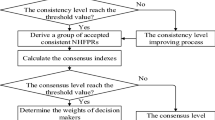
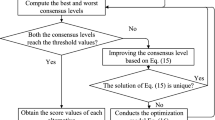
Abstract
As a generalized fuzzy number, probabilistic hesitant fuzzy element (PHFE) improves the flexibility for decision makers in expressing hesitant information, and it has been receiving increased attention. This study develops a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) approach that considers consensus reaching among decision makers with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information. To obtain this aim, first, a new approach to derive normalized PHFE (NPHFE) is proposed to overcome the shortcomings in previous studies. Subsequently, a new Euclidean distance and some operations related to PHFEs are developed based on the new proposed NPHFEs. At the same time, the effectiveness and rationality of the new proposed approaches are discussed. Second, a consensus index of group with PHFEs is presented, which based on the proposed Euclidean distance of decision-makers’ evaluation information on all the criteria. Third, if the consensus level of the group does not reach the expect threshold value, an iteration algorithm is designed to improve its consensus level. Moreover, the proof of the convergence of the proposed algorithm is provided to verify its effectiveness, and a MCDM approach based on group consensus is proposed. Finally, the most comprehensive candidate selection problems are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed MCDM approach. And a comparative study with other methods is conducted with the same illustrative example.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng D, Zhou ZL, Cheng FX, Zhou YF, Xie YJ (2018) Modeling the minimum cost consensus problem in an asymmetric costs context. Eur J Oper Res 270(3):1122–1137
Chu JF, Liu XW, Wang YM, Chin KS (2016) A group decision making model considering both the additive consistency and group consensus of intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Comput Ind Eng 101:227–242
Ding J, Xu ZS, Zhao N (2017) An interactive approach to probabilistic hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making with incomplete weight information. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(3):2523–2536
Ding RX, Palomares I, Wang X, Yang G-R, Liu B, Dong Y, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2020) Large-scale decision-making: characterization, taxonomy, challenges and future directions from an artificial intelligence and applications perspective. Inf Fusion 59:84–102
Dong YC, Chen X, Liang HM, Li CC (2016a) Dynamics of linguistic opinion formation in bounded confidence model. Inf Fusion 32:52–61
Dong YC, Zhang HJ, Herrera-Viedma E (2016b) Integrating experts’ weights generated dynamically into the consensus reaching process and its applications in managing non-cooperative behaviors. Decis Support Syst 84:1–15
Dong YC, Ding ZG, Martínez L, Herrera F (2017) Managing consensus based on leadership in opinion dynamics. Inf Sci 397–398:187–205
Dong YC, Liu YT, Liang HM, Chiclana F, Herrera-Viedma E (2018a) Strategic weight manipulation in multiple attribute decision making. Omega 75:154–164
Dong YC, Zha QB, Zhang HJ, Kou G, Fujita H, Chiclana F, Herrera-Viedma E (2018b) Consensus reaching in social network group decision making: research paradigms and challenges. Knowl-Based Syst 162:3–13
Du YW, Yang N, Ning J (2018) IFS/ER-based large-scale multiattribute group decision-making method by considering expert knowledge structure. Knowl-Based Syst 162:124–135
Hao ZN, Xu ZS, Zhao H, Su Z (2017) Probabilistic dual hesitant fuzzy set and its application in risk evaluation. Knowl-Based Syst 127(Supplement C):16–28
He Y, Xu Z (2019) Multi-attribute decision making methods based on reference ideal theory with probabilistic hesitant information. Expert Syst Appl 118:459–469
He SS, Wang JQ, Cheng PF, Li L (2020) A novel risk assessment model based on failure mode and effect analysis and probabilistic linguistic ELECTRE II method. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-191398
Jiang F, Ma Q (2018) Multi-attribute group decision making under probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment with application to evaluate the transformation efficiency. Appl Intell 48:953–965
Li J, Wang JQ (2017a) An extended QUALIFLEX method under probability hesitant fuzzy environment for selecting green suppliers. Int J Fuzzy Syst 19(6):1866–1879
Li J, Wang JQ (2017b) Multi-criteria outranking methods with hesitant probabilistic fuzzy sets. Cogn Comput 9(5):611–625
Li J, Wang JQ (2019) Multi-criteria decision-making with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information based on expected multiplicative consistency. Neural Comput Appl 31(12):8897–8915
Li J, Wang JQ, Hu JH (2019a) Consensus building for hesitant fuzzy preference relations with multiplicative consistency. Comput Ind Eng 128:387–400
Li J, Wang JQ, Hu JH (2019b) Multi-criteria decision-making method based on dominance degree and BWM with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10(7):1671–1685
Li J, Chen Q, Niu LL, Wang ZX (2020) An ORESTE approach for multi-criteria decision-making with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01060-3
Nie RX, Tian ZP, Wang JQ, Chin KS (2020) Hotel selection driven by online textual reviews: applying a semantic partitioned sentiment dictionary and evidence theory. Int J Hosp Manag 88:102495
