Abstract
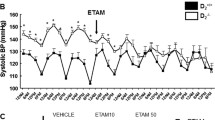
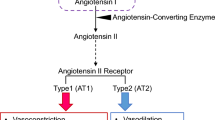
Renalase is an amine oxidase expressed in kidney, heart, liver, and brain that metabolizes catecholamines. Tissue and plasma levels are decreased in models of hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Its expression is modulated by salt intake, and urinary renalase may regulate catecholamines levels and effect renal sodium and phosphate transport. The renalase knockout mouse is hypertensive in the absence of significant changes in renal function. Sympathetic tone is increased as evidenced by elevated plasma and urine catecholamines. Studies in humans with resistant hypertension indicate that plasma renalase levels are inversely associated with systolic blood pressure. Additionally, a functional mutation in renalase (Glu37Asp), known to be associated with essential hypertension, also predicts more severe cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction. Lastly, a single dose of recombinant renalase administered subcutaneously to rats with chronic kidney disease or to Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke Prone rats significantly decreases blood pressure for more than 24 h. Available data suggest that renalase deficiency is associated with increased sympathetic tone and resistant hypertension, and recombinant renalase is a potent antihypertensive agent that may provide a valuable option for treating hypertension in chronic kidney disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oberg BP, McMenamin E, Lucas FL, McMonagle E, Morrow J, Ikizler TA, Himmelfarb J (2004) Increased prevalence of oxidant stress and inflammation in patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 65:1009–1016
Koomans HA, Blankestijn PJ, Joles JA (2004) Sympathetic hyperactivity in chronic renal failure: a wake-up call. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:524–537
Hostetter TH (2004) Chronic kidney disease predicts cardiovascular disease. N Eng J Med 351:1344–1346
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY (2004) Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Eng J Med 351:1296–1305
Anavekar NS, McMurray JJ, Velazquez EJ, Solomon SD, Kober L, Rouleau JL, White HD, Nordlander R, Maggioni A, Dickstein K, Zelenkofske S, Leimberger JD, Califf RM, Pfeffer MA (2004) Relation between renal dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes after myocardial infarction. N Eng J Med 351:1285–1295
Go AS, Lo JC (2006) Epidemiology of non-dialysis-requiring chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15:296–302
Schlaich MP, Socratous F, Hennebry S, Eikelis N, Lambert EA, Straznicky N, Esler MD, Lambert GW (2009) Sympathetic activation in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:933–939
Xu J, Li G, Wang P, Velazquez H, Yao X, Li Y, Wu Y, Peixoto A, Crowley S, Desir GV (2005) Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. J Clin Invest 115:1275–1280
Desir GV (2009) Regulation of blood pressure and cardiovascular function by renalase. Kidney Int 76:366–370
Hennebry SC, Eikelis N, Socratous F, Desir G, Lambert G, Schlaich M (2010) Renalase, a novel soluble FAD-dependent protein, is synthesized in the brain and peripheral nerves. Mol Psychiatry 15:234–236
Feng W, Nian-song W, Tao X, Yang C, Hai-yan X (2009) The cloning and expression of renalase and the preparation of its monoclonal antibody. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ Sci 14:376–379
Li G, Xu J, Wang P, Velazquez H, Li Y, Wu Y, Desir GV (2008) Catecholamines regulate the activity, secretion, and synthesis of renalase. Circulation 117:1277–1282
Wang J, Qi S, Cheng W, Li L, Wang F, Li YZ, Zhang SP (2008) Identification, expression and tissue distribution of a renalase homologue from mouse. Mol Biol Rep 35:613–620
Boomsma F, Tipton KF (2007) Renalase, a catecholamine-metabolising enzyme? J Neural Transm 114:775–776
Desir G, Wang P, Velazquez H (2009) On the mechanisms mediating the cardioprotective effect of renalase. J Am Soc Nephrol Abstracts Issue 20:2009. Accessed online at http://www.asn-online.org/education_and_meetings/renal_week/archives/
Farzaneh-Far RM, Desir GV, Schiller NB, Whooley MA (2010) A functional mutation in renalase (Glu37Asp) is associated with cardiac hypertrophy, dysfunction, and ischemia: data from the Heart and Soul Study. PLoS ONE 5(10):e13496
Desir GV (2008) Renalase deficiency in chronic kidney disease, and its contribution to hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:181–185
Wang F, N-s W, Xing T, Cao Y, H-y X (2009) The cloning and expression of renalase and the preparation of its monoclonal antibody. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ Sci 14:376–379
Schlaich M, Socratous F, Eikelis N, Chopra R, Lambert G, Hennebry S (2010) Renalase plasma levels are associated with systolic blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension: 9C.01. J Hypertens 28:e437 410.1097/1001.hjh.0000379519.0000382971.0000379502
Xu B, Gu R (2010) Renalase deficiency in heart failure: a novel mechanism underlying circulating norepinephrine accumulation. European Society of Cardiology Congress Accessed online at http://spo.escardio.org/eslides/view.aspx?eevtid=40&fp=P2485
Pestana M, Sampaio-Maia B, Moreira-Rodrigues M, Fernandes-Cerqueira C, Quelhas-Santos J (2009) Expression of renalase in a 3/4 nephrectomy rat model. NDT Plus 2:ii55-
