Abstract
For the assessment of the long-term stability of deep geological repositories of high-level radioactive waste (HLW), the information on in-situ stress field is a key parameter. We recently performed a great number of hydraulic fracturing tests within 1000 m vertical depths in the Shazaoyuan rock block, a new candidate site for HLW disposal in northwest China to clarify its stress field. The results show that the maximum (σH) and minimum (σh) horizontal stresses increase in gradients of 0.0193 ± 0.0018 MPa/m and 0.0143 ± 0.001 MPa/m, respectively, and the largest value is less than 30.65 MPa within the tested depths. The Shazaoyuan rock block is characterized by a thrust stress regime (σH > σh > σv) at depths above 426 m, whereas strike-slip (σH > σv > σh) within 426–1000 m depths interval where σv is the vertical stress. The stress field of the Shazaoyuan is rotated by 90° with respect to the larger regional trend, but parallel to the NW-striking fault system inside the site. Our findings manifest that the Shazaoyuan stress field which shows NW-oriented σH and greater horizontal stresses is a rare local stress field generated under the NE regional forces. One possible explanation for this dramatic rotation is the potential perturbation of the NW-trending fault system on the regional stress field. Finally, we discuss the geomechanical stability of the site and find that it is currently in stability state, being suitable for HLW disposal. This study provides important information for site suitability assessment of HLW disposal, also a reference for stress field prediction in similar geological settings.
Highlights
-
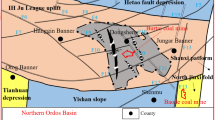
To assess the stress field of Shazaoyuan, a new site for HLW disposal in NW China, 119 sets of stress value and 50 sets of orientation data were successfully obtained up to a depth of 1000 m.
-
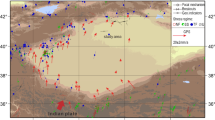
The Shazaoyuan block is a local stress field with an NW orientation of σH and a greater horizontal stress level, which is generated under the NE-oriented regional stress forces.
-
The σH orientation in the Shazaoyuan rock block is parallel to the fault system that bounds the block which allows the hypothesis that this is causing the local σH rotation.
-
The Shazaoyuan site is in geomechanical stability because the rock mass is far away from generating new fractures and faults striking in NW and NE are far away from re-activation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data, models, or code that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Amadei B, Stephansson O (1997) Rock stress and its measurement. Chapman & Hall, London
Anderson EM (1951) The dynamics of faulting and dyke formation with application to Britain. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh
Ask D (2006) New development in the integrated stress determination method and their application to rock stress at Äspö HRL, Sweden. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 43(1):107–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/i.ijrmms.2005.04.011
Bröker K, Ma XD (2022) Estimation the least principal stress in a granitic rock mass: systematic mini-frac tests and elaborated pressure transient analysis. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55:1931–1954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02743-1
Brooke-Barnett S, Flottmann T, Paul PK, Busetti S, Hennings P, Reid R, Rosenbaum G (2015) Influence of basement structures on in situ stresses over the Surat Basin, southeast Queensland. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120(7):4946–4965. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JB011964
Brown ET, Hoek E (1978) Trends in relationship between measured in-situ stresses and depth. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 15:211–215
Chang CD, Jo Y (2015) Heterogeneous in situ stress magnitudes due to the presence of weak natural discontinuities in granitic rock. Tectonophysics 664:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.08.044
Chen WM, Jin YX, Luo H, Tian X, Li YF (2018) Geology of Shazaoyuan intrusion in Beishan region pre-selected for disposal of high-level radioactive waste. In: Wang J (ed) The 7th symposium on underground waste disposal. Atomic Energy Press, Beijing, pp 41–45
China Earthquake Disaster Prevention Center (2016) Research on seismic safety analysis for Shazaoyuan and Suanjingzi site, Beijing
Connolly P, Cosgrove J (1999). Prediction of static and dynamic fluid pathways within and around dilational jogs. In: McCaffrey KJW, Lonergan L, Wilkinson JJ (eds) Fractures, fluid flow and mineralization, vol 155. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, pp 105–121. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1999.155.01.09
Corkum AG, Damjanac B, Lam T (2018) Variation of horizontal in situ stress with depth for long-term performance evaluation of the deep geological repository project access shaft. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 107:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.04.035
Cornet F, Röckel T (2012) Vertical stress profiles and the significance of “stress decoupling.” Tectonophysics 581:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.020
