Abstract
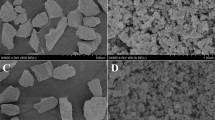
Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) particles for malachite green (MG) were prepared by emulsion polymerization using methacrylic acid as the functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as the cross-linker, and a combination of Span-80 and Tween-80 as an emulsifier. The MIP particles were characterized by SEM micrographs and FT-IR spectra. Their binding capacity for MG was evaluated based on kinetic and isothermal adsorption experiments and compared to non-imprinted polymer particles. Analytical figures of merit include an adsorption equilibrium time of 15 min, an adsorption capacity of 1.9 mg∙g‾1 in acetonitrile-water (20:80), and an imprinting factor of 1.85. The MIP particles were successfully applied to the extraction of MG from fish samples spiked with MG and the other interfering substances prior to its determination of MG by HPLC. Spiked samples gave recoveries of MG that ranged from 86 to 104 %, much higher than that of the other interfering substance.

Molecularly imprinted polymer particles for malachite green (MG) were prepared by emulsion polymerization. They show adsorption capacity of 1.9 mg∙g‾¹ with imprinting factor of 1.85, and were successfully applied to the extraction of MG from spiked fish samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderman DJ, Clifton Hadley RS (1993) Malachite green: a pharmacokinetic study in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 16(4):297–311
Srivastava SJ, Srivastava AK, Singh ND, Sinha R (1995) Acute toxicity of malachite green and its effects on certain blood parameters of a catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis. Aquat Toxicol 31(3):241–247
Rao KVK (1995) Inhibition of DNA synthesis in primary rat hepatocyte cultures by malachite green: a new liver tumor promoter. Toxicol Lett 81(2–3):107–113
Culp SJ, Beland FA (1996) Malachite green: a toxicological review. Int J Toxicol 15(3):219–238
Stammati A, Nebbia C, Angelis ID, Albo AG, Carletti M, Rebecchi C, Zampaglioni F, Dacasto M (2005) Effects of malachite green (MG) and its major metabolite, leucomalachite green (LMG), in two human cell lines. Toxicol in Vitro 19(7):853–858
Bilandžić N, Varenina I, Kolanović BS, Oraić D, Zrnčić S (2012) Malachite green residues in farmed fish in Croatia. Food Control 26(2):393–396
Sagar K, Smyth MR, Wilson JG, McLaughlin K (1994) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of the triphenylmethane dye, malachite green, using amperometric detection at a carbon fibre microelectrode. J Chromatogr A 659(2):329–336
Dowling G, Mulder PPJ, Duffy C, Regan L, Smyth MR (2007) Confirmatory analysis of malachite green, leucomalachite green, crystal violet and leucocrystal violet in salmon by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 586(1–2):411–419
Aprea C, Colosio C, Mammone T, Minoia C, Maroni M (2002) Biological monitoring of pesticide exposure: a review of analytical methods. J Chromatogr B 769(2):191–219
Hennion M, Pichon V (2003) Immuno-based sample preparation for trace analysis. J Chromatogr A 1000(1):29–52
Rodríguez EE, Navarro-Villoslada F, Benito-Peña E, Marazuela MD, Moreno-Bondi MC (2011) Multiresidue determination of ultratrace levels of fluoroquinolone antimicrobials in drinking and aquaculture water samples by automated online molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 83(6):2046–2055
Zhang QC, Xiao XH, Li GK (2014) Porous molecularly imprinted monolithic capillary column for on-line extraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography for trace analysis of antimicrobials in food samples. Talanta 123:63–70
Wulff G (2013) Fourty years of molecular imprinting in synthetic polymers: origin, features and perspectives. Mikrochim Acta 180(15–16):1359–1370
Pardeshi S, Dhodapkar R, Kumar A (2014) Molecularly imprinted microspheres and nanoparticles prepared using precipitation polymerisation method for selective extraction of gallic acid from Emblica officinalis. Food Chem 146:385–393
Li YH, Yang T, Qi XL, Qiao YW, Deng AP (2008) Development of a group selective molecularly imprinted polymers based solid phase extraction of malachite green from fish water and fish feed samples. Anal Chim Acta 624(2):317–325
Long CY, Mai ZB, Yang YF, Zhu BH, Xu XM, Lu L, Zou XY (2009) Determination of multi-residue for malachite green, gentian violet and their metabolites in aquatic products by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 1216(12):2275–2281
Guo ZY, Gai PP, Hao TT, Duan J, Wang S (2011) Determination of malachite green residues in fish using a highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence method combined with molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction. J Agric Food Chem 59(10):5257–5262
Yan SL, Gao ZX, Fang YJ, Cheng YY, Zhou HY, Wang HY (2007) Characterization and quality assessment of binding properties of malachite green molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by precipitation polymerization in acetonitrile. Dyes Pigments 74(3):572–577
Bueno MJM, Herrera S, Uclés A, Agüera A, Hernando MD, Shimelis O, Rudolfsson M, Fernández-Alba AR (2010) Determination of malachite green residues in fish using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography–linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 665(1):47–54
Lian ZR, Wang JT (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of malachite green from seawater and seafood coupled with high-performance liquid chromatographic determination. Mar Pollut Bull 64(12):2656–2662
Dai JD, Pan JM, Xu LC, Li XX, Zhou ZP, Zhang RX, Yan YS (2012) Preparation of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with superparamagnetic susceptibility through atom transfer radical emulsion polymerization for the selective recognition of tetracycline from aqueous medium. J Hazard Mater 205–206:179–188
Shinoda K, Takeda H (1970) The effect of added salts in water on the hydrophile-lipophile balance of nonionic surfactants: the effect of added salts on the phase inversion temperature of emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 32(4):642–646
Vaihinger D, Landfester K, Kräuter I, Brunner H, Tovar GE (2002) Molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres as synthetic affinity receptors obtained by miniemulsion polymerisation. Macromol Chem Phys 203(13):1965–1973
Pérez N, Whitcombe MJ, Vulfson EN (2000) Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles prepared by core shell emulsion polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 77(8):1851–1859
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by SRF for ROCS, SEM (201210100002); the Science and Technology Planning Project of Fujian Province, China (2012Y0052, 2014Y0045); the Science and Technology Planning Project of Xiamen, China (3502Z20143018); Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Food Microbiology and Enzyme Engineering (M20140902); the Foundation for Innovative Research Team of Jimei University, China (2010A007); National Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (201410390009, 20141039047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 608 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Lin, Zz., Chen, Xm. et al. Molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of malachite green from fish samples prior to its determination by HPLC. Microchim Acta 182, 1791–1796 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1513-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1513-9