Abstract
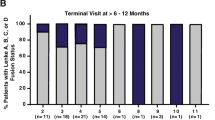
Few studies have specifically examined the outcomes following rhBMP-2 usage in patients 65 years and older. The purpose of this retrospective study is to evaluate the efficacy of rhBMP-2 with allograft versus autograft for posterolateral lumbar fusion in patients 65 years and older. One hundred twenty-seven patients were divided into three groups based on fusion material and age. Subjects in group A (n = 34) consisted of patients 65 years and older who received rhBMP-2 and allograft. Group B (n = 52) was composed of patients under 65 years of age with rhBMP-2 and allograft. Subjects in group C (n = 41) were 65 years and older with autograft use. A comparison was made of fusion rate, fusion time (noticed, solid), clinical outcome, VAS, perioperative complications and revision rate between each group. The fusion rate and fusion time were similar in groups A and C; however, these were lower than that observed in group B. Clinical outcomes were similar amongst the groups. There were no significant differences in VAS and perioperative complication rate between groups A and C. In patients 65 years and older, rhBMP-2 with allograft may lead to acceptable fusion rates and fusion times, good clinical outcomes and reduced perioperative complications. The combination of rhBMP-2 with allograft yields equivalent outcomes as autograft in elderly patients undergoing instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion. Additionally, when compared to patients under 65 years of age undergoing posterolateral lumbar fusion, the use of rhBMP-2 was not sufficient to overcome all aspects of the age-related weakened osteoinductive capacity encountered in elderly patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glassman SD, Carreon LY, Dimar JR et al (2007) Clinical outcomes in older patients after posterolateral lumbar fusion. Spine J 7:547–551
Li G, Patil CG, Lad SP et al (2008) Effects of age and comorbidities on complication rates and adverse outcomes after lumbar laminectomy in elderly patients. Spine 33:1250–1255
Wang MY, Green BA, Shah S et al (2003) Complications associated with lumbar stenosis surgery in patients older than 75 years of age. Neurosurg Focus 14:1–4
Hamilton DK, Jones-Quaidoo SM, Sansur C et al (2008) Outcomes of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in mature adults: posterolateral non-instrument-assisted lumbar decompression and fusion. Surg Neurol 69:457–461
Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT (1991) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 73:802–808
Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M, Yoshimura Y et al (2008) Union versus nonunion after posterolateral lumbar fusion: a comparison of long-term surgical outcomes in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17:1107–1112
Wu CH, Kao YH, Yang SC et al (2008) Supplementary pedicle screw fixation in spinal fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis in patients aged 65 and over. Acta Orthop 79:67–73
Bae HW, Stambaugh J, Glassman SD et al (2007) Level-1 data comparing rhBMP-2/ACS combined with an osteoconductive bulking agent with iliac crest bone graft in posterolateral lumbar fusion. Spine J 7:9s
Dimar JR, Glassman SD, Burkus KJ et al (2006) Clinical outcomes and fusion success at 2 years of single-level instrumented posterolateral fusions with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/compression resistant matrix versus iliac crest bone graft. Spine 31:2534–2539
Glassman SD, Carreon LY, Djurasovic M et al (2007) Posterolateral lumbar fusion with INFUSE bone graft. Spine J 7:44–49
Singh K, Smucker JD, Boden SD (2006) Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 as an adjunct in posterolateral lumbar spine fusion. A prospective CT-scan analysis at one and 2 years. J Spinal Disord Tech 19:416–423
Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Djurasovic M et al (2009) RhBMP-2 versus iliac crest bone graft for lumbar spine fusion in patients over 60 years of age. A cost-utility study. Spine 34:238–243
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Paine KWE, Cauchoz J (1974) Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 99:30–52
Gibson S, McLeod I, Wardlaw D et al (2002) Allograft versus autograft in instrumented posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion. A randomized control trial. Spine 27:1599–1603
Nasca RJ, Whelchel ILL (1987) Use of cryopreserved bone in spinal surgery. Spine 12:222–227
An HS, Lynch K, Toth J (1995) Prospective comparison of autograft vs. allograft for posterolateral lumbar spine fusion: differences among freeze-dried, frozen, and mixed grafts. J Spinal Disord 8:131–135
Nugent PJ, Dawson EG (1993) Intertransverse process lumbar arthrodesis with allogeneic fresh-frozen bone graft. Clin Orthop Relat Res 287:107–111
Weiss LE, Vaccaro AR, Scuderi G et al (1997) Pseudarthrosis after postoperative wound infection in the lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord 10:482–487
Burkus JK, Sandhu HS, Gornet MF et al (2005) Use of rhBMP-2 in combination with structural cortical allografts: clinical and radiographic outcomes in anterior lumbar spinal surgery. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87:1205–1212
Slosar PJ, Josey R, Reynolds J (2007) Accelerating lumbar fusions by combining rhBMP-2 with allograft bone: a prospective analysis of interbody fusion rates and clinical outcomes. Spine J 7:301–307
Glassman SD, Carreon LY, Djurasovic M et al (2008) RhBMP-2 versus iliac crest bone graft for lumbar spine fusion. A randomized, controlled trial in patients over sixty years of age. Spine 33:2843–2849
Epstein NE (2008) Fusion rates and SF-36 outcomes after multiple laminectomy and noninstrumented lumbar fusions in a predominantly geriatric population. J Spinal Disord Tech 21:159–164
Liang CT, Barnes J, Seedor JG et al (1992) Impaired bone activity in aged rats: alterations at the cellular and molecular levels. Bone 13:435–441
Muller SM, Glowacki J (2001) Age-related decline in the osteogenic potential of human bone marrow cells cultured in three-dimensional collagen sponges. J Cell Biochem 82:583–590
Nyssen-Behets C, Delaere O, Duchesne PY et al (1996) Aging effect on inductive capacity of human demineralized bone matrix. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 115:303–306
Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Loeser JD (1992) Morbidity and mortality in association with operations on the lumbar spine. The influence of age, diagnosis, and procedure. J Bone Jt Surg Am 74:536–543
Carreon LY, Puno RM, Dimar JR et al (2003) Perioperative complications of posterior lumbar decompression and arthrodesis in older adults. J Bone Jt Surg Am 85:2089–2092
Cassinelli EH, Eubanks J, Vogt M et al (2007) Risk factors for the development of perioperative complications in elderly patients undergoing lumbar decompression and arthrodesis for spinal stenosis: an analysis of 166 patients. Spine 32:230–235
Brodsky ARE, Kovalsky ES, Khalil MA (1991) Correlation of radiologic assessment of lumbar spine fusions with surgical exploration. Spine 6(Suppl 6):S261–S265
Carreon LY, Djurasovic M, Glassman SD et al (2007) Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of fine-cut CT scans with reconstructions to determine the status of an instrumented posterolateral fusion with surgical exploration as reference standard. Spine 32:892–895
Etminan M, Girardi FP, Khan SN et al (2002) Revison surgeries for lumbar pseudoarthrosis. Orthop Clin N Am 33:381–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KB., Taghavi, C.E., Hsu, M.S. et al. The efficacy of rhBMP-2 versus autograft for posterolateral lumbar spine fusion in elderly patients. Eur Spine J 19, 924–930 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-1248-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-1248-6