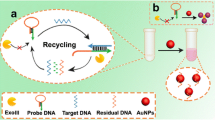
Abstract
Patients with prostate cancer and systemic lupus erythematosus exhibit reduced DNase I activity, and patients with myocardial infarction exhibit increased DNase I activity. So the assay of DNase I is of high importance. A colorimetric assay is described here for the determination of the activity of DNase. It is based on strand scission of dsDNA as catalyzed by DNase I. The products of digestion (nucleoside monophosphates) can better stabilize citrate capped AuNPs than dsDNA. In the absence of DNase I, the AuNPs aggregate in presence of NaCl and then display a blue color. In the presence of the analyte (DNase I), AuNPs do not aggregate but rather remain dispersed and display a red color. These findings were exploited to design a DNase I activity assay that is based on the measurement of ratio of absorbances at 520 nm (red) to 650 nm (blue). The detection limit for DNase I activity is found to be 7.1 U⋅L−1. In our perception, this assay has a large potential with respect to diagnoses of DNase I activity-related diseases and in drug screening.

A method is described for the determination of the activity of DNase I. It is based on the capability of nucleoside monophosphates (dNMPs; formed by DNase-catalyzed scission of dsDNA) to stabilize red gold NPs against NaCl-induced aggregation. AuNPs stabilized with dsDNA, in contrast, readily aggregate in presence of NaCl to form blue clusters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunitz M (1950) Crystalline desoxyribonuclease.2. digestion of thymus nucleic acid (desoxyribonucleic acid) - the kinetics of the reaction. J Gen Physiol 33:363–377
Vanecko S, Laskowski M (1961) Studies of specificity of deoxyribonuclease i.3. hydrolysis of chains carrying a monoesterified phosphate on carbon. J Biol Chem 236:3312–3316
Mannherz HG, Peitsch MC, Zanotti S, Paddenberg R, Polzar B (1995) A new function for an old enzyme: the role of DNase I in apoptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 198:161–174
Napirei M, Karsunky H, Zevnik B, Stephan H, Mannherz HG, Moroy T (2000) Features of systemic lupus erythematosus in Dnase1-deficient mice. Nat Genet 25:177–181
Macanovic M, Sinicropi D, Shak S, Baughman S, Thiru S, Lachmann PJ (1996) The treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in NZB/W F-1 hybrid mice; Studies with recombinant murine DNase and with dexamethasone. Clin Exp Immunol 106:243–252
Arakawa K, Kawai Y, Kumamoto T, Morikawa N, Yoshida M, Tada H, Kawaguchi R, Taniguchi K, Miyamori I, Kominato Y, Kishi K, Yasuda T (2005) Serum deoxyribonuclease I activity can be used as a sensitive marker for detection of transient myocardial ischaemia induced by percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J 26:2375–2380
Cherepanova AV, Tamkovich SN, Bryzgunova OE, Vlassov VV, Laktionov PP (2008) Deoxyribonuclease activity and circulating DNA concentration in blood plasma of patients with prostate tumors. Ann Ny Acad Sci 1137:218–221
Kawai Y, Yoshida M, Arakawa K, Kumamoto T, Morikawa N, Masamura K, Tada H, Ito S, Hoshizaki H, Oshima S, Taniguchi K, Terasawa H, Miyamori I, Kishi K, Yasuda T (2004) Diagnostic use of serum deoxyribonuclease I activity as a novel early-phase marker in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 109(20):2398–2400
Macanovic M, Lachmann PJ (1997) Measurement of deoxyribonuclease I (DNase) in the serum and urine of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-prone NZB/NZW mice by a new radial enzyme diffusion assay. Clin Exp Immunol 108:220–226
Morikawa N, Kawai Y, Arakawa K, Kumamoto T, Miyamori I, Akao H, Kitayama M, Kajinami K, Lee JD, Takeshita H, Kominato Y, Yasuda T (2007) Serum deoxyribonuclease I activity can be used as a novel marker of transient myocardial ischaemia: results in vasospastic angina pectoris induced by provocation test. Eur Heart J 28:2992–2997
Zhu B, Gong YW, Chen PM, Zhang HJ, Zhao TT, Li P (2014) Increased DNase I activity in diabetes might be associated with injury of pancreas. Mol Cell Biochem 393:23–32
Valle FM, Balada E, Ordi-Ros J, Vilardell-Tarres M (2008) DNase 1 and systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 7:359–363
Martinez-Valle F, Balada E, Ordi-Ros J, Bujan-Rivas S, Sellas-Fernandez A, Vilardell-Tarres M (2009) DNase 1 activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship with epidemiological, clinical, immunological and therapeutical features. Lupus 18:418–423
Tamkovich SN, Cherepanova AV, Kolesnikova EV, Rykova EY, Pyshnyi DV, Vlassov VV, Laktionov PP (2006) Circulating DNA and DNase activity in human blood. In: Swaminathan R, Butt A, Gahan P (eds) Circulating Nucleic Acids in Plasma and Serum Iv, vol 1075. Ann N Y Acad Sci. pp 191–196.
