Abstract
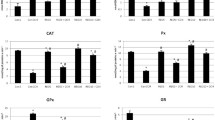
Apigenin (APG) is a phytopolyphenol widely distributed in the human diet and has been reported to exert antioxidant effects, such as lowering oxidative stress. This study has been designed to investigate the ameliorating effect of APG against oxidative stress induced by bisphenol A(BPA) in the liver and testis of male rats. Rats were divided into five groups of five animals each: G1 (control group), G2 (BPA 1 mg/kg B.wt), G3 (BPA 10 mg/kg B.wt), G4 (BPA + APG; 1 + 20 mg/kg/B.wt) and G5 (BPA + APG; 10 + 20 mg / kg/B.wt).The treatments have been given by gavage to rats daily for 30 days. After the last day of treatment, rats were sacrificed by decapitation after exposure to ether. The results showed that BPA exhibited a decrease in the body weight of rats. In addition, BPA significantly decreased the level of testosterone, LH, and reduced glutathione (GSH) and increased the level of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, and glutathione S-transferase (GST) compared with the control group. Moreover, the administration of APG decreased the levels of the liver biomarkers and improved the antioxidant stress state. The results suggested that APG supplementation with BPA-treated rats elicited a reduction of the toxic effects of the endocrine disruptors by improving the studied parameters, which was confirmed by the histological study of the testis structure and gonadal axis. Apigenin appears to have a promising prophylactic effect through its effective anti-radical action against the hepatotoxic and reprotoxic effects of BPA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah AAM, Nasr El-Deen NAM, Neamat-Allah ANF et al (2020a) Evaluation of the hematoprotective and hepato-renal protective effects of Thymus vulgaris aqueous extract on thermally oxidized oil-induced hematotoxicity and hepato-renal toxicity. Comp Clin Pathol 29:451–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-03078-8
Abdallah AAM, Nasr El-Deen NAM, Abd El-Aziz HI et al (2020b) Effect of the aqueous root extract of Curcuma longa L. (turmeric) against thermally oxidized oil-induced hematological, biochemical and histopathological alterations. Comp Clin Pathol 29:837–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03108-w
Abdel-Rahman HG, Abdelrazek HMA, Zeidan DW, Mohamed RM, Abdelazim AM (2018) Lycopene: Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects toward bisphenol A-induced toxicity in female Wistar rats. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity
Abdel-Wahab WM (2014) Thymoquinone attenuates toxicity and oxidative stress induced by bisphenol a in liver of male rats. Pak J Biol Sci 17(11):1152–1160
Aboul Ezz HS, Khadrawy YA, Mourad IM (2015) The effect of bisphenol a on some oxidative stress parameters and acetylcholinesterase activity in the heart of male albino rats. Cytotechnology 67(1):145–155
Akingbemi BT, Sottas CM, Koulova AI, Klinefelter GR, Hardy MP (2004) Inhibition of testicular steroidogenesis by the xenoestrogen bisphenol a is associated with reduced pituitary luteinizing hormone secretion and decreased steroidogenic enzyme gene expression in rat Leydig cells. Endocrinology 145(2):592–603
Ali F, Naz F, Jyoti S, Siddique YH (2014) Protective effect of apigenin against N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA)-induced hepatotoxicity in albino rats. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 767:13–20
Alonso-Magdalena P, Vieira E, Soriano S, Menes L, Burks D, Quesada I, Nadal A (2010) Bisphenol a exposure during pregnancy disrupts glucose homeostasis in mothers and adult male offspring. Environ Health Perspect 118(9):1243–1250
Biedermann S, Tschudin P, Grob K (2010) Transfer of bisphenol a from thermal printer paper to the skin. Anal Bioanal Chem 398(1):571–576