Ghosh SS, Gehr TWB, Sica DA, Masilamani S, Fakhry I, Wang R, McGuire E, Ghosh S (2006) Renalase regulates blood pressure in salt sensitive Dahl rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:208A
Wu Y, Velazquez H, Xu J, Wang P, Li G, Liu D, Sampaio-Maia B, Quelhas-Santos J, Russell K, Russell R, Flavell R, Pestana M, Giordano G, Desir G (2010) Renalase deficiency aggravates ischemic myocardial damage. Kidney Int. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.488
Desir GV, Wu Y, Wang P, Xu J, Velazquez H (2008) Renalase deficiency increases sympathetic tone and causes hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol Abstracts Issue 2008. Accessed online at http://www.asn-online.org/education_and_meetings/renal_week/archives/
Desir G, Giordano F, Liu D, Wu Y (2009) Renalase deficiency aggravates cardiac ischemia and myocardial infarction. NDT Plus 2:ii55
Carey RM (2001) Theodore cooper lecture: renal dopamine system: paracrine regulator of sodium homeostasis and blood pressure. Hypertension 38:297–302
Greger R (2000) Physiology of renal sodium transport. Am J Med Sci 319:51–62
Pestana M, Jardim H, Correia F, Vieira-Coelho MA, Soares-da-Silva P (2001) Renal dopaminergic mechanisms in renal parenchymal diseases and hypertension. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16(Suppl 1):53–59
Ferreira A, Bettencourt P, Pimenta J, Frioes F, Pestana M, Soares-da-Silva P, Cerqueira-Gomes M (2002) The renal dopaminergic system, neurohumoral activation, and sodium handling in heart failure. Am Heart J 143:391–397
Ferro A (2003) Renal dopamine receptors and hypertension. J Hypertens 21:37–38
Jose PA, Eisner GM, Felder RA (2003) Dopamine and the kidney: a role in hypertension? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12:189–194
Wilk S, Mizoguchi H, Orlowski M (1978) gamma-Glutamyl dopa: a kidney-specific dopamine precursor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 206:227–232
Wang ZQ, Way D, Shimizu K, Fong F, Trigg L, McGrath BP (1993) Beneficial acute effects of selective modulation of renal dopamine system by gamma-L-glutamyl-L-dopa in rabbits with congestive heart failure. J Cardiovas Pharmacol 21:1004–1011
Barthelmebs M, Caillette A, Ehrhardt JD, Velly J, Imbs JL (1990) Metabolism and vascular effects of gamma-L-glutamyl-L-dopa on the isolated rat kidney. Kidney Int 37:1414–1422
Cummings J, Matheson LM, Maurice L, Smyth JF (1990) Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, metabolism, tissue distribution and urinary excretion of gamma-L-glutamyl-L-dopa in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 42:242–246
Worth DP, Harvey JN, Brown J, Lee MR (1985) gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-dopa is a dopamine pro-drug, relatively specific for the kidney in normal subjects. Clin Sci Lond 69:207–214
MacDonald TM, Jeffrey RF, Lee MR (1989) The renal and haemodynamic effects of a 10 h infusion of glutamyl-L-dopa in normal man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 27:811–822
Seri I, Kone BC, Gullans SR, Aperia A, Brenner BM, Ballermann BJ (1990) Influence of Na+ intake on dopamine-induced inhibition of renal cortical Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. Am J Physiol 258:F52–F60
Oates NS, Ball SG, Perkins CM, Lee MR (1979) Plasma and urine dopamine in man given sodium chloride in the diet. Clin Sci Lond 56:261–264
Soares-da-Silva P (1993) Enhanced protein kinase C mediated inhibition of renal dopamine synthesis during high sodium intake. Biochem Pharmacol 45:1791–1800
Chan YL (1976) Cellular mechanisms of renal tubular transport of I-dopa and its derivatives in the rat: microperfusion studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199:17–24
Sampaio-Maia B, Serrao P, Guimaraes JT, Vieira-Coelho MA, Pestana M (2005) Renal dopaminergic system activity in the rat remnant kidney. Nephron Exp Nephrol 99:e46–e55
Sampaio-Maia B, Moreira-Rodrigues M, Pestana M (2006) Role of chronic inhibition of dopamine-metabolizing enzymes in the regulation of renal sodium and phosphate excretion in the rat remnant kidney. Nephron Physiol 103:p14–p24
Desir G, Tang L, Wang P, Li G, Velazquez H (2010) Antihypertensive effect of recombinant renalase in spontaneously hypertensive stroke prone (SHRSP) Rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:748A
Zhao Q, Fan Z, He J, Chen S, Li H, Zhang P, Wang L, Hu D, Huang J, Qiang B, Gu D (2007) Renalase gene is a novel susceptibility gene for essential hypertension: a two-stage association study in northern Han Chinese population. J Mol Med 85:877–885
Farzaneh-Far R, Desir GV, Na B, Schiller NB, Whooley MA (2010) A functional polymorphism in renalase (Glu37Asp) is associated with cardiac hypertrophy, dysfunction, and ischemia: data from the heart and soul study. PLoS ONE 5:e13496
Acknowledgements
Support from NIH (1R01DK081037, 1RC1DK086402, 1RC1DK086465)
Conflicts of interest
Gary V Desir: Inventor of patent #US 7,700,095 B2: “Detection, Isolation and Uses of Renalase (Monoamine Oxidase C).”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desir, G. Novel insights into the physiology of renalase and its role in hypertension and heart disease. Pediatr Nephrol 27, 719–725 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1828-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1828-7