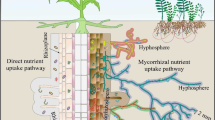
Abstract
Invasive species often reduce ecosystem services and lead to a serious threat to native biodiversity. Roots of invasive plants are often linked to roots of native plants by common mycorrhizal networks (CMNs) of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, but whether and how CMNs mediate interactions between invasive and native plant species remains largely uninvestigated. We conducted two microcosm experiments, one in which we amended the soil with mineral N and another in which we amended the soil with mineral P. In each experiment, we grew a pair of test plants consisting of Kummerowia striata (native to our research site) and Solidago canadensis (an invasive species). CMNs were established between the plants, and these were either left intact or severed. Intact CMNs increased growth and nutrient acquisition by S. canadensis while they decreased nutrient acquisition by K. striata in comparison with severed CMNs. 15N and P analyses indicated that compared to severed CMNs, intact CMNs preferentially transferred mineral nutrients to S. canadensis. CMNs produced by different species of AM fungi had slightly different effects on the interaction between these two plant species. These results highlight the role of CMNs in the understanding of interactions between the invasive species S. canadensis and its native neighbor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames RN, Reid CPP, Porter LK, Cambardella C (1983) Hyphal uptake and transport of nitrogen from two 15N labeled sources by Glomus mosseae. New Phytol 95:381–396. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1983.tb03506.x
Babikova Z, Gilbert L, Bruce TJA, Birkett M, Caulfield JC, Woodcock C, Pickett JA, Johnson D (2013) Underground signals carried through common mycelial networks warn neighbouring plants of aphid attack. Ecol Lett 16:835–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12115
Barto EK, Hilker M, Müller F, Mohney BK, Weidenhamer JD, Rillig MC (2011) The fungal fast lane: common mycorrhizal networks extend bioactive zones of allelochemicals in soils. PLoS One 6:e27195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027195
Bunn RA, Ramsey PW, Lekberg Y (2015) Do native and invasive plants differ in their interactions with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi? A meta-analysis. J Ecol 103:1547–1556. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12456
Callaway RM, Thelen GC, Rodriguez A, Holben WE (2004) Soil biota and exotic plant invasion. Nature 427:731–733. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02322
Chen X, Tang JJ, Fang ZG, Shimizu K (2004) Effects of weed communities with various species numbers on soil features in a subtropical orchard ecosystem. Agric Ecosyst Environ 102:377–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2003.08.006
Cheng L, Booker FL, Tu C, Burkey KO, Zhou L, Shew HD, Rufty TW, Hu S (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increase organic carbon decomposition under elevated CO2. Science 337:1084–1087. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224304
Cheng L, Chen W, Adams TS, Wei X, Li L, McCormack ML, DeForest JL, Koide RT, Eissenstat DM (2016) Mycorrhizal fungi and roots are complementary in foraging within nutrient patches. Ecology 97:2815–2823. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1514
Cronk QCB, Fuller JL (1995) Plant invaders: the threat to natural ecosystems. People and Plants Conservation Manuals. Chapman & Hall, London
Dickie IA, Bufford JL, Cobb RC, Desprez-Loustau ML, Grelet G, Hulme PE, Klironomos J, Makiola A, Nuñez MA, Pringle A, Thrall PH, Tourtellot SG, Waller L, Williams NM (2017) The emerging science of linked plant-fungal invasions. New Phytol 215:1314–1332. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14657
Dong M, Lu JZ, Zhang WJ, Chen JK, Li B (2006) Canada goldenrod (Solidago canadensis): an invasive alien weed rapidly spreading in China. Acta Phytotaxon Sin 44:72–85. https://doi.org/10.1360/aps050068
Dong L-J, Sun Z-K, Gao Y, He W-M (2015) Two-year interactions between invasive Solidago canadensis and soil decrease its subsequent growth and competitive ability. J Plant Ecol 8:617–622. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtv003
Fellbaum CR, Mensah JA, Cloos AJ, Strahan GE, Pfeffer PE, Kiers ET, Bücking H (2014) Fungal nutrient allocation in common mycorrhizal networks is regulated by the carbon source strength of individual host plants. New Phytol 203:646–656. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12827
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) Evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol 84:489–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1980.tb04556.x
Hart MM, Reader RJ (2002) Taxonomic basis for variation in the colonization strategy of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 153:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0028-646X.2001.00312.x
Hart MM, Reader RJ, Klironomos JN (2003) Plant coexistence mediated by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Trends Ecol Evol 18:418–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-5347(03)00127-7