Bindhumol V, Chitra KC, Mathur PP (2003) Bisphenol a induces reactive oxygen species generation in the liver of male rats. Toxicology 188(2–3):117–124
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantities of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Choi JS, Islam MN, Ali MY, Kim EJ, Kim YM, Jung HA (2014) Effects of C-glycosylation on anti-diabetic, anti-Alzheimer’s disease and anti-inflammatory potential of apigenin. Food Chem Toxicol 64:27–33
Derbel M, Igarashi T, Satoh T (1993) Differential induction of glutathione S-transferase subunits by phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene and ethoxyquin in rat liver and kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta 1158(2):175–180
Drewes SE, Georges J, Khan F (2003) Recent findings on natural products with erectile-dysfunction activity. Phytochemistry 62(7):1019–1025
Fang Y, Zhou Y, Zhong Y, Gao X., Tan T (2013) Effect of vitamin E on reproductive functions and anti-oxidant activity of adolescent male mice exposed to bisphenol A. Wei sheng yan jiu= Journal of hygiene research 42(1); 18
Grün F, Blumberg B (2007) Perturbed nuclear receptor signaling by environmental obesogens as emerging factors in the obesity crisis. Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders 8(2):161–171
Gurmeet K, Rosnah I, Normadiah MK, Das S, Mustafa AM (2014) Detrimental effects of bisphenol a on development and functions of the male reproductive system in experimental rats. EXCLI J 13:151–160
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Biol Chem 249(22):7130–7139
Hashem MA, Neamat-Allah ANF, Hammza HEE, Abou-Elnaga HM (2020) Impact of dietary supplementation with Echinacea purpurea on growth performance, immunological, biochemical, and pathological findings in broiler chickens infected by pathogenic E. coli. Trop Anim Health Prod 52:1599–1607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-019-02162-z
Hassan ZK, Elobeid MA, Virk P, Omer SA, ElAmin M, Daghestani MH, AlOlayan EM (2012) Bisphenol A induces hepatotoxicity through oxidative stress in rat model. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity
Hould R (1984) Techniques d’histopathologie et de cytopathologie. Ed Maloine 19(21):225–227
Jandegian CM, Deem SL, Bhandari RK, Holliday CM, Nicks D, Rosenfeld CS, Tillitt DE, Vom Saal FS, Vélez-Rivera V, Yang Y, Holliday DK (2015) Developmental exposure to bisphenol a (BPA) alters sexual differentiation in painted turtles (Chrysemys picta). Gen Comp Endocrinol 216:77–85
Jin P, Wang X, Chang F, Bai Y, Li Y, Zhou R, Chen L (2013) Low dose bisphenol a impairs spermatogenesis by suppressing reproductive hormone production and promoting germ cell apoptosis in adult rats. J Biomed Res 27(2):135–144
John N, Rehman H, Razak S, David M, Ullah W, Afsar T, Almajwal A, Alam I, Jahan S (2019) Comparative study of environmental pollutants bisphenol a and bisphenol S on sexual differentiation of anteroventral periventricular nucleus and spermatogenesis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 17(1):53
Jollow DJ, Mitche JR, Zamppaglione Z, Gillette JR (1974) Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolites. Pharmacology 11:51–57
Kabuto H, Amakawa M, Shishibori T (2004) Exposure to bisphenol a during embryonic/fetal life and infancy increases oxidative injury and causes underdevelopment of the brain and testis in mice. Life Sci 74(24):2931–2940
Kim JY, Han EH, Kim HG, Oh KN, Kim SK, Lee KY, Jeong HG (2010) Bisphenol A-induced aromatase activation is mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 up-regulation in rat testicular Leydig cells. Toxicol Lett 193(2):200–208
Knaak JB, Sullivan LJ (1966) Metabolism of bisphenol a in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 8(2):175–184
