Abstract
Background
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) in infants with varying degrees of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and its associated outcomes, including mortality and length of stay (LOS).
Methods
The study used the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) dataset from 2010 to 2018. Regression analysis was used to control confounding variables.
Results
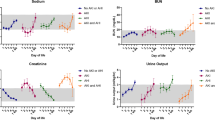
Of 31,220,784 infants included in the study, 30,130 (0.1%) had HIE. The prevalence of AKI was significantly higher in infants with HIE (9.0%) compared to those without (0.04%), with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 77.6 (CI:70.1–85.7, p < 0.001), with the highest prevalence of AKI in infants with severe HIE (19.7%), aOR:130 (CI: 107–159), p < 0.001). Infants with AKI had a higher mortality rate compared to those without AKI in those diagnosed with any degree of HIE (28.9% vs. 8.8%), aOR 3.5 (CI: 3.2–3.9, p < 0.001), particularly among those with severe HIE, aOR:1.4 (1.2–1.6, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
HIE is associated with an increased prevalence of AKI. Infants with severe HIE had the highest prevalence of AKI and associated mortality. The study highlights the need for close monitoring and early detection of AKI in infants with HIE, particularly those with severe HIE, to ameliorate the associated adverse outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
Acute kidney injury
- BW:
-
Birth weight
- CDH:
-
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
- CHD:
-
Congenital heart disease
- GA:
-
Gestational age
- HIE:
-
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
References
Douglas-Escobar M, Weiss MD (2015) Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review for the clinician. JAMA Pediatr 169:397–403
Sweetman DU, Strickland T, Isweisi E, Kelly L, Slevin MT, Donoghue V et al (2022) Multi-organ dysfunction scoring in neonatal encephalopathy (MODE Score) and neurodevelopmental outcomes. Acta Paediatr 111:93–98
Durkan AM, Alexander RT (2011) Acute kidney injury post neonatal asphyxia. J Pediatr 158:29–33
Alaro D, Bashir A, Musoke R, Wanaiana L (2014) Prevalence, and outcomes of acute kidney injury in term neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Afr Health Sci 14:682–688
Elgendy MM, Othman HF, Younis M, Puthuraya S, Matar RB, Aly H (2021) Trends and racial disparities for acute kidney injury in premature infants: the US national database. Pediatr Nephrol 36:2789–2795
Gallo D, de Bijl-Marcus KA, Alderliesten T, Lilien M, Groenendaal F (2021) Early acute kidney injury in preterm and term neonates: incidence, outcome, and associated clinical features. Neonatology 118:174–179
Jetton JG, Boohaker LJ, Sethi SK, Wazir S, Rohatgi S, Soranno DE, Neonatal Kidney Collaborative (NKC) et al (2017) Incidence and outcomes of neonatal acute kidney injury (AWAKEN): a multicentre, multinational, observational cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 1:184–194
Jetton JG, Askenazi DJ (2012) Update on acute kidney injury in the neonate. Curr Opin Pediatr 24:191–196
Silveira RC, Procianoy RS (2015) Hypothermia therapy for newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr 91:78–83
Zappitelli M, Ambalavanan N, Askenazi DJ, Moxey-Mims MM, Kimmel PL, Star RA et al (2017) Developing a neonatal acute kidney injury research definition: a report from the NIDDK neonatal AKI workshop. Pediatr Res 82:569–573
Kariholu U, Montaldo P, Markati T, Lally PJ, Pryce R, Teiserskas J et al (2020) Therapeutic hypothermia for mild neonatal encephalopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 105:225–228
Cavallin F, Rubin G, Vidal E, Cainelli E, Bonadies L, Suppiej A et al (2020) Prognostic role of acute kidney injury on long-term outcome in infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Nephrol 35:477–483
Robertsson Grossmann K, Bárány P, Blennow M, Chromek M (2022) Acute kidney injury in infants with hypothermia-treated hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy: An observational population-based study. Acta Paediatr 111:86–92
Kirkley MJ, Boohaker L, Griffin R, Soranno DE, Gien J, Askenazi D, Neonatal Kidney Collaborative (NKC) et al (2019) Acute kidney injury in neonatal encephalopathy: an evaluation of the AWAKEN database. Pediatr Nephrol 34:169–176
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (2013) Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). https://www.ahrq.gov/data/hcup/index.html. Accessed 31 January 2021
Devarajan P (2006) Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1503–1520
Bienholz A, Walter B, Pless-Petig G, Guberina H, Kribben A, Witzke O et al (2017) Characterization of injury in isolated rat proximal tubules during cold incubation and rewarming. PLoS One 12:e0180553
Santos EB, Koff WJ, Grezzana Filho Tde J, De Rossi SD, Treis L, Bona SR et al (2013) Oxidative stress evaluation of ischemia and reperfusion in kidneys under various degrees of hypothermia in rats. Acta Cir Bras 28:568–573
Sarkar S, Askenazi DJ, Jordan BK, Bhagat I, Bapuraj JR, Dechert RE, Selewski DT (2014) Relationship between acute kidney injury and brain MRI findings in asphyxiated newborns after therapeutic hypothermia. Pediatr Res 75:431–435
Steflik HJ, Charlton JR, Briley M, Selewski DT, Gist KM, Hanna MH, Neonatal Kidney Collaborative et al (2023) Neonatal nephrotoxic medication exposure and early acute kidney injury: results from the AWAKEN study. J Perinatol 43:1029–1037
Parker SJ, Kuzniewicz M, Niki H, Wu YW (2018) Antenatal and intrapartum risk factors for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in a US birth cohort. J Pediatr 203:163–169
Podymow T, August P (2008) Update on the use of antihypertensive drugs in pregnancy. Hypertension 51:960–969
Gungor O, Aydin Z, Inci A, Oguz EG, Arici M (2023) Seizures in patients with kidney diseases: a neglected problem? Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:291–299
Greco P, Nencini G, Piva I, Scioscia M, Volta CA, Spadaro S, Neri M et al (2020) Pathophysiology of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review of the past and a view on the future. Acta Neurol Belg 120:277–288
Rumpel JA, Spray BJ, Frymoyer A, Rogers S, Cho SH, Ranabothu S et al (2023) Renal oximetry for early acute kidney injury detection in neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy receiving therapeutic hypothermia. Pediatr Nephrol 38:2839–2849
Funding
Authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Drs. Elgendy, Mohamed, and Aly participated in the conception and design of the work, including the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the statistical analyses, drafting the initial manuscript, and reviewing and revising the manuscript. They coordinated, supervised data collection, and critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content.
Drs. Cortez, Saker, and Acun conceptualized and designed the study, carried out the initial analyses, drafted the work, and critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. Dr. Bou Matar reviewed the results and statistical work; he critically reviewed, edited, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not required.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Informed consent for participants
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
No conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Mohamed A. Mohamed and Hany Aly have joint senior authorship.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Elgendy, M.M., Cortez, J., Saker, F. et al. Acute kidney injury in infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Nephrol 39, 1271–1277 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-023-06214-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-023-06214-3