Pérez IJ, Cabrerizo FJ, Alonso S, Dong YC, Chiclana F, Herrera-Viedma E (2018) On dynamic consensus processes in group decision making problems. Inf Sci 459:20–35
Rodríguez RM, Labella Á, Tré GD, Martínez L (2018) A large scale consensus reaching process managing group hesitation. Knowl-Based Syst 159:86–97
Song C, Xu Z, Zhao H (2019) New correlation coefficients between probabilistic hesitant fuzzy sets and their applications in cluster analysis. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21:355–368
Song C, Wang XK, Cheng PF, Wang JQ, Li L (2020) SACPC: a framework based on probabilistic linguistic terms for short text sentiment analysis. Knowl-Based Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105572
Tian ZP, Nie RX, Wang JQ (2019) Social network analysis-based consensus-supporting framework for large-scale group decision-making with incomplete interval type-2 fuzzy information. Inf Sci 502:446–471
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25(6):529–539
Triantaphyllou E, Yanase J, Hou F (2020) Post-consensus analysis of group decision making processes by means of a graph theoretic and an association rules mining approach. Omega 4:102208
Ureña R, Chiclana F, Melançon G, Herrera-Viedma E (2019) A social network based approach for consensus achievement in multiperson decision making. Inf Fusion 47:72–87
Wu ZB, Xu JP (2012) A concise consensus support model for group decision making with reciprocal preference relations based on deviation measures. Fuzzy Sets Syst 206(11):58–73
Wu ZB, Xu JP (2018) A consensus model for large-scale group decision making with hesitant fuzzy information and changeable clusters. Inf Fusion 41:217–231
Wu ZB, Jin BM, Xu JP (2018) Local feedback strategy for consensus building with probability-hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Appl Soft Comput 67:691–705
Wu HY, Ren PJ, Xu ZS (2019) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic consensus model based on trust-recommendation mechanism for hospital expert consultation. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2019.2896836
Wu T, Liu X, Gong Z, Zhang H, Herrera F (2020) The minimum cost consensus model considering the implicit trust of opinions similarities in social network group decision-making. Int J Intell Syst 35(3):470–493
Xia MM, Xu ZS (2011) Hesitant fuzzy information aggregation in decision making. Int J Approx Reason 52(3):395–407
Xu ZS, Xia MM (2011) Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 181(11):2128–2138
Xu ZS, Zhou W (2017) Consensus building with a group of decision makers under the hesitant probabilistic fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Optim Decis Mak 16(4):481–503
Xu ZS, He Y, Wang XZ (2019) An overview of probabilistic-based expressions for qualitative decision-making: techniques, comparisons and developments. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10(6):1513–1528
Zhai YL, Xu ZS, Liao HC (2018) Measures of probabilistic interval-valued intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy sets and the application in reducing excessive medical examinations. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26(3):1651–1670
Zhang S, Xu ZS, He Y (2017) Operations and integrations of probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information in decision making. Inf Fusion 38:1–11
Zhang HJ, Palomares I, Dong YC, Wang WW (2018) Managing non-cooperative behaviors in consensus-based multiple attribute group decision making: an approach based on social network analysis. Knowl-Based Syst 162:29–45
Zhou W, Xu ZS (2017) Expected hesitant VaR for tail decision making under probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment. Appl Soft Comput 60:297–311
Zhou W, Xu ZS (2018) Probability calculation and element optimization of probabilistic hesitant fuzzy preference relations based on expected consistency. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst PP(99):1367–1378
Zhu B (2014) Decision method for research and application based on preference relation. Southeast University, Nanjing
Zhu B, Xu ZS (2014) Consistency measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(1):35–45
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their insightful and constructive comments and suggestions that have led to an improved version of this paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61866006), Guangxi innovation-driven development of special funds project (gui ke AA17204091), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (No. AB17292095), the Research Funds for the Guangxi University Xingjian College of Science and Liberal Arts (No. Y2018ZKT01) and Promotion project of Middle-aged and Young Teachers’ Basic Scientific Research Ability in Universities of Guangxi (No. 2019KY0963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors Jian Li, Li-li Niu, Qiongxia Chen and Guang Wu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Niu, Ll., Chen, Q. et al. A consensus-based approach for multi-criteria decision making with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information. Soft Comput 24, 15577–15594 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04886-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04886-9