Abstract
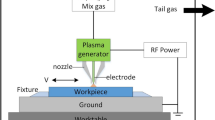
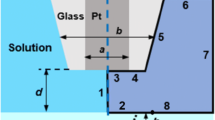
In this study, an in-process depth monitoring method was developed to improve the atmospheric-pressure plasma jet (APPJ) etching process. Although the APPJ etching process has attracted significant attention as a micromachining technology, it has low processing precision. Therefore, we propose an etching time control method based on in-process monitoring to improve the precision and accuracy of the APPJ etching process. In the conventional method, the APPJ etching time is set to achieve the desired etch depth based on the etching rate investigated in advance. In the proposed method, the etch depth is measured in real time using a confocal laser displacement sensor, and APPJ irradiation is stopped when the etch depth is reached. Therefore, under- and over-etching can be prevented, thus improving the etching accuracy and precision of APPJ etching. A special confocal laser displacement sensor that can be operated under APPJ etching was developed for in-process monitoring. The response time and the depth resolution of the sensor were 0.11 s and 0.10 μm, respectively, under the APPJ irradiation condition. Using the developed sensor, the etch depth was successfully monitored during the APPJ etching process. The standard deviation of the etch depth, corresponding to the etching precision, was reduced by 50% compared with that without in-process monitoring. The average error of the etch depth, corresponding to etching accuracy, was eliminated, demonstrating an improvement in etching precision and accuracy by the in-process monitoring system. The study findings provide insights for the development of APPJ etching systems for post-fabrication processes of microdevices.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barankin MD, Creyghton Y, Schmidt-Ott A (2006) Synthesis of nanoparticles in an atmospheric pressure glow discharge. J Nanopart Res 8:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-005-9013-1
Gao Z (2012) Influence of environmental humidity on plasma etching polyamide 6 films. Appl Surf Sci 258:5574–5578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.02.004
Han C, Lai C, Chao Y, Leou K, Lin T (2011) Assessment of interface roughness during plasma etching through the use of real-time ellipsometry. Appl Surf Sci 257:2536–2539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.018
Hutzler P, Fischbach R, Heller W, Jungblut TP, Reuber S, Schmitz R, Veit M, Weissenbock G, Schnitzler J-P (1998) Tissue localization of phenolic compounds in plants by confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Exp Bot 49:953–965. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/49.323.953
Ichiki T, Taura R, Horiike Y (2004) Localized and ultrahigh-rate etching of silicon wafers using atmospheric-pressure microplasma jets. J Appl Phys 95:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1630375
Ideno T, Ichiki T (2006) Maskless etching of microstructures using a scanning microplasma etcher. Thin Solid Films 506:235–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2005.08.271
Kakei R, Ogino A, Iwata F, Nagatsu M (2010) Production of ultrafine atmospheric pressure plasma jet with nano-capillary. Thin Solid Films 518:3457–3460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2009.11.055
Lange DA, Jennings HM, Shah SP (1993) Analysis of surface roughness using confocal microscopy. J Mater Sci 28:3879–3884. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00353195
Nakazawa K, Sasaki T, Furuta H, Kamiya J, Sasaki H, Kamiya T, Hane K (2017) Confocal laser displacement sensor using a micro-machined varifocal mirror. Appl Opt 56:6911–6916. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.56.006911
Nakazawa K, Yamamoto S, Nakagawa E, Ogino A, Shimomura M, Iwata F (2020) Atmospheric He/O 2 plasma jet fine etching with a scanning probe microscope. AIP Adv 10:095103. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0017952
Ohtsu Y, Nagamatsu K (2018) Atmospheric-pressure plasma jet system for silicon etching without fluorocarbon gas feed. Jpn J Appl Phys 57:01AB01. https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.57.01AB01
Paetzelt H, Bohm G, Arnold T (2015) Etching of silicon surfaces using atmospheric plasma jets. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 24:025002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/24/2/025002
Sternheim M, Gelder W, Hartman AW (1983) A laser interferometer system to monitor dry etching of patterned silicon. J Electrochem Soc 130:655. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2119775
Sun J, Yao L, Gao Z, Peng S, Wang C, Qiu Y (2010) Surface modification of PET films by atmospheric pressure plasma-induced acrylic acid inverse emulsion graft polymerization. Surf Coat Technol 204:4101–4106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.05.038
Tan Y, Wang W, Xu C, Zhang S (2013) Laser confocal feedback tomography and nano-step height measurement. Sci Rep 3:2971. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02971
Wang L, Zheng Y, Wu C, Jia S (2016) Experimental investigation of photoresist etching by kHz AC atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Appl Surf Sci 385:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.126
Yamamoto S, Nakazawa K, Ogino A, Iwata F (2022) Sub-micrometer plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition using an atmospheric pressure plasma jet localized by a nanopipette scanning probe microscope. J Micromech Microeng 32:015006. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6439/ac3afe
Yin S, Yu FTS, Wu S (1992) Optical monitoring for plasma-etching depth process. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 4:894–896. https://doi.org/10.1109/68.149900
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP22K14158 and JST ACT-X Grant Number JPMJAX21KD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tomita, T., Nakazawa, K., Hiraoka, T. et al. In-process monitoring of atmospheric pressure plasma jet etching using a confocal laser displacement sensor. Microsyst Technol 29, 1107–1116 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-023-05462-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-023-05462-5