Deere DU (1968) Geological consideration. In: Stagg KG, Zienkiewicz OC (eds) Rock mechanics in engineering practice. Wiley, New York, pp 1–20
Desroches J, Peyret E, Gisolf A, Wilcox A, Giovanni MD, de Schram AJ, Sepehri S, Garrard R, Giger S (2021) Stress measurement campaign in scientific deep boreholes: focus on tool and methods. In: SPWLA 62nd ann logging sym. https://doi.org/10.30632/SPWLA-2021-0056
Engelder T (1992) Stress regimes in the lithosphere. Princeton University Press, New York
Evans KF, Scholz CH, Engelder T (1988) An analysis of horizontal initiation during hydrofrac stress measurements in granite at North Conway, New Hampshire. Geophys J 93:251–264
Fairhurst C (2004) Nuclear waste disposal and rock mechanics: contributions of the Underground Research Laboratory (URL), Pinawa, Manitoba, Canada. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:1221–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.001
Faulkner DR, Mitchell TM, Healy D, Heap J (2006) Slip on ‘weak’ faults by the rotation of regional stress in the fracture damage zone. Nature 444:922–925. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05353
Gronseth JM, Kry PR (1983) Instantaneous shut-in pressure and its relationship to the minimum in situ stress in hydraulic fracturing stress measurements. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Haimson BC (1978) The hydrofracturing stress measurement method and recent field results. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 15:167–178
Haimson BC, Cornet FH (2003) ISRM suggested methods for rock stress estimation-part 3: hydraulic fracturing (HF) and/or hydraulic testing of pre-existing fractures (HTPF). Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40:1011–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.08.002
Harper T (2020) Dependence of stress state on the histories of burial, erosion, mechanical properties, pore pressure and faulting. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 136:104523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104523
Hayashi K, Haimson BC (1991) Characteristics of shut-in curves in hydraulic fracturing stress measurements and determination of in situ stress minimum compressive stress. J Geophys Res 96:18311–18321. https://doi.org/10.1029/91JB01867
Heidbach O, Iaffaldano G, Bunge HP (2008) Topography growth drives stress rotation in the central Andes: observation and models. Geophys Res Lett 35(8):L08301. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL032782
Heidbach O, Rajabi M, Cui XF, Fuchs K, Muller B, Reinecker J, Reiter K, Tinga M, Wenzel F, Xie FR, Ziegler MO, Zoback ML, Zoback M (2018) The World Stress Map database release 2016: crustal stress pattern across scales. Tectonophysics 74:484–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2018.07.007
Hergert T, Heidbach O, Reiter K, Giger SB, Marschall P (2015) Stress field sensitivity analysis in a sedimentary sequence of the Alpine foreland, north Switzerland. Solid Earth 6:533–552. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-6-533-2015
Hickman SH, Zoback MD (2004) Stress orientations and magnitudes in the SAFOD pilot hole. Geophys Res Lett 31:L15S12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL020043
Hoek E (2007) Practical rock engineering. https://www.rocscience.com
Hu XP, Zang A, Heidbach O, Cui XF, Xie FR, Chen JW (2017) Crustal stress pattern in China and adjacent areas. J Asian Earth Sci 149:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.07.005
Huo L, Wang GB, Yang CH, Wei X, Tang MH (2019) Geometric characteristics of multi-scale discontinuities of Shazaoyuan granite masses in Beishan. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39(9):1848–1859. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0015
Ito T, Evans K, Kawai K, Hayashi K (1999) Hydraulic fracture reopening pressure and the estimation of maximum horizontal stress. Int J Rock Mech Sci 36:811–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(99)00053-4
Ito T, Satoh T, Kato H (2010) Deep rock stress measurement by hydraulic fracturing method taking account system compliance effect. In: Xie FR (ed) Rock stress and earthquake. CRC Press, Beijing, pp 43–49
Jaeger JC, Cook NGW, Zimmerman RW (2007) Fundamentals of rock mechanics, 4th edn. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford
Jin YX, Chen WM, Luo H, Tian X (2015) Research on surface investigation and geochemical characteristics of the Shazaoyuan and Suanjingzi regions. Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing
Jo Y, Chang C, Ji SH, Park KW (2019) In situ stress states at KURT, an underground research laboratory in South Korea for the study of high-level radioactive waste disposal. Eng Geol 259:105198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105198
Ju W, Li ZL, Sun WF, Xu HR (2018) In-situ stress orientations in the Xiagou tight oil reservoir of Qingxi Oilfield, Jiuxi Basin, northwestern, China. Mar Petrol Geol 98:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.08.020
Kaga N, Matsuki K, Sakaguchi K (2003) The in situ stress state associated with core discing estimated by analysis of principal tensile stress. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(5):653–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00057-1