Hoeksema JD (2015) Experimentally testing effects of mycorrhizal networks on plant-plant interactions and distinguishing among mechanisms. In: Horton T (ed) Mycorrhizal networks. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 255–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-7395-9_9
Horton TR (2015) Mycorrhizal networks. Springer, Dordrecht
Jakobsen I, Hammer EC (2015) Nutrient dynamics in arbuscular mycorrhizal networks. In: Horton T (ed) Mycorrhizal Networks. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 91–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-7395-9_4
Janos DP (2007) Plant responsiveness to mycorrhizas differs from dependence upon mycorrhizas. Mycorrhiza 17:75–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-006-0094-1
Johnson D, Gilbert L (2015) Interplant signalling through hyphal networks. New Phytol 205:1448–1453. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13115
Johnson D, Leake J, Read D (2001) Novel in-growth core system enables functional studies of grassland mycorrhizal mycelial networks. New Phytol 152:555–562 https://doi.org/http://www.jstor.org/stable/1353726
Kiers ET, Duhamel M, Beesetty Y, Mensah JA, Franken O, Verbruggen E, Fellbaum CR, Kowalchuk GA, Hart MM, Bago A, Palmer TM, West SA, Vandenkoornhuyse P, Jansa J, Bucking H (2011) Reciprocal rewards stabilize cooperation in the mycorrhizal symbiosis. Science 333:880–882. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208473
Klironomos JN (2003) Variation in plant response to native and exotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecology 84:2292–2301. https://doi.org/10.1890/02-0413
Koide RT, Li M (1989) Appropriate controls for vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhiza research. New Phytol 111:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1989.tb04215.x
Kormanik PP, Bryan WC, Schultz RC (1980) Procedures and equipment for staining large numbers of plant root samples for endomycorrhizal assay. Can J Microbiol 26:536–538. https://doi.org/10.1139/m80-090
Lekberg Y, Hammer EC, Olsson PA (2010) Plants as resource islands and storage units—adopting the mycocentric view of arbuscular mycorrhizal networks. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:336–345. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00956.x
Lu JZ, Weng ES, Wu XW, Weber E, Zhao B, Li B (2007) Potential distribution of Solidago canadensis in China. Acta Phytotaxon Sin 45:670–674. https://doi.org/10.1360/aps06200
Menzel A, Hempel S, Klotz S, Moora M, Pyšek P, Rillig MC, Zobel M, Kühn I (2017) Mycorrhizal status helps explain invasion success of alien plant species. Ecology 98:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1621
Merrild MP, Ambus P, Rosendahl S, Jakobsen I (2013) Common arbuscular mycorrhizal networks amplify competition for phosphorus between seedlings and established plants. New Phytol 200:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12351
Mitchell CE, Agrawal AA, Bever JD, Gilbert GS, Hufbauer RA, Klironomos JN, Maron JL, Morris WF, Parker IM, Power AG, Seabloom EW, Torchin ME, Vazquez DP (2006) Biotic interactions and plant invasions. Ecol Lett 9:726–740. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00908.x
Nuccio EE, Hodge A, Pett-Ridge J, Herman DJ, Weber PK, Firestone MK (2013) An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus significantly modifies the soil bacterial community and nitrogen cycling during litter decomposition. Environ Microbiol 15:1870–1881. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12081
Nunez MA, Dickie IA (2014) Invasive belowground mutualists of woody plants. Biol Invasions 16:645–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-013-0612-y
Pringle A, Bever JD, Gardes M, Parrent JL, Rillig MC, Klironomos JN (2009) Mycorrhizal symbioses and plant invasions. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 40:699–715. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.39.110707.173454
Reinhart KO, Callaway RM (2006) Soil biota and invasive plants. New Phytol 170:445–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01715.x
Richardson DM, Allsopp N, D’Antonio CM, Milton SJ, Rejmanek M (2000) Plant invasions—the role of mutualisms. Biol Rev 75:65–93. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0006323199005435
Rudgers JA, Orr S (2009) Non-native grass alters growth of native tree species via leaf and soil microbes. J Ecol 97:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2008.01478.x
Schüßler A, Walker C (2010) The Glomeromycota: a species list with new families and new genera. http://www.amf-phylogenycom. Accessed 8 June 2018
Selosse M-A, Richard F, He X, Simard SW (2006) Mycorrhizal networks: des liaisons dangereuses? Trends Ecol Evol 21:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2006.07.003
Shah MA, Reshi ZA, Khasa DP (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizas: drivers or dassengers of alien plant invasion. Bot Rev 75:397–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-009-9039-7
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd edn. Elsevier Academic Press Inc, San Diego
Song YY, Ye M, Li C, He X, Zhu-Salzman K, Wang RL, Su YJ, Luo SM, Zeng RS (2014) Hijacking common mycorrhizal networks for herbivore-induced defence signal transfer between tomato plants. Sci Rep 4(3915). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03915
