Abstract
A biocomposite film for sensing hydrogen peroxide (HP) is described that is based on nanospheres made from hemoglobin (Hb), graphene, and zinc oxide. The composition, morphology and size of the film were studied by transmission electron microscopy. UV-vis spectroscopy revealed that the Hb entrapped in the graphene and ZnO nanosphere retains its native structure. A pair of stable and well-defined quasi-reversible redox peaks of Hb was obtained, with a formal potential of −30 mV at pH 6.5. Hb exhibits excellent long-term bioelectrocatalytic activity towards HP. The apparent heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant is 1.0 s−1, indicating that the presence of graphene in the composite film facilitates the electron transfer between matrix and the electroactive center of Hb. The sensor responds linearly to HP in the range from 1.8 μM to 2.3 mM, with a detection limit of 0.6 μM (at S/N = 3). The apparent Michaelis-Menten constant is 1.46 mM. The biosensor displays high sensitivity, good reproducibility, and long-term stability.

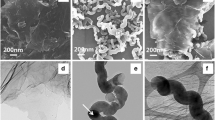
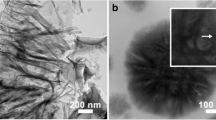
TEM images of graphene insert: graphene-ZnO nanosphere






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu JJ, Zhao T, Zhao FQ, Zeng BZ (2008) Direct electron transfer of hemoglobin immobilized in a mesocellular siliceous foams supported room temperature ionic liquid matrix and the electrocatalytic reduction of H2O2. Electrochim Acta 53:5760
Gooding JJ, Wibowo R, Liu JQ, Yang WR, Losic D, Orbons S, Mearns FJ, Shapter JG, Hibbert DB (2003) Protein electrochemistry using aligned carbon nanotube arrays. J Am Chem Soc 125:9006
Zhou YL, Hu NF, Zeng YH, Rusling JF (2002) Heme protein-clay films: direct electrochemistry and eletrochemical catalysis. Langmuir 18:211
Hill HAO (1996) The development of bioelectrochemistry. Coord Chem Rev 151:115
Li J, Guo SJ, Zhai YM, Wang EK (2009) Nafion–graphene nanocomposite film as enhanced sensing platform for ultrasensitive determination of cadmium. Electrochem Commun 11:1085
Armstrong FA, Heering HA, Hirst J (1997) Reactions of complex metalloproteins studied by protein film voltammetry. Chem Soc Rev 26:169
Yu JJ, Ma JR, Zhao FQ, Zeng BZ (2007) Direct electron-transfer and electrochemical catalysis of hemoglobin immobilized on mesoporous Al2O3. Electrochim Acta 53:1995
Qi HL, Zhang CX, Li XR (2006) Amperometric third-generation hydrogen peroxide biosensor incorporating multiwall carbon nanotubes and hemoglobin. Sens Actuators B 114:364
Zhang RY, Wang XM, Shiu KK (2007) Accelerated direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin based on hemoglobin–carbon nanotube (Hb–CNT) assembly. J Colloid Interface Sci 316:517
Feng JJ, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2007) Direct electron transfer and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin adsorbed on mesoporous carbon through layer-by-layer assembly. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1618
Geim AK, Novoselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6:183
Li D, Muller MB, Gilje S, Kaner RB, Wallace GG (2008) Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat Nanotechnol 3:101
Ponomarenko LA, Schedin F, Katsnelson MI, Yang R, Hill EW, Novoselov KS, Geim AK (2008) Chaotic dirac billiard in graphene quanyum dots. Science 320:356
Park S, Ruoff RS (2009) Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat Nanotechnol 4:217
Chen H, Müller MB, Gilmore KJ, Wallace GG, Li D (2008) Mechanically strong, electrically conductive and biocimpatible graphene paper. Adv Mater 20:3557
Shan CS, Yang HF, Song JF, Han DX, Ivaska A, Niu L (2009) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on graphene. Anal Chem 81:2378
Wang Y, Li YM, Tang LH, Lu J, Li JH (2009) Application of graphene-modified electrode for selective detection of dopamine. Electrochem Commun 11:889
Lu XB, Zhang HJ, Ni YW, Zhang Q, Chen JP (2008) Porous nanosheet-based ZnO microspheres for the construction of direct electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 24:93
Hummers WS, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80:1339
Compton OC, Nguyen ST (2010) Graphene oxide, highly reduced graphene oxide, and graphene: versatile building blocks for carbon-based materials. Small 6:711
Hirsch A (2009) Unzipping carbon nanotubes: a peeling method for the formation of graphene nanoribbons. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:2
Laviron E (1979) The use of linear potential sweep voltammetry and of a.c. voltammetry for the study of the surface electrochemical reaction of strongly adsorbed systems and of redox modified electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 100:263
Xu HF, Dai H, Chen GN (2010) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin protein entrapped in graphene and chitosan composite film. Talanta 81:334
Zhao GC, Xu MQ, Ma J, Wei XW (2007) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin on a room temperature ionic liquid modified electrode and its electrocatalytic activity for the reduction of oxygen. Electrochem Commun 9:920
Liu YG, Lu CL, Hou WH, Zhu JJ (2008) Direct electron transfer of hemoglobin in layered a-zirconium phosphate with a high thermal stability. Anal Biochem 375:27
Trushina E, Oda R, Landers J, McMurray C (1997) Determination of nitrite and nitrate reduction by capillary ion electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 18:1890
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem 101:19
Sun W, Gao RF, Jiao K (2007) Electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemogolobin in Nafion/Nano-CaCO3 film on a new ionic liquid BPPF6 modified carbon paste electrode. J Phys Chem B 111:4560
Wang YH, Gu HY (2009) Hemoglobin co-immobilized with silver–silver oxide nanoparticles on a bare silver electrode for hydrogen peroxide electroanalysis. Microchim Acta 164:41
Zou Y, Xiang C, Sun L, Xu F (2008) Glucose biosensor based on electrodeposition of platinum nanoparticles onto carbon nanotubes and immobilizing enzyme with chitosan–SiO2 sol–gel. Biosens Bioelectron 23:1010
Kamin A, Wilson GS (1980) Rotating ringdisk enzyme electrode for biocatalysis kinetic studies and characterization of the immobilized enzyme layer. Anal Chem 52:1198
Yu CM, Guo JW, Gu HY (2009) Direct electrochemical behavior of hemoglobin at surface of Au@Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 166:215
Zhao G, Feng JJ, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2005) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of heme proteins immobilized on self-assembled ZrO2 film. Electrochem Commun 7:724
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 71 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Liu, C. & Wu, Z. Direct electrochemistry and enhanced electrocatalytic activity of hemoglobin entrapped in graphene and ZnO nanosphere composite film. Microchim Acta 172, 425–430 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0515-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0515-x