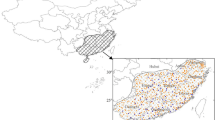
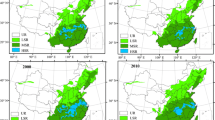
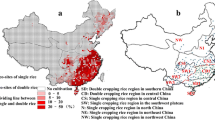
Abstract
As an important food crop in China, changes in suitable areas for rice planting are critical to agricultural production. In this study, the maximum entropy model (MaxEnt) was utilized to pick the main climatic factors affecting single-season rice planting distribution and project the potential changes under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios. It was clear that rice planting distribution was significantly affected by annual total precipitation, the accumulated temperature during a period in which daily temperature was ≥ 10 °C, the moisture index, total precipitation during April–September, and continuous days during the period of daily temperature ≥ 18 °C, with their contribution being 97.6%. There was a continuous decrease in the area of good and high suitability for rice planting projected from 2021–2040 to 2061–2080, with a respective value ranging from 1.49 × 106 km2 to 0.93 × 106 km2 under the RCP4.5 scenario and from 1.42 × 106 km2 to 0.66 × 106 km2 under RCP8.5 scenarios. In 2081–2100, there was a bit increase in the area of good and high suitability under the RCP4.5 scenario. The most significant increases in good and high suitability were detected in Northeast China, while obvious decreases were demonstrated in the Yangtze River Basin which might be exposed to extreme temperature threat. The spatial potential planting center was characterized by the largest planting area in 25°N–37°N and 98°E–134°E. The north boundary and center of rice cultivation arose to 53.5°N and 37.52°N, respectively. These potential distributions for single-season rice under future climate change can provide a theoretical basis for optimizing rice planting layout, improving cultivation, and adjusting variety and management systems in response to climate change.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Available on request.
References
Ali NIM, Aiyub K, Lam KC, Abas A (2022) A bibliometric review on the inter-connection between climate change and rice farming. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:30892–30907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18880-1
Asselen SV, Verburg PH (2014) Land cover change or land-use intensification: simulating land system change with a global-scale land change model. Glob Change Biol 19(12):3648–3667. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12331
Bai HZ, Tao FL, Xiao DP, Liu FS, Zhang H (2016) Attribution of yield change for rice-wheat rotation system in China to climate change, cultivars and agronomic management in the past three decades. Clim Change 135:539–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1579-8
Döll P (2002) Impact of climate change and variability on irrigation requirements: a global perspective. Clim Change 54(3):269–293. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016124032231
Duan JQ, Zhou GS (2012) Climatic suitability of single cropping rice planting region in China. Chin J Appl Ecol 23(2):426–432 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Duan JQ, Zhou GS (2013) Dynamics of decadal changes in the distribution of double-cropping rice cultivation in China. Chin Sci Bull 58(16):1955–1963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5608-y
Elith J, Graham CH, Anderson RP, Dudík M, Ferrier S, Guisan A, Hijmans R, Huettmann F, Leathwick JR, Lehmann A, Li J, Lohmann LG, Loiselle BA, Manion G, Moritz C, Nakamura M, Nakazawa Y, McC Overton J, Peterson AT, Phillips SJ, Richardson KS, Scachetti-Pereira R, Schapire RE, Sobero´n J, Williams S, Wisz MS, Zimmermann NE (2006) Novel methods improve prediction of species’ distributions from occurrence data. Ecography 29(2):129–151. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2006.0906-7590.04596.x
Elith J, Phillips SJ, Hastie T, Dudík M, Chee YE, Yates CJ (2010) A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists. Divers Distrib 17(1):43–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2010.00725.x
Evangelista P, Young N, Burnett J (2013) How will climate change spatially affect agriculture production in Ethiopia? Case studies of important cereal crops. Clim Change 119(3–4):855–873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-013-0776-6
FAO (2018) FAO Rice Market Monitor. Food Agric Organ United States 21:1–38, available at: https://www.fao.org/3/I9243EN/i9243en.pdf
FAO (2020) Food and agricultural organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT, access on Dec 22, available at: http://www.fao.org/ faostat/en/#data/QC. Accessed 22 Dec 2020.