Krietsch H, Gischig V, Evans K, Doetsch J, Dutler NO, Valley B, Amann F (2019) Stress measurements for an in situ stimulation experiment in crystalline rock: integration of induced seismicity, stress relief and hydraulic methods. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(2):517–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1597-8
Lee MY, Haimson BC (1989) Statistical evaluation of hydraulic fracturing stress measurement parameter. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 26:447–456
Lim SS, Martin CD (2010) Core disking and its relationship with stress magnitude for Lac du Bonnet granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(2):254–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.11.007
Ljunggren C, Chang Y, Janson T, Christiansson R (2003) An overview of rock stress measurement methods. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(7):975–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.07.003
Lund Snee JE, Zoback MD (2018) State of stress in the Permian Basin, Texas and New Mexico: Implications for induced seismicity. Lead Edge 37(2):127–134. https://doi.org/10.1190/tle37020127.1
Ma XD, Zhang SH, Zhang XW, Liu JD, Jin J, Cheng W, Jiang WD, Zhang GM, Chen ZW, Zoback MD (2022) Lithology-controlled stress variations of Longmaxi shale-example of an appraisal wellbore in the Changning area. Rock Mech Bull. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rockmb.2022.100002
Magnenet V, Cornet FH, Fond C (2017) A nontectonic origin for the present-day stress field in the Paris Basin (France). J Geophys Res 122(11):9313–9327. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB014345
Martel SJ (2016) Effects of small-amplitude periodic topography on combined stresses due to gravity and tectonics. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 89:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.07.026
Martin CD (1990) Characterizing in situ stress domains at the AECL Underground Research Laboratory. Can Geotech J 27(5):631–646. https://doi.org/10.1139/t90-077
Martin CD, Chandler NA (1993) Stress heterogeneity and geological structures. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 30(7):993–999
Martin CD, Lanyon GW (2003) Measurement of in situ stress in weak rocks at Mont Terri Rock Laboratory, Switzerland. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40:1077–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1365-1609(03)00113-8
Morris A, Ferrill DA, Henderson DB (1996) Slip-tendency analysis and fault reactivation. Geology 24(3):275–278. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024%3c0275:STAAFR%3e2.3.CO;2
Pan E, Amadei B, Savage WZ (1995) Gravitational and tectonic stresses in anisotropic rock with irregular topography. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 31(1):201–214
Qin XH, Chen QC, Zhao XG, Zhang CY, Sun DS, Meng W, Feng CJ, Wang B, Yang YH (2020) Experimental study on the crucial effect of test system compliance on hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress measurements. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39(6):1189–1202. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.1204
Rajabi M, Tingay M, Heidbach O (2016) The present-day stress field of New South Wales, Australia. Aust J Earth Sci 63(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/08120099.2016.1135821
Rajabi M, Tingay M, King R, Heidbach O (2017) Present-day stress orientation in the Clarence-Moreton Basin of New South Wales, Australia: a new high density dataset reveals local stress rotations. Basin Res 29:622–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/bre.12175
Reinecker J, Tingay M, Müller B, Heidbach O (2010) Present-day stress orientation in the Molasse basin. Tectonophysics 482:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2009.07.021
Reiter K (2021) Stress rotation-impact and interaction of rock stiffness and faults. Solid Earth 12:1287–1307. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-12-1287-2021
Reiter K, Heidbach O, Ziegler M (2023) Impact of fault on the remote stress state. EGUsphere (preprint). https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-2023-1829.2023
Roche V, van der Baan M (2017) Modeling of the in situ stress state of stress in elastic layered rock subject to stress and strain-driven tectonic forces. Solid Earth 8:479–498. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-8-479-2017
Rutqvist J, Tsang CF, Stephansson O (2000) Uncertainty in the maximum principal stress estimated from hydraulic fracturing measurements due to the presence of the induced fracture. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37:107–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(99)00097-0
Savage WZ, Morin RH (2002) Topographic stress perturbations in southern Davis Mountains, west Texas 1: polarity reversal of principal stress. J Geophys Res 107(B12):ETG5-1–15. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000484
Schmitt DR, Currie CA, Zhang L (2012) Crustal stress determination from boreholes and rock cores: fundamental principles. Tectonophysics 580:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.08.029
