Abstract
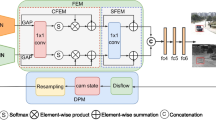
RGBT tracking combines visible and thermal infrared images to achieve tracking and faces challenges due to motion blur caused by camera and target movement. In this study, we observe that the tracking in motion blur is significantly affected by both frequency and spatial aspects. And blurred targets exhibit sharp texture details that are represented as high-frequency information. But existing trackers capture low-frequency components while ignoring high-frequency information. To enhance the representation of sharp information in blurred scenes, we introduce multi-frequency and multi-spatial information in network, called FSBNet. First, we construct a modality-specific unsymmetrical architecture and integrate an adaptive soft threshold mechanism into a DCT-based multi-frequency channel attention adapter (DFDA). DFDA adaptively integrates rich multi-frequency information. Second, we propose a masked frequency-based translation adapter (MFTA) to refine drifting failure boxes caused by camera motion. Moreover, we find that small targets get more affected by motion blur compared to larger targets, and we mitigate this issue by designing a cross-scale mutual conversion adapter (CFCA) between the frequency and spatial domains. Extensive experiments on GTOT, RGBT234 and LasHeR benchmarks demonstrate the promising performance of our method in the presence of motion blur.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Wang T, Shi C (2023) Basketball motion video target tracking algorithm based on improved gray neural network. Neural Comput Appl 35(6):4267–4282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07026-6
Zhai M, Xiang X (2021) Geometry understanding from autonomous driving scenarios based on feature refinement. Neural Comput Appl 33(8):3209–3220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05192-z
Abbasi A, Zadeh SM, Yazdani A, Moshayedi AJ (2022) Feasibility assessment of Kian-i mobile robot for autonomous navigation. Neural Comput Appl 34(2):1199–1218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06428-2
Zhang C, Ren K (2022) LRATD: a lightweight real-time abnormal trajectory detection approach for road traffic surveillance. Neural Comput Appl 34(24):22417–22434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07626-2
Yuan D, Chang X, Huang P-Y, Liu Q, He Z (2020) Self-supervised deep correlation tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:976–985
Yang K, He Z, Pei W, Zhou Z, Li X, Yuan D, Zhang H (2021) Siamcorners: Siamese corner networks for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed 24:1956–1967
Ke X, Li Y, Guo W, Huang Y (2022) Learning deep convolutional descriptor aggregation for efficient visual tracking. Neural Comput Appl 34(5):3745–3765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06638-8
Liu Q, Yuan D, He Z (2017) Thermal infrared object tracking via siamese convolutional neural networks. In: 2017 international conference on security, pattern analysis, and Cybernetics (SPAC), pp. 1–6. IEEE
Liu Q, Yuan D, Fan N, Gao P, Li X, He Z (2022) Learning dual-level deep representation for thermal infrared tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed 25:1269–1281
Liu Q, Li X, He Z, Fan N, Yuan D, Wang H (2020) Learning deep multi-level similarity for thermal infrared object tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed 23:2114–2126
Li C, Cheng H, Hu S, Liu X, Tang J, Lin L (2016) Learning collaborative sparse representation for grayscale-thermal tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2614135
Yun X, Jing Z, Xiao G, Jin B, Zhang C (2016) A compressive tracking based on time-space Kalman fusion model. Sci China Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-015-5356-0
Cvejic N, Nikolov SG, Knowles HD, Loza A, Achim A, Bull DR, Canagarajah CN (2007) The effect of pixel-level fusion on object tracking in multi-sensor surveillance video. In: 2007 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR 2007), 18-23 June 2007, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2007.383433
Li C, Hu S, Gao S, Tang J (2016) Real-time grayscale-thermal tracking via laplacian sparse representation. In: Tian Q, Sebe N, Qi G, Huet B, Hong R, Liu X (eds.) MultiMedia modeling : 22nd international conference, MMM 2016, Miami, FL, USA, January 4-6, 2016, Proceedings, Part II. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9517, pp. 54–65 . https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27674-8_6
Lu A, Li C, Yan Y, Tang J, Luo B (2021) RGBT tracking via multi-adapter network with hierarchical divergence loss. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3087341
