Abstract
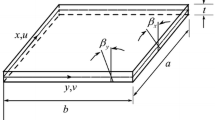
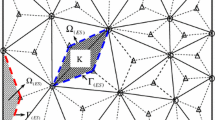
In this paper, a node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) using 3-node triangular elements is formulated for static, free vibration and buckling analyses of Reissner–Mindlin plates. The discrete weak form of the NS-FEM is obtained based on the strain smoothing technique over smoothing domains associated with the nodes of the elements. The discrete shear gap (DSG) method together with a stabilization technique is incorporated into the NS-FEM to eliminate transverse shear locking and to maintain stability of the present formulation. A so-called node-based smoothed stabilized discrete shear gap method (NS-DSG) is then proposed. Several numerical examples are used to illustrate the accuracy and effectiveness of the present method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leissa AW (1987) Plate vibration research: 1981–1985: classical theory. Shock Vib Dig 19: 11–18
Leissa AW (1987) A review of laminated composite plate buckling. Appl Mech Rev 40: 575–591
Liew KM, Xiang Y, Kitipornchai S (1995) Research on thick plate vibration: a literature survey. J Sound Vib 180: 163–176
Mackerle J (1997) Finite element linear and nonlinear, static and dynamic analysis of structural elements: a bibliography (1992–1995). Eng Comput 14: 347–440
Mackerle J (2002) Finite element linear and nonlinear, static and dynamic analysis of structural elements: a bibliography (1999–2002). Eng Comput 19: 520–594
Zienkiewicz OC, Lefebvre D (1988) A robust triangular plate bending element of the ReissnerMindlin type. Int J Numer Methods Eng 26: 1169–1184
Ayad R, Dhatt G, Batoz JL (1998) A new hybrid-mixed variational approach for ReissnerMindlin plate. Int J Numer Methods Eng 42: 1149–1179
Lovadina C (1998) Analysis of a mixed finite element method for the ReissnerMindlin plate problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 163: 71–85
Taylor RL, Auricchio F (1993) Linked interpolation for Reissner–Mindlin plate element: Part II-A simple triangle. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 3043–3056
Belytschko T, Tsay CS (1983) A stabilization procedure for the quadrilateral plate element with one-point quadrature. Int J Numer Meth Eng 19: 405–419
Belytschko T, Leviathan I (1992) Physical stabilization of the 4-node shell element with one-point quadrature. Comput Meth Appl Mech Eng 113: 321–350
Simo JC, Rifai MS (1990) A class of mixed assumed strain methods and the method of incompatible modes. Int J Numer Methods Eng 29: 1595–1638
César de Sá JMA, Natal Jorge RM (1999) New enhanced strain elements for incompatible problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 44: 229–248
Bathe KJ, Dvorkin EN (1985) A four-node plate bending element based on Mindlin–Reissener plate theory and a mixed interpolation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 21: 367–383
Tessler A, Hughes TJR (1985) A three-node Mindlin plate element with improved transverse shear. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 50: 71–101
César de Sá JMA, Natal Jorge RM, Fontes Valente RA, Areias PMA (2002) Development of shear locking-free shell elements using an enhanced assumed strain formulation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 53: 1721–1750
Cardoso RPR, Yoon JW, Mahardika M, Choudhry S, Alvesde Sousa RJ, Fontes Valente RA (2008) Enhanced assumed strain (EAS) and assumed natural strain (ANS) methods for one-point quadrature solid-shell elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 75: 156–187
Bletzinger KU, Bischoff M, Ramm E (2000) A unified approach for shear-locking free triangular and rectangular shell finite elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 75: 321–334
Chen JS, Wu CT, Yoon S, You Y (2001) A stabilized conforming nodal integration for Galerkin mesh-free methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50: 435–466
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T, Xiao SP (2004) Stable particle methods based on lagrangian kernels. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193: 1035–1063
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T (2005) Adaptivity for structured meshfree particle methods in 2D and 3D. Int J Numer Methods Engineering 63(11): 1559–1582
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T (2004) Cracking particles: a simplified meshfree method for arbitrary evolving cracks. Int J Numer Methods Engineering 61(13): 2316–2343
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T (2007) A three dimensional large deformation meshfree method for arbitrary evolving cracks. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196(29–30): 2777–2799
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T (2006) Application of meshfree particle methods to static fracture of reinforced concrete structures. Int J Fract 137(1-4): 19–49
Rabczuk T, Areias PMA, Belytschko T (2007) A simplified meshfree method for shear bands with cohesive surfaces. Int J Numer Methods Eng 69(5): 993–1021
Rabczuk T, Bordas S, Zi G (2007) A three dimensional meshfree method for static and dynamic multiple crack nucleation/propagation with crack path continuity. Comput Mech 40(3): 473–495
Rabczuk T, Zi G (2007) A meshfree method based on the local partition of unity for cohesive cracks. Comput Mech 39(6): 743–760
Liu GR, Dai KY, Nguyen TT (2007) A smoothed element method for mechanics problems. Comput Mech 39: 859–877
Liu GR, Nguyen TT, Dai KY, Lam KY (2007) Theoretical aspects of the smoothed finite element method (SFEM). Int J Numer Methods Eng 71: 902–930