Gao JC, Yang XG, Zheng BY, Liu ZJ, Zhao J, Sun S, Li KN, Dong Y (2019) Effects of climate change on the extension of the potential double cropping region and crop water requirements in Northern China. Agric for Meteorol 268:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.01.009
Guo JP (2010) Chinese agroclimate resource changing trend under global change. Meteorological Press, Beijing, China ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Hargreaves GH, Allen RG (2003) History and evaluation of Hargreaves evapotranspiration equation. J Irrig Drain Eng 129(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9437(2003)129:1(53)
IPCC (2021) Climate Change 2021: The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157896
Kim HY, Ko JH, Kang SC, Tenhunen J (2013) Impacts of climate change on paddy rice yield in a temperate climate. Glob Change Biol 19(2):548–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12047
Kozak KH, Graham CH, Wiens JJ (2008) Integrating GIS-based environmental data into evolutionary biology. Trends Ecol Evol 23(3):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2008.02.001
Lobell DB, Schlenker W, Costa-Roberts J (2011) Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 333(6042):616–620. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1204531
Lv ZF, Zhu Y, Liu XJ, Ye HB, Tian YC, Li FF (2018) Climate change impacts on regional rice production in China. Clim Change 147:523–537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-018-2151-0
Machovina B, Feeley KJ (2013) Climate change driven shifts in the extent and location of areas suitable for export banana production. Ecol Econ 95:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2013.08.004
Marotzke J, Jakob C, Bony S, Dirmeyer PA, O’Gorman PA, Hawkins E, Perkins-Kirkpatrick S, Quéré CL, Nowicki S, Paulavets K, Seneviratne SI, Stevens B, Tuma M (2017) Climate research must sharpen its view. Nat Clim Chang 7(2):89–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3206
Moore F (2020) The fingerprint of anthropogenic warming on global agriculture [Preprint]. EarthArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31223/x5q30z.
Ning L, Riddle EE, Bradley RS (2015) Projected changes in climate extremes over the northeastern United States. J Clim 28(8):3289–3310. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-14-00150.1
Ohta SJ, Kimura A (2007) Impacts of climate changes on the temperature of paddy waters and suitable land for rice cultivation in Japan. Agric for Meteorol 147(3–4):186–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2007.07.009
Olesen JE, Trnka M, Kersebaum KC, Skjelvag AO, Seguin B, Peltonrn-Sainio P, Rossi F, Kozyra J, Micalei F (2011) Impacts and adaptation of European crop production systems to climate change. Eur J Agron 34:96–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2010.11.003
Ortiz R, Sayre KD, Govaerts B, Gupta R, Reynolds M (2008) Climate change: can wheat beat the heat? Agr Ecosyst Environ 126(1–2):46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2008.01.019
Peng SB, Huang JL, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong XH, Centeno CG, Khush GS, Cassman KG (2004) Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(27):9971–9975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0403720101
Peterson AT (2003) Predicting the geography of species’ invasions via ecological niche modeling. Q Rev Biol 78(4):419–433. https://doi.org/10.1086/378926
Phillips SJ (2008) Transferability, sample selection bias and background data in presence-only modelling: a response to Peterson et al (2007). Ecography 31(2):272–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0906-7590.2008.5378.x
Piao SL, Ciais P, Huang Y, Shen ZH, Peng SS, Li JS, Zhou LP, Liu HY, Ma YC, Ding YH, Friedkingstein P, Liu CZ, Tan K, Yu YQ, Zhang TY, Fang JY (2010) The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 467(7311):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09364
Shi WJ, Tao FL, Liu JY, Xu XL, Kuang WH, Dong JW, Shi XL (2014) Has climate change driven spatio-temporal changes of cropland in northern China since the 1970s? Clim Change 124(1–2):163–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-014-1088-1
Singh G, Gupta MK, Chaurasiya S, Sharma VS, Pimenov DY (2021) Rice straw burning: a review on its global prevalence and the sustainable alternatives for its effective mitigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(25):32125–32155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14163-3
Tao FL, Yokozawa M, Xu YL, Hayashi Y, Zhang Z (2006) Climate changes and trends in phenology and yields of field crops in China, 1981–2000. Agric for Meteorol 138(1–4):82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.014
Thrasher B, Maurer EP, McKellar C, Duffy PB (2012) Technical note: bias correcting climate model simulated daily temperature extremes with quantile mapping. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16(9):3309–3314. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-3309-2012