Zhu Y, Li C, Tang J, Luo B (2021) Quality-aware feature aggregation network for robust RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans Intell Veh. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIV.2020.2980735
Li C, Xiang Z, Tang J, Luo B, Wang F (2022) RGBT tracking via noise-robust cross-modal ranking. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3067107
Mao Z, Chen X, Wang Y, Yan J (2021) Robust tracking for motion blur via context enhancement. In: 2021 IEEE international conference on image processing, ICIP 2021, Anchorage, AK, USA, September 19-22, . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP42928.2021.9506594
Iraei I, Faez K (2021) A motion parameters estimating method based on deep learning for visual blurred object tracking. IET Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12189
Wang Z, Yao Z, Wang Q (2017) Improved scheme of estimating motion blur parameters for image restoration. Digit Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2017.02.010
Zhang Y, Li Q, Qi M, Liu D, Kong J, Wang J (2022) Multi-scale frequency separation network for image deblurring. CoRR https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2206.00798
Liu K, Yeh C, Chung J, Chang C (2020) A motion deblur method based on multi-scale high frequency residual image learning. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985220
Jung I, Son J, Baek M, Han B (2018) Real-time mdnet. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision - ECCV 2018 - 15th European conference, Munich, Germany, September 8-14, 2018, Proceedings, Part IV . https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_6
Xu Q, Mei Y, Liu J, Li C (2022) Multimodal cross-layer bilinear pooling for RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3055362
Zhang P, Wang D, Lu H, Yang X (2021) Learning adaptive attribute-driven representation for real-time RGB-T tracking. Int J Comput Vis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01495-3
Li C, Liu L, Lu A, Ji Q, Tang J (2020) Challenge-aware RGBT tracking. In: Vedaldi A, Bischof H, Brox T, Frahm J (eds.) Computer vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23-28 Proceedings, Part XXII (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58542-6_14
Qin Z, Zhang P, Wu F, Li X (2021) Fcanet: frequency channel attention networks. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, ICCV 2021, Montreal, QC, Canada, October 10-17, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00082
Xu ZJ, Zhang Y, Luo T, Xiao Y, Ma Z (2019) Frequency principle: Fourier analysis sheds light on deep neural networks. CoRR
Basri R, Galun M, Geifman A, Jacobs DW, Kasten Y, Kritchman S (2020) Frequency bias in neural networks for input of non-uniform density. In: Proceedings of the 37th international conference on machine learning, ICML 2020, 13-18 July 2020, Virtual Event
Hai J, Yang R, Yu Y, Han S (2022) Combining spatial and frequency information for image deblurring. IEEE Signal Process Lett. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2022.3194807
Yin D, Lopes RG, Shlens J, Cubuk ED, Gilmer J (2019) A fourier perspective on model robustness in computer vision. In: Wallach HM, Larochelle H, Beygelzimer A, d’Alché-Buc F, Fox EB, Garnett R (eds.) Advances in neural information processing systems 32: annual conference on neural information processing systems 2019, NeurIPS 2019, December 8-14, Vancouver, BC, Canada (2019)
Wang H, Wu X, Huang Z, Xing EP (2020) High-frequency component helps explain the generalization of convolutional neural networks. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, June 13-19, 2020, pp. 8681–8691 . https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00871
Ding J, Huang Y, Liu W, Huang K (2016) Severely blurred object tracking by learning deep image representations. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2406231
Mozhdehi RJ, Reznichenko Y, Siddique A, Medeiros H (2018) Deep convolutional particle filter with adaptive correlation maps for visual tracking. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on image processing, ICIP 2018, Athens, Greece, October 7-10, 2018 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2018.8451069
Yuan D, Chang X, Li Z, He Z (2022) Learning adaptive spatial-temporal context-aware correlation filters for UAV tracking. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl TOMM 18(3):1–18
Yuan D, Chang X, Liu Q, Yang Y, Wang D, Shu M, He Z, Shi G (2023) Active learning for deep visual tracking. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst
Yang K, He Z, Pei W, Zhou Z, Li X, Yuan D, Zhang H (2021) Siamcorners: Siamese corner networks for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed 24:1956–1967