Korkmaz A, Ahbab MA, Kolankaya D, Barlas N (2010) Influence of vitamin C on bisphenol a, nonylphenol and octylphenol induced oxidative damages in liver of male rats. Food Chem Toxicol 48(10):2865–2871
Kourouma A, Peng D, Chao Q, Changjiang L, ChengminW WF, Suqin Q, Tingting Y, Kedi Y (2014) Bisphenol a induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the liver and affect epididymal semen quality in adults Sprague-Dawley rats. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences 6(4):103–112
Kumar V, Chakraborty A, Kural MR, Roy P (2009) Alteration of testicular steroidogenesis and histopathology of reproductive system in male rats treated with triclosan. Reprod Toxicol 27(2):177–185
Lakind JS, Naiman DQ (2011) Daily intake of bisphenol a and potential sources of exposure: 2005–2006 National Health and nutrition examination survey. Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology 21(3):272–279
Lang IA, Galloway TS, Scarlett A, Henley WE, Depledge M, Wallace RB, Melzer D (2008) Association of urinary bisphenol a concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. Jama 300(11):1303–1310
Lefort ÉC, Blay J (2013) Apigenin and its impact on gastrointestinal cancers. Mol Nutr Food Res 57(1):126–144
Liu C, Duan W, Li R, Xu S, Zhang L, Chen C et al (2013) Exposure to bisphenol a disrupts meiotic progression during spermatogenesis in adult rats through estrogen-like activity. Cell Death Dis 4(6):e676–e676
Mantovani A (2002) Hazard identification and risk assessment of endocrine disrupting chemicals with regard to developmental effects. Toxicology 181:367–370
Marmugi A, Ducheix S, Lasserre F, Polizzi A, Paris A, Priymenko N, Bertrand-Michel J, Pineau T, Guillou H, Martin PGP, Mselli-Lakhal L (2012) Low doses of bisphenol a induce gene expression related to lipid synthesis and trigger triglyceride accumulation in adult mouse liver. Hepatology 55(2):395–407
Moon MK, Kim MJ, Jung IK, Koo YD, Ann HY, Lee KJ, Kim SH, Yoon YC, Cho BJ, Park KS, Jang HC, Park YJ (2012) Bisphenol a impairs mitochondrial function in the liver at doses below the no observed adverse effect level. J Korean Med Sci 27(6):644–652
Mourad IM, Khadrawy YA (2012) The Sensetivity of liver, kidney andtestis of rats to oxidative stress induced by different doses of bisphenol a. Life Sci J(1)50; 19
Munir B, Qadir A, Tahir M (2017) Negative effects of bisphenol a on testicular functions in albino rats and their abolitions with Tribulus terristeris L. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 53(3)
Olukole SG, Lanipekun DO, Ola-Davies EO, Oke BO (2019) Melatonin attenuates bisphenol A-induced toxicity of the adrenal gland of Wistar rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):5971–5982
Patel D, Shukla S, Gupta S (2007) Apigenin and cancer chemoprevention: progress, potential and promise. Int J Oncol 30(1):233–245
Prins GS, Tang WY, Belmonte J, Ho SM (2008) Developmental exposure to bisphenol a increases prostate cancer susceptibility in adult rats: epigenetic mode of action is implicated. Fertil Steril 89(2):e41
Pupo M, Pisano A, Lappano R, Santolla MF, De Francesco EM, Abonante S et al (2012) Bisphenol a induces gene expression changes and proliferative effects through GPER in breast cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Environ Health Perspect 120(8):1177–1182
Qiu W, Chen J, Li Y, Chen Z, Jiang L, Yang M, Wu M (2016) Oxidative stress and immune disturbance after long-term exposure to bisphenol a in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:93–102
Rašković A, Pavlović N, Kvrgić M, Sudji J, Mitić G, Čapo I, Mikov M (2015) Effects of pharmaceutical formulations containing thyme on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 15(1):1–11
Rithidech KN, Tungjai M, Reungpatthanaphong P, Honikel L, Simon SR (2012) Attenuation of oxidative damage and inflammatory responses by apigenin given to mice after irradiation. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 749(1–2):29–38