Spandidos DA, Ramandanis G, Garas J, Kottaridis SD (1980) Serum Deoxyribonucleases in Patients with Breast-Cancer. Eur J Cancer 16:1615–1619
Schill WB, Schumach G (1972) Radial diffusion in gel for micro-determination of enzymes.1. muramidase, alpha-amylase, DNase i, RNase a, acid-phosphatase, and alkaline-phosphatase. Anal Biochem 46:502–533
Lutter LC (1979) Precise location of DNase-i cutting sites in the nucleosome core determined by high-resolution gel-electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res 6:41–56
Nakajima T, Takagi R, Tajima Y, Makita C, Kominato Y, Kuribara J, Ohshima S, Tada H, Tsurugaya H, Kobayashi Y, Takeshita H, Kawai Y, Yasuda T (2009) Development of a sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measurement of DNase I in human serum. Clin Chim Acta 403:219–222
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li XN, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112:2739–2779
Valentini P, Pompa PP (2013) Gold nanoparticles for naked-eye DNA detection: smart designs for sensitive assays. RSC Adv 3:19181–19190
Li YB, Ling LS (2015) Aptamer-based fluorescent solid-phase thrombin assay using a silver-coated glass substrate and signal amplification by glucose oxidase. Microchim Acta 182:1849–1854
Chudinov AV, Kolganova NA, Egorov AE, Fesenko DO, Kuznetsova VE, Nasedkina TV, Vasiliskov VA, Zasedatelev AS, Timofeev EN (2015) Bridge DNA amplification of cancer-associated genes on cross-linked agarose microbeads. Microchim Acta 182:557–563
Lang MJ, Li Q, Huang HM, Yu F, Chen QH (2016) Highly sensitive exonuclease III-assisted fluorometric determination of silver(I) based on graphene oxide and self-hybridization of cytosine-rich ss-DNA. Microchim Acta 183:1659–1665
Xu XY, Han MS, Mirkin CA (2007) A gold-nanoparticle-based real-time colorimetric screening method for endonuclease activity and inhibition. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:3468–3470
Zhao WA, Ali MM, Aguirre SD, Brook MA, Li YF (2008) Paper-Based bioassays using gold nanoparticle colorimetric probes. Anal Chem 80:8431–8437
Zhao WA, Lam JCF, Chiuman W, Brook MA, Li YF (2008) Enzymatic cleavage of nucleic acids on gold nanoparticles: a generic platform for facile colorimetric biosensors. Small 4:810–816
Zhang Y, Ying JY (2015) Homogeneous immunochemical assay on the lateral flow strip for measurement of DNase I activity. Anal Chem 87:10193–10198
Shen QP, Nie Z, Guo ML, Zhong CJ, Lin B, Li W, Yao SZ (2009) Simple and rapid colorimetric sensing of enzymatic cleavage and oxidative damage of single-stranded DNA with unmodified gold nanoparticles as indicator. Chem Commun 8:929–931
Liu ZH, Zhan YH, Bai Y, Sun JW (2012) And logic gate application based on colorimetric screening of enzyme activity. Solid State Sci 14:870–873
Hill HD, Mirkin CA (2006) The bio-barcode assay for the detection of protein and nucleic acid targets using DTT-induced ligand exchange. Nat Protoc 1:324–336
Cheng F, He Y, Xing XJ, Tan DD, Lin Y, Pang DW, Tang HW (2015) A gold nanoparticle-based label free colorimetric aptasensor for adenosine deaminase detection and inhibition assay. Analyst 140:1572–1577
Wang ZD, Lee JH, Lu Y (2008) Label-free colorimetric detection of lead ions with a nanomolar detection limit and tunable dynamic range by using gold nanoparticles and DNAzyme. Adv Mater 20:3263–3267
Liu P, Yang XH, Sun S, Wang Q, Wang KM, Huang J, Liu JB, He LL (2013) Enzyme-free colorimetric detection of dna by using gold nanoparticles and hybridization chain reaction amplification. Anal Chem 85:7689–7695
Xu W, Xie ZH, Tong CY, Peng L, Xiao CH, Liu XM, Zhu YH, Liu B (2016) A rapid and sensitive method for kinetic study and activity assay of DNase I in vitro based on a GO-quenched hairpin probe. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:3801–3809
Sato S, Fujita K, Kanazawa M, Mukumoto K, Ohtsuka K, Takenaka S (2009) Reliable ferrocenyloligonucleotide-immobilized electrodes and their application to electrochemical DNase I assay. Anal Chim Acta 645:30–35
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21275110, 81572086, 21535005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.03 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Cheng, F., Pang, DW. et al. Colorimetric and visual determination of DNase I activity using gold nanoparticles as an indicator. Microchim Acta 184, 101–106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2003-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2003-4