Tanaka Y, Yano K (2005) Nitrogen delivery to maize via mycorrhizal hyphae depends on the form of N supplied. Plant Cell Environ 28:1247–1254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01360.x
van der Heijden MGA, Horton TR (2009) Socialism in soil? The importance of mycorrhizal fungal networks for facilitation in natural ecosystems. J Ecol 97:1139–1150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2009.01570.x
van der Heijden MGA, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal species are potential determinants of plant community structure. Ecology 79:2082–2091. https://doi.org/10.2307/176711
van der Heijden MGA, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (2003) Different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alter coexistence and resource distribution between co-occurring plant. New Phytol 157:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00688.x
Vogelsang KM, Bever JD (2009) Mycorrhizal densities decline in association with nonnative plants and contribute to plant invasion. Ecology 90:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-2144.1
Walder F, van der Heijden MGA (2015) Regulation of resource exchange in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nat Plants 1(15159). https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.159
Walder F, Niemann H, Natarajan M, Lehmann MF, Boller T, Wiemken A (2012) Mycorrhizal networks: common goods of plants shared under unequal terms of trade. Plant Physiol 159:789–797 https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.195727
Wan L-Y, Qi S-S, Zou CB, Dai Z-C, Zhu B, Song Y-G, Du D-L (2018) Phosphorus addition reduces the competitive ability of the invasive weed Solidago canadensis under high nitrogen conditions. Flora 240:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flora.2017.12.012
Weber E (1997) Morphological variation of the introduced perennial Solidago canadensis L. sensu lato (Asteraceae) in Europe. Bot Jo Linn Soc 123:197–210. https://doi.org/10.1006/bojl.1996.0086
Weremijewicz J, Janos DP (2013) Common mycorrhizal networks amplify size inequality in Andropogon gerardii monocultures. New Phytol 198:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12125
Weremijewicz J, Sternberg LSLOR, Janos DP (2016) Common mycorrhizal networks amplify competition by preferential mineral nutrient allocation to large host plants. New Phytol 212:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14041
Weremijewicz J, Sternberg LSLOR, Janos DP (2017) Arbuscular common mycorrhizal networks mediate intra- and interspecific interactions of two prairie grasses. Mycorrhiza 28:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-017-0801-0
Wolfe BE, Klironomos JN (2005) Breaking new ground: soil communities and exotic plant invasion. Bioscience 55:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2005)055[0477:BNGSCA]2.0.CO;2
Workman RE, Cruzan MB (2016) Common mycelial networks impact competition in an invasive grass. Am J Bot 103:1041–1049. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1600142
Wu BY, Nara K, Hogetsu T (2001) Can 14C labeled photosynthetic products move between Pinus densiflora seedlings linked by ectomycorrhizal mycelia? New Phytol 149:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00010.x
Yang R, Zan S, Tang J, Chen X (2011) Invasion mechanisms of Solidago canadensis L.:a review. Acta Ecol Sin 31:1185–1194
Yu H-W, Yang J-X, Gao Y, He W-M (2016) Soil organic nitrogen endows invasive Solidago canadensis with greater advantages in low-phosphorus conditions. Ecosphere 7. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.1254
Yuan Y, Wang B, Zhang S, Tang J, Tu C, Hu S, Yong JWH, Chen X (2013) Enhanced allelopathy and competitive ability of invasive plant Solidago canadensis in its introduced range. J Plant Ecol 6:253–263. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rts033
Zhang Q, Yang RY, Tang JJ, Yang HS, Hu SJ, Chen X (2010) Positive feedback between mycorrhizal fungi and plants influences plant invasion success and resistance to invasion. PLoS One 5:e12380. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012380
Zhang S, Zhu W, Wang B, Tang J, Chen X (2011) Secondary metabolites from the invasive Solidago canadensis L. accumulation in soil and contribution to inhibition of soil pathogen Pythium ultimum. Appl Soil Ecol 48:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.04.011
Acknowledgements
We highly appreciate Dr. Dave Janos’ and two anonymous reviewers’ insightful comments and suggestions on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC# 31500416, 31422010, and 31670501), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0502704), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Zhejiang University K. P. Chao’s High Technology Development Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awaydul, A., Zhu, W., Yuan, Y. et al. Common mycorrhizal networks influence the distribution of mineral nutrients between an invasive plant, Solidago canadensis, and a native plant, Kummerowa striata. Mycorrhiza 29, 29–38 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-018-0873-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-018-0873-5