Abstract
Purpose
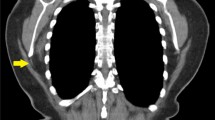
Elastofibroma dorsi (ED) is a rare, benign soft tissue tumor arising from connective tissue and usually found in the subscapular region. We conducted this retrospective study to contribute to a better understanding of this tumor, the pathogenesis of which is still unclear.
Methods
We reviewed the medical records of eight patients treated for ED at our institution between 2003 and 2008.
Results
All patients were right-handed and all except one were female. The tumor was located on the right in two patients, on the left in one, and bilaterally in five. All patients underwent complete marginal resections. The resected tumors ranged in size from 5 cm to 12 cm. The only postoperative complication was seroma, observed in two patients. No recurrences have been observed in follow-up ranging from 15 days to 5 years.
Conclusions
We could not establish a relationship between the side of the dominant hand and the tumor location. If this tumor becomes symptomatic, local excision is the best treatment; however, as malignant transformation has not been reported, follow-up is recommended for asymptomatic lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jarvi O, Saxen E. Elastofibroma dorsi. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 1961;51(suppl 144):83–84.
Mortman KD, Hochheiser GM, Giblin EM, Manon-Matos Y, Frankel KM. Elastofibroma dorsi: clinicopathologic review of 6 cases. Ann Thorac Surg 2007;83(5):1894–1897.
Greenberg JA, Lockwood RC. Elastofibroma dorsi. A case report and review of the literature. Orthop Rev 1989;18(3):329–333.
Guha AR, Raja RCS, Devadoss VG. Elastofibroma dorsi: A case report and review of the literature. J Clin Pract 2004;58(2):218–220.
Briccoli A, Casadei R, Di Renzo M, Favale L, Bacchini P, Bertoni F. Elastofibroma dorsi. Surg Today 2000;30(2):147–152.
Daigeler A, Vogt PM, Busch K, Pennekamp W, Weyhe D, Lehnhardt M, et al. Elastofibroma dorsi — differential diagnosis in chest wall tumors. World J Surg Oncol 2007;5:5–15.
Brandser EA, Goree JC, El-Khoury GY. Elastofibroma dorsi: prevalence in an elderly patient population as revealed by CT. AJR 1998;171(4):977–980.
Nagamine N, Nohara Y, Ito E. Elastofibroma in Okinawa. A clinicopathologic study of 170 cases. Cancer 1982;50(9):1794–1805.
McComb EN, Feely MG, Neff JR, Johansson SL, Nelson M, Bridge JA. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2001;126:68–72.
Fibla J, Molins L, Marco V, Pérez J, Vidal G. Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi. Joint Bone Spine. 2007;74(2):194–196.
Kara M, Dikmen E, Kara SA, Atasoy P. Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi: proper positioning for an accurate diagnosis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2002;22:839–841.
Enzinger FM, Weiss SW. In: Enzinger FM, Weiss SW, editors. Soft tissue tumors. St. Louis: Mosby; 1995. p. 187–191.
Marin ML, Perzin KH, Markowitz AM. Elastofibroma dorsi: benign chest wall tumor. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1989;98(2):234–238.
Chang CC, Wu MM, Chao C, Lin SS, Liu JT, Lee KJ, et al. Prevalence study of elastofibroma dorsi with retrospective evaluation of computed tomography. Chin J Radiol 2003;28:367–371.
Brandser EA, Goree JC, El-Khoury GY. Elastofibroma dorsi: prevalence in an elderly patient population as revealed by CT. AJR 1998;171:977–980.
Ochsner JE, Sewall SA, Brooks GN, Agni R. Elastofibroma dorsi. RadioGraphics 2006;26:1873–1876.
Bianchi S, Martinoli C, Abdelwahab IF, Gandolfo N, Derchi LE, Damiani S. Elastofibroma dorsi: sonographic findings. AJR 1997;169:1113–1115.
Naylor MF, Nascimento AG, Sherrick AD, McLeod RA. Elastofibroma dorsi: radiologic findings in 12 patients. AJR 1996;167:683–687.
Pierce JC, Henderson R. Hypermetabolism of elastofibroma dorsi on PET-CT. AJR 2004;183:35–37.
Sundaram M, McLeod RA. MR imaging of tumor and tumorlike lesions of bone and soft tissue. AJR 1990;155:817–824.
Sundaram M, McGuire MH, Schajowicz F. Soft tissue masses: histologic basis for decreased signal (short T2) on T2-weighted MR images. AJR 1987;148:1247–1250.
Muramatsu K, Ihara K, Hashimoto T, Seto S, Taguchi T. Elastofibroma dorsi: diagnosis and treatment. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2007;16(5):591–595.
Malghem J, Baudrez V, Lecouvet F, Lebon C, Maldague B, Vande Berg B. Imaging study findings in elastofibroma dorsi. Joint Bone Spine 2004;71(6):536–541.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koksel, O., Demir Apaydin, F., Ayan, E. et al. Elastofibroma dorsi: Review of eight cases. Surg Today 40, 423–427 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-008-4071-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-008-4071-5