Tong CL, Hall CAS, Wang HQ (2003) Land use change in rice, wheat and maize production in China (1961–1998). Agr Ecosyst Environ 95(2–3):523–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-8809(02)00182-2
Oort PAJ, Zwart SJ (2017) Impacts of climate change on rice production in Africa and causes of simulated yield changes. Glob Change Biol 24(3):1029–1045. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13967
Wang LX, Ren JQ, Li Q (2014) Simulation of the heat injury on rice production in Jiangsu Province under the climate change scenarios II: adaptability analysis of the rice to heat injury from booting to heading stage. Chin J Agrometeorol 35(02):206–213. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2014.02.014.(inChinesewithEnglishabstract)
Werner AT, Cannon AJ (2016) Hydrologic extremes - an intercomparison of multiple gridded statistical downscaling methods. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20(4):1483–1508. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-1483-2016
Wu WB, Verburg PH, Tang HJ (2013) Climate change and the food production system: impacts and adaptation in China. Reg Environ Change 14(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0528-1
Xing DL, Hao ZQ (2011) The principle of maximum entropy and its applications in ecology. Biodiversity Science 19(3):295–302 (( in Chinese with English abstract))
Xiong W, Holman IP, You LZ, Yang J, Wu WB (2013) Impacts of observed growing-season warming trends since 1980 on crop yields in China. Reg Environ Change 14(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0418-6
Ye LM, Xiong W, Li ZG, Yang P, Wu WB, Yang GX, Fu YJ, Zou JQ, Chen ZX, Ranst EV, Tang HJ (2012) Climate change impact on China food security in 2050. Agron Sustain Dev 33(2):363–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-012-0102-0
Ye T, Zong S, Kleidon A, Yuan WB, Wang Y, Shi PJ (2019) Impacts of climate warming, cultivar shifts, and phenological dates on rice growth period length in China after correction for seasonal shift effects. Clim Change 155(1):127–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-019-02450-5
Yu E, Sun J, Chen H, Xiang W (2014a) Evaluation of a high-resolution historical simulation over China: climatology and extremes. Clim Dyn 45(7–8):2013–2031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2452-6
Yu YQ, Zhang W, Huang Y (2014b) Impact assessment of climate change, carbon dioxide fertilization and constant growing season on rice yields in China. Clim Change 124:763–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-014-1129-9
Zhang TY, Huang Y, Yang XG (2012) Climate warming over the past three decades has shortened rice growth duration in China and cultivar shifts have further accelerated the process for late rice. Glob Change Biol 19(2):563–570. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12057
Zhang S, Tao FL, Zhang Z (2014) Rice reproductive growth duration increased despite of negative impacts of climate warming across China during 1981–2009. Eur J Agron 54:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2013.12.001
Zhang L, Yang BY, Li S, Hou YY, Huang DP (2018) Potential rice exposure to heat stress along the Yangtze River in China under RCP8.5 scenario. Agric for Meteorol 248:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.09.020
Zhang LL, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Feng BY (2019) Yield losses caused by extreme high-temperature events and potential adaptive measures for single rice in Hunan Province based on the CERES-Rice model. Acta Ecol Sin 39(17):6293–6303. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201804260948
Zhang L, Xu YL, Meng CC, Li XH, Wang CG (2020) Comparison of statistical and dynamic downscaling techniques in generating high resolution temperature in China from CMIP5 GCMs. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 59:207–235. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D19-0048.1
Funding
This study was co-funded by the National Key R&D Program of China [grant No. 2018YFC1505605, 2019YFC1510204, 2018YFC1507802, and 2017YFD03001].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinhua Li and Lei Zhang conceived the topic of the work. Nong Chen, Yingwei Huang, and Fangying Tan archived the datasets and drew the figures. Xinhua Li drafted the manuscript, and Lei Zhang, Sen Li, and Yiwen Shi revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The author gives consent to the publication of all details of the manuscript, including texts, figures, and tables.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhang, L., Chen, N. et al. Potential dynamic changes of single-season rice planting suitability across China. Int J Biometeorol 67, 875–886 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-023-02462-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-023-02462-y