Abstract
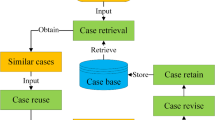
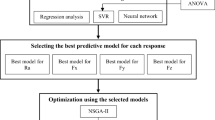
In the machining process, the machining performance which mainly refers to machined surface quality and cutting forces is hard to predict under different tool wear status. In this work, an improved case-based reasoning (ICBR) method is proposed to predict both the cutting force and machined surface roughness. With the emergence of new problem, ICBR method obtains solutions to new problem through case retrieval and reuse. In case retrieval stage, K similar cases to the new problem were retrieved using K nearest neighbor method. By means of the K similar cases, support vector regression machine (SVR) model was established to give the solution of the new problem in case of the reuse stage of ICBR method. Artificial neural network (ANN) was introduced to estimate the influence of machining parameters and tool wear on machining performance. As the ANN and SVR models contain unknown parameters, the novel particle swarm optimization algorithm was proposed to train these models for its capability of fast convergence and global optimum. The proposed ICBR method was used to predict the surface roughness and cutting force. The results showed the proposed ICBR method can give superior prediction accuracy and lower Mean square error than other popular intelligent models. Meantime, the ICBR method possesses good robustness and can be used for the actual machining process.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asilturk I, Kahramanli H, El Mounayri H (2012) Prediction of cutting forces and surface roughness using artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector regression (SVR) in turning 4140 steel. Mater Sci Technol 28(8):980–986
Biswas S, Nidul S, Biswajit P, Leniency M (2014) Hybrid expert system using case based reasoning and neural network for classification. Biol Inspir Cogn Archit 9:57–70
Chakraborty S, Boral S (2017) A developed case-based reasoning system for machine tool selection. Benchmarking Int J 24(5):1364–1385
Chatterjee N, Campbell JA (1997) Interpolation as a means of fast adaptation in case-based problem solving. In Proceedings fifth german workshop on case-based reasoning, pp 65–74
Diaz F, Fdze-Riverola F, Corchado JM (2006) Gene-CBR: a case-based reasoning tool for cancer diagnosis using microarray datasets. Comput Intell 22(3–4):254–258
Eberhart RC, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proc sixth int symp micro mach hum sci, vol 1, pp 39–43
Felhőa C, Karpuschewskib B, Kundráka J (2015). Surface roughness modelling in face milling. In: 15th cirp conference on modeling of machining oprerations, vol 31, pp 136–141
Guo Y, Hu J, Peng Y (2011) Research on a CBR system based on datamining. Appl Soft Comput 11:5006–5014
Guo Y, Hu J, Peng Y (2012) A CBR system for injection mould design based on ontology: a case study. Comput Aided Des 44:496–508
Han M, Cao Z (2015) An improved case-based reasoning method and its application in endpoint prediction of basic oxygen furnace. Neurocomputing 149:1245–1252
Henriet J, Leni PE, Laurent R, Roxin A, Chebel-Morello B, Salomon M (2012) Adapting numerical representations of lung contours using case-based reasoning and artificial neural networks. In Daz Agudo B, Watson I (eds) Artificial intelligence series ICCBR 2012. LNCS 7466, pp 137–151
Huang S, Chang J, Huang Q (2014) Monthly stream flow prediction using modified EMD-based support vector machine. J Hydrol 511:764–775
Hyuk I, Sang P (2007) Case-based reasoning and neural network based expert system for personalization. Expert Syst Appl 32:77–85
Jiang Z, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Zhang H, Cao H, Tian G (2019) A hybrid approach of rough set and case-based reasoning to remanufacturing process planning. J Intell Manuf 30(1):19–32
Jung S, Lim T, Kim D (2009) Integrating radial basis function networks with case-based reasoning for product design. Expert Syst Appl 36:5695–5701
Lee KS, Luo C (2002) Application of case-based reasoning in die casting die design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 20:284–295
Li X, Ma S, Hu J (2017) Multi-search differential evolution algorithm. Appl Intell 47:231–256
Mata A, Juan M (2009) Forecasting the probability of finding oilslicks using a CBR system. Expert Syst Appl 36:8239–8246
Mehmet A, Cihan K, Mehmet U, Abdulkadir C, Mehmet A (2013) Prediction of surface roughness and cutting zone temperature in dry turning processes of AISI304 stainless steel using ANFIS with PSO learning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67:957–967
Qi J, Hu J, Peng YH, Wang W, Zhang Z (2009) A case retrieval method combined with similarity measurement and multi-criteria decision making for concurrent design. Expert Syst Appl 36:10357–10366
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2014) Long term learning in image retrieval systems using case based reasoning. Eng Appl Artif Intell 35:26–37
Saeed N, Ahmad B, Farid N (2018) PSOSCALF: a new hybrid PSO based on sine cosine algorithm and Levy flight for solving optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 73:697–726
Wang Y, Shao H (2000) Uncertain case indexing and retrieval method of case-based reasoning system. Control Decis 15:750–754. https://doi.org/10.13195/j.cd.2000.06.110.wangyy.030
Wang G, Zhou X, Liu J, Zhu P, Zhou H (2017) Polishing process planning based on fuzzy theory and case-based reasoning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90:907–915
Xavior AM, Anouncia MS (2012) Case-based reasoning (CBR) model for hard machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61(9–12):1269–1275
Xiang Y, Gou L, He L, Xia S, Wang W (2018) A SVR–ANN combined model based on ensemble EMD for rainfall prediction. Appl Soft Comput 73:874–883
Xu L, Huang C, Li C, Wang J, Liu H, Wang X (2020) Estimation of tool wear and optimization of cutting parameters based on novel ANFIS-PSO method toward intelligent machining. J Intell Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01559-0
Yeganefar A, Niknam S, Asadi R (2019) The use of support vector machine, neural network, and regression analysis to predict and optimize surface roughness and cutting forces in milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105(4):951–965
Zhou J, Huang P (2006) Intelligent selection system for tool materials with case-based-reason technology. Int J Mach Mach Mater 1(3):354–366
Zhu GN, Hu J, Qi J, Ma J, Peng YH (2015) An integrated feature selection and cluster analysis techniques for case-based reasoning. Eng Appl Artif Intell 39:14–22
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51675312, 51675313).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Huang, C., Niu, J. et al. An improved case-based reasoning method and its application to predict machining performance. Soft Comput 25, 5683–5697 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05564-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05564-6