Abstract
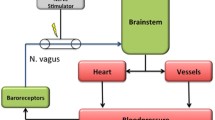
The effects of pancuronium and vecuronium, each in doses of 0.05 and 0.08 mg·kg−1, on the baroreflex control of the heart rate were studied in 40 adult patients of either sex (21 men and 19 women) during stable nitrous oxide-oxygen-fentanyl anesthesia. The blood pressure was elevated by intravenous infusion of phenylephrine (4 μgg·kg−1·min−1) for the pressor test, and lowered by a bolus injection of nitroglycerin (0.3–0.5 mg) for the depressor test. Baroreflex sensitivity was judged from the slope of the regression of the systolic blood pressure on the succeeding R-R intervals on the ECG. There was no significant difference between the baseline blood pressure at which both tests were carried out. Nitrous oxide-oxygen-fentanyl anesthesia alone suppressed the baroreflex sensitivity to a level which was at the lower limit of the physiological and non-anesthetized state. The 0.08 mg·kg−1 dose of pancuronium significantly suppressed the reflex sensitivity in both the pressor and depressor tests. However, the 0.05 mg·kg−1 dose of pancuronium and both doses of vecuronium did not cause any significant change in the test results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stoelting RK: The hemodynamic effects of pancuronium and d-tubocurarine in anesthetized patients. Anesthesiology 36:612–615, 1972
Miller RD, Eger EI II, Stevens WC, Gibbons R: Pancuronium-induced tachycardia in relation to alveolar halothane, dose of pancuronium, and prior atropine. Anesthesiology 42:352–355, 1975
Booij LHDJ, Edwards RP, Sohn YJ, Miller RD: Cardiovascular and neuromuscular effects of Org NC 45, pancuronium, metocurine, and d-tubocurarine in dogs. Anesth Analg 59:26–30, 1980
Smyth HS, Sleight P, Pickering GW: Reflex regulation of arterial pressure during sleep in man: A quantitative method of assessing baroreflex sensitivity. Circ Res 24:109–121, 1964
Bristow JD, Prys-Roberts C, Fisher A, Pickering TG, Sleight P: Effects of anesthesia on baroreflex control of heart rate in man. Anesthesiology 31:422–428, 1969
Duke PC, Fownes D, Wade JG: Halothane depresses baroreflex control of heart rate in man. Anesthesiology 46:184–187, 1977
Morton M, Duke PC, Ong B: Baroreflex control of heart rate in man awake and during enflurane and enflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesthesiology 52:221–223, 1980
Seagard JL, Hopp FA, Donegan JH, Kalbfleisch JH, Kampine JP: Halothane and the carotid sinus reflex: Evidence for multiple sites of action. Anesthesiology 57:191–202, 1982
Dohi S, Tsuchida H, Mayumi T: Baroreflex control of heart rate during cardiac sympathectomy by epidural anesthesia in lightly anesthetized humans. Anesth Analg 62:815–820, 1983
Vatner SF, Braunwald EB: Cardiovascular control mechanisms in the conscious state. N Eng J Med 293:970–976, 1975
Schwartz PJ, Vanoli E, Stramba-Badiale M, De Ferrari GM, Billman GE, Foreman RD: Autonomic mechanisms and sudden death: New insights from analysis of baroreceptor reflexes in conscious dogs with and without a myocardial infaction. Circulation 78:969–979, 1988
Miller RD, Rupp SM, Fisher DM, Cronnelly R, Fahey MR, Solin YJ: Clinical pharmacology of vecuronium and atracurium. Anesthesiology 61:444–453, 1984
Pickering TG, Gribbin B, Petersen ES, Cunningham DJC, Sleight P: Effects of autonomic blockade on the baroreflex in man at rest and during exercise. Circ Res 30:177–185, 1972
Durant NN, Marshall IG, Savage DS, Nelson DJ, Sleight T, Carlyle IC: The neuromuscular and autonomic blocking activities of pancuronium, Org NC 45, and other pancuronium analogues, in the cat. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:831–836, 1979
Domenech JS, Garcia RC, Sasiain JMR, Loyola AQ, Oroz JS: Pancuronium bromide: An indirect sympathomimetic agent. Br J Anaesth 48:1143–1148, 1976
Downing SE: Baroreceptor regulation of the heart. In: Berne RN, Sperelakis N, Geiger SR, eds. Handbook of Physiology, Section 2: The cardiovascular system, Volume 1: The heart. Maryland: American Physiological Society, 1979, pp. 621–652
Kotrly KJ, Ebert TJ, Vucins EJ, Roerig DL, Stadnicka A, Kampine JP: Effects of fentanyl-diazepam-nitrous oxide anaesthesia on arterial baroreflex control of heart rate in man. Br J Anaesth 58:406–414, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuchida, H., Seki, S., Nakae, Y. et al. Difference in the effect of pancuronium and vecuronium on baroreflex control of heart rate in humans. J Anesth 5, 255–259 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054010050255
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054010050255