Rubin BS, Murray MK, Damassa DA, King JC, Soto AM (2001) Perinatal exposure to low doses of bisphenol a affects body weight, patterns of estrous cyclicity, and plasma LH levels. Environ Health Perspect 109(7):675–680
Salian S, Doshi T, Vanage G (2009) Neonatal exposure of male rats to Bisphenol a impairs fertility and expression of sertoli cell junctional proteins in the testis. Toxicology 265(1–2):56–67
Salian S, Doshi T, Vanage G (2011) Perinatal exposure of rats to bisphenol a affects fertility of male offspring- an overview. Reprod Toxicol 31(3):359–362
Schecter A, Malik N, Haffner D, Smith S, Harris TR, Paepke O, Birnbaum L (2010) Bisphenol a (BPA) in US food. Environmental science & technology 44(24):9425–9430
Sharma H, Kanwal R, Bhaskaran N, Gupta S (2014) Plant flavone apigenin binds to nucleic acid bases and reduces oxidative DNA damage in prostate epithelial cells. PLoS One 9(3):e91588
Singh JPV, Selvendiran K, Banu SM, Padmavathi R, Sakthisekaran D (2004) Protective role of Apigenin on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense against hepatocarcinogenesis in Wistar albino rats. Phytomedicine 11(4):309–314
Takahashi O, Oishi S (2001) Testicular toxicity of dietary 2, 2-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) propane (bisphenol a) in F344 rats. Arch Toxicol 75(1):42–51
Tohei A, Suda S, Taya K, Hashimoto T, Kogo H (2001) Bisphenol a inhibits testicular functions and increases luteinizing hormone secretion in adult male rats. Exp Biol Med 226(3):216–221
Tsaroucha AK, Tsiaousidou A, Ouzounidis N, TsalkidouE LM, Giakoustidis D, Chatzaki E, Simopoulos C (2016) Intraperitoneal administration of apigenin in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury protective effects. Saudi journal of gastroenterology 22(6):415–422
Vawda AI, Mandlwana JG (1990) The effects of dietary protein deficiency on rat testicular function. Andrologia 22(6):575–583
Wang E, Chen F, Hu X, Yuan Y (2014) Protective effects of apigenin against furan-induced toxicity in mice. Food Funct 5(8):1804–1812
Welshons WV, Nagel SC, vom Saal FS (2006) Large effects from small exposures. III Endocrine mechanisms mediating effects of bisphenol A at levels of human exposure. Endocrinology 147(6):s56–s69
Wu M, Xu H, Shen Y, Qiu W, Yang M (2011) Oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos induced by short-term exposure to bisphenol a, nonylphenol, and their mixture. Environ Toxicol Chem 30(10):2335–2341
Yamasaki K, Takeyoshi M, Noda S, Takatsuki M (2002) Subacute oral toxicity study of ethynyl estradiol and bisphenol a, based on the draft protocol for the 'Enhanced OECD test guideline no. 407′. Arch Toxicol 76(2):65–74
Yang J, Wang XY, Xue J, Gu ZL, Xie ML (2013) Protective effect of apigenin on mouse acute liver injury induced by acetaminophen is associated with increment of hepatic glutathione reductase activity. Food Funct 4(6):939–943
Yousaf B, Amina LG, Wang R, Qadir A, Ali MU, Kanwal Q, Munir B, Asmatullah AZ (2016) Bisphenol a exposure and healing effects of Adiantum capillus-veneris L. plant extract (APE) in bisphenol A-induced reproductive toxicity in albino rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(12):11645–11657
Zhang S, Qin C, Safe SH (2003) Flavonoids as aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists/antagonists: effects of structure and cell context. Environ Health Perspect 111(16):1877–1882
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asma, M., Fouzia, T., Lazhari, T. et al. Protective effects of apigenin against Bisphenol A-induced testis toxicity in Wistar rats through modulating hepatic biochemical biomarkers and histological changes. Comp Clin Pathol 29, 1041–1049 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03158-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03158-0