Yuan D, Chang X, Huang P-Y, Liu Q, He Z (2020) Self-supervised deep correlation tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:976–985
El-Shafie AA, Zaki MH, Habib SE (2019) Fast CNN-based object tracking using localization layers and deep features interpolation. In: 15th international wireless communications & mobile computing conference, IWCMC 2019, Tangier, Morocco, June 24-28, 2019 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/IWCMC.2019.8766466
Ning G, Zhang Z, Huang C, Ren X, Wang H, Cai C, He Z (2017) Spatially supervised recurrent convolutional neural networks for visual object tracking. In: IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, ISCAS 2017, Baltimore, MD, USA, May 28-31, 2017 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS.2017.8050867
Gan W, Wang S, Lei X, Lee M, Kuo C-J (2018) Online CNN-based multiple object tracking with enhanced model updates and identity association. Signal Process Image Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2018.05.008
Yuan D, Shu X, Liu Q, Zhang X, He Z (2023) Robust thermal infrared tracking via an adaptively multi-feature fusion model. Neural Comput Appl 35(4):3423–3434
Yuan D, Shu X, Liu Q, He Z (2022) Aligned spatial-temporal memory network for thermal infrared target tracking. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 70(3):1224–1228
Yuan D, Shu X, Liu Q, He Z (2022) Structural target-aware model for thermal infrared tracking. Neurocomputing 491:44–56
Zhang P, Zhao J, Bo C, Wang D, Lu H, Yang X (2021) Jointly modeling motion and appearance cues for robust RGB-T tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 30: 3335–3347 https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3060862
Xiao Y, Yang M, Li C, Liu L, Tang J (2022) Attribute-based progressive fusion network for RGBT tracking. In: Thirty-Sixth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI 2022, thirty-fourth conference on innovative applications of artificial intelligence, IAAI 2022, The twelveth symposium on educational advances in artificial intelligence, EAAI 2022 Virtual Event, February 22 - March 1, 2022
Lu A, Qian C, Li C, Tang J, Wang L (2020) Duality-gated mutual condition network for RGBT tracking. CoRR
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Guyon I, Luxburg U, Bengio S, Wallach HM, Fergus R, Vishwanathan SVN, Garnett R (eds.) Advances in neural information processing systems 30: annual conference on neural information processing systems 2017, December 4-9, 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 5998–6008 (2017). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/hash/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Abstract.html
Hong D, Wu X, Ghamisi P, Chanussot J, Yokoya N, Zhu XX (2020) Invariant attribute profiles: a spatial-frequency joint feature extractor for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2957251
Li Q, Shen L, Guo S, Lai Z (2021) Wavecnet: wavelet integrated CNNS to suppress aliasing effect for noise-robust image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3101395
Gal R, Hochberg DC, Bermano A, Cohen-Or D (2021) SWAGAN: a style-based wavelet-driven generative model. ACM Trans Graph. https://doi.org/10.1145/3450626.3459836
Koh J, Lee J, Yoon S (2021) Single-image deblurring with neural networks: a comparative survey. Comput Vis Image Underst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2020.103134
Jiang W, Liu A (2022) Image motion deblurring based on deep residual shrinkage and generative adversarial networks. Comput Intell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5605846
Liu Y, Fang F, Wang T, Li J, Sheng Y, Zhang G (2022) Multi-scale grid network for image deblurring with high-frequency guidance. IEEE Trans Multimed. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3090206
Ahmed N, Natarajan TR, Rao KR (1974) Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Trans Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/T-C.1974.223784
Zhao M, Zhong S, Fu X, Tang B, Pecht MG (2020) Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans Ind Inf. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2019.2943898
Stone HS, Orchard MT, Chang E, Martucci SA (2001) A fast direct Fourier-based algorithm for subpixel registration of images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.957286
Ren J, Vlachos T, Zhang Y, Zheng J, Jiang J (2014) Gradient-based subspace phase correlation for fast and effective image alignment. J Vis Commun Image Represent. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.07.001