Song I (1998) Borehole breakouts and core disking in Westerly granite: mechanisms of formation and relationship to in situ stress. University of Wisconsin-Madison, New York
Townend J, Zoback MD (2000) How faulting keeps the crust strong. Geology 28:399–402. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029%3c0189:HFKTCS%3e2.0.CO;2
Wang J (2014) On area-specific underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2014.01.002
Wang M, Shen ZK (2020) Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 125:e2019JB018774. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB018774
Wang F, Wang J, Fan HM, Su G, Xu J, Wang HZ (2005) Distribution of Late Quaternary active faults and its tectonic significance in the Beishan region, Gansu Province, China. Geol Rev 151(3):250–256
Wang YH, Cui XF, Hu XP, Xie FR (2012) Study on the stress state in upper crust of China mainland based on in-situ stress measurements. Chin J Geophys 55(9):3016–3027. https://doi.org/10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.020
Wang J, Chen L, Su R, Zhao XG (2018) The Beishan underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China: planning, site selection, site characterization and in situ stress. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 10:411–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.03.002
Warpinski NR (1989) Determining the minimum in situ stress from hydraulic fracturing through perforations. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 26(6):523–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(89)91430-7
Warpinski NR, Teufel LW (1991) In situ stress measurements at Rainier Mesa, Nevada Test Site—influence of topography and lithology on the stress state in tuff. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 28(2–3):143–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(91)92163-S
Xie FR (2015) Recent tectonic stress map of China and its adjacent areas. Sinomaps Press, Jiangsu
Yang HB, Yang XP, Cunningham D, Huang XN, Hu ZK, Yang HL (2021) Late Miocene to Quaternary development of the Jiujing basin southern Beishan Block, China: implications for the kinematics and timing of crustal reactivation north of Tibet. Lithosphere 2021:6670365. https://doi.org/10.2113/2021/6670365
Zang A, Stephansson O (2010) Stress field of the earth’s crust. Springer, Heidelberg
Zhang SH, Ma XD (2021) How does in situ stress rotate within a fault zone? Insight from explicit modeling of the frictional, fractured rock mass. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 126:e2021JB022348. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JB022348
Zhang CY, Chen QC, Qin XH, Hong B, Meng W, Zhang QF (2017) In-situ stress and fracture characterization of a candidate repository for spent nuclear fuel in Gansu, northwestern China. Eng Geol 231:218–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.10.007
Zhao XG, Wang J, Cai M, Ma LK, Zong ZH, Wang XY, Su R, Chen WM, Zhao HG, Chen QC, An QM, Qin XH, Ou MY, Zhao JS (2013) In-situ stress measurements and regional stress field assessment of the Beishan area, China. Eng Geol 163:26–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.05.020
Zhao XG, Wang J, Qin XH, Cai M, Su R, He JG, Zong ZH, Ma LK, Ji RL, Zhang M, Zhang S, Yu L, Chen QC, Niu LL, An QM (2015) In-situ stress measurements and regional stress field assessment in the Xinjiang candidate area for China′s HLW disposal. Eng Geol 197:42–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.015
Zhao HG, Liang JW, Wang J, Sui R, Jin YX, Tiao X, Luo H (2020) Geochronology, geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of the Shazaoyuan composite pluton in the southern Beishan Mountains, Gansu Province, China. Acta Geol Sin 94:396–425. https://doi.org/10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2019150
Zoback ML (1992) First- and second-order patterns of stress in the lithosphere: the word stress map project. J Geophys Res 97:11703–11728. https://doi.org/10.1029/92JB00132
Zoback MD (2007) Reservoir geomechanics. Cambridge University Press, New York
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the China Atomic Energy Authority through the geological disposal program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42177175, 11972149), Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (DZLXJK202204), and the National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2016ZX05034–003). The excellent collaboration of all participants is greatly appreciated. The authors also thank the two anonymous reviewers and the editor for their valuable comments and suggestions that significantly improved this paper.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XQ: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft. XZ: conceptualization, writing-review and editing. CZ: formal analysis, investigation. PL: investigation. QC: investigation, supervision. JW: supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, X., Zhao, X., Zhang, C. et al. Measurement and Assessment of the In-Situ Stress of the Shazaoyuan Rock Block, a Candidate Site for HLW Disposal in Northwest China. Rock Mech Rock Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-03775-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-03775-z