Shekarforoush H, Berthod M, Zerubia J (1996) Subpixel image registration by estimating the polyphase decomposition of cross power spectrum. In: 1996 conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR ’96), June 18-20, 1996 San Francisco, CA, USA . https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.1996.517123
Xu Q, Mei Y, Liu J, Li C (2022) Multimodal cross-layer bilinear pooling for RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3055362
Li C, Liang X, Lu Y, Zhao N, Tang J (2019) RGB-T object tracking: benchmark and baseline. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.106977
Li C, Xue W, Jia Y, Qu Z, Luo B, Tang J, Sun D (2022) Lasher: a large-scale high-diversity benchmark for RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3130533
Gao Y, Li C, Zhu Y, Tang J, He T, Wang F (2019) Deep adaptive fusion network for high performance RGBT tracking. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision workshops, ICCV workshops 2019, Seoul, Korea (South), October 27-28, 2019 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00017
Zhu Y, Li C, Luo B, Tang J, Wang X (2019) Dense feature aggregation and pruning for RGBT tracking. In: Amsaleg L, Huet B, Larson MA, Gravier G, Hung H, Ngo C, Ooi WT (eds.) Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on multimedia, MM 2019, Nice, France, October 21-25, 2019 . https://doi.org/10.1145/3343031.3350928
Nam H, Han B (2016) Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 27-30, 2016 . https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.465
Danelljan M, Robinson A, Khan FS, Felsberg M (2016) Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds.) Computer vision: ECCV 2016: 14th European conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11-14, 2016, Proceedings, Part V. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46454-1_29
Valmadre J, Bertinetto L, Henriques JF, Vedaldi A, Torr PHS (2017) End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, July 21-26, 2017 . https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.531
Zhang J, Ma S, Sclaroff S (2014) MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. In: Fleet, D.J., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) Computer Vision - ECCV 2014 - 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, Proceedings, Part VI. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_13
Lu A, Li C, Yan Y, Tang J, Luo B (2021) RGBT tracking via multi-adapter network with hierarchical divergence loss. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3087341
Tu Z, Lin C, Zhao W, Li C, Tang J (2022) M\({}^{\text{5}}\)l: Multi-modal multi-margin metric learning for RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 31: 85–98 https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3125504
Zhang H, Zhang L, Zhuo L, Zhang J (2020) Object tracking in RGB-T videos using modal-aware attention network and competitive learning. Sensors 20(2):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020393
Zhang L, Danelljan M, Gonzalez-Garcia A, Weijer J, Khan FS (2019) Multi-modal fusion for end-to-end RGB-T tracking. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision workshops, ICCV Workshops 2019, Seoul, Korea (South), October 27-28, 2019 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00278
Li C, Zhu C, Huang Y, Tang J, Wang L (2018) Cross-modal ranking with soft consistency and noisy labels for robust RGB-T tracking. In: Ferrari V, Hebert M, Sminchisescu C, Weiss Y (eds.) Computer vision—ECCV 2018: 15th european conference, Munich, Germany, September 8-14, 2018, Proceedings, Part XIII . https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_49
Chen Z, Zhong B, Li G, Zhang S, Ji R (2020) Siamese box adaptive network for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 6668–6677
Bhat G, Danelljan M, Van Gool L, Timofte R (2020) Know your surroundings: exploiting scene information for object tracking. In: Computer vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XXIII 16, pp. 205–221 . Springer
Wang N, Zhou W, Wang J, Li H (2021) Transformer meets tracker: exploiting temporal context for robust visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1571–1580
Danelljan M, Gool LV, Timofte R (2020) Probabilistic regression for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 7183–7192
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41371342) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0803000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, S., Chen, X., He, C. et al. Multiple frequency–spatial network for RGBT tracking in the presence of motion blur. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 24389–24406 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-09024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-09024-8