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Dai KY, Lam KY (2009) On the essence and the evaluation of the shape functions for the smoothed finite element method (sfem) (letter to editor). Int J Numer Methods Eng 77: 1863–1869
Nguyen-Xuan H, Bordas S, Nguyen-Dang H (2008) Smooth finite element methods: convergence, accuracy and properties. Int J Numer Methods Eng 74: 175–208
Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thoi T (2010) A theoretical study on NS/ES-FEM: properties, accuracy and convergence rates. Int J Numer Methods Eng (in press). doi:10.1002/nme.2941
Dai KY, Liu GR, Nguyen TT (2007) An n-sided polygonal smoothed finite element method (nSFEM) for solid mechanics. Finite Elements Anal Des 43: 847–860
Dai KY, Liu GR (2007) Free and forced vibration analysis using the smoothed finite element method (SFEM). J Sound Vib 301: 803–820
Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thoi T (2008) A stabilized smoothed finite element method for free vibration analysis of Mindlin– Reissner plates. Commun Numer Methods Eng (in press). doi:10.1002/cnm.1137
Nguyen-Xuan H, Rabczuk T, Bordas S, Debongnie JF (2008) A smoothed finite element method for plate analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197: 1184–1203
Nguyen-Thanh N, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Bordas S (2008) A smoothed finite element method for shell analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198: 165–177
Le CV, Nguyen-Xuan H, Askes H, Bordas S, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Vinh H (2010) A cell-based smoothed finite element method for kinematic limit analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng (in press). doi:10.1002/nme.2897
Bordas S, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen Vinh P, Natarajan S, Bog T, Do Minh Q, Nguyen Vinh H (2008) Strain smoothing in FEM and XFEM. Comput Struct (in press). doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2008.07.006
Liu GR (2010) A G space theory and a weakened weak (W 2) form for a unified formulation of compatible and incompatible methods: Part I theory and Part II applications to solid mechanics problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 81:1093–1156
Liu GR (2008) A generalized gradient smoothing technique and the smoothed bilinear form for Galerkin formulation of a wide class of computational methods. Int J Comput Methods 2: 199–236
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Lam KY (2009) A node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) for upper bound solutions to solid mechanics problems. Comput Struct 87: 14–26
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H (2009) Additional properties of the node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) for solid mechanics problems. Int J Comput Methods 6: 633–666
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Lam KY (2009) An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for static, free and forced vibration analyses of solids. J Sound Vib 320: 1100–1130
Nguyen-Xuan H, Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Nguyen-Tran C (2009) An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for analysis of two-dimensional piezoelectric structures. Smart Mater Struct 18: 065015
Nguyen-Xuan H, Liu GR, Thai-Hoang C, Nguyen-Thoi T (2010) An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner–Mindlin plates. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199: 471–489
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Vu-Do HC, Nguyen-Xuan H (2009) An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for visco-elastoplastic analyses in 2d solids using triangular mesh. Comput Mech 45: 23–44
Tran TN, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thoi T (2010) An edge-based smoothed finite element method for primal-dual shakedown analysis of structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82: 917–938
Cui X, Liu GR, Li G, Zhang GY, Zheng G (2010) Analysis of plates and shells using an edge-based smoothed finite element method. Comput Mech 45: 141–156
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Lam KY, Zhang GY (2009) A face-based smoothed finite element method (FS-FEM) for 3d linear and nonlinear solid mechanics problems using 4-node tetrahedral elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 78: 324–353
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Vu-Do HC, Nguyen-Xuan H (2009) A face-based smoothed finite element method (FS-FEM) for visco- elastoplastic analyses of 3d solids using tetrahedral mesh. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 198: 3479–3498
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Tran C (2009) Adaptive analysis using the node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM). Commun Numer Methods Eng (in press). doi:10.1002/cnm.1291
Zhang ZQ, Liu GR (2010) Temporal stabilization of the node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) and solution bound of linear elastostatics and vibration problems. Comput Mech (in press). doi:10.1007/s00466-009-0420-5
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Lam KY (2008) A novel alpha finite element method (αFEM) for exact solution to mechanics problems using triangular and tetrahedral elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197: 3883–3897
Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thoi T, Xu X (2009) A novel Galerkin-like weakform and a superconvergent alpha finite element method (SαFEM) for mechanics problems using triangular meshes. J Comput Phys 228: 4055–4087
Nguyen-Thanh N, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Bordas S (2010) An alternative alpha finite element method (Aαfem) free and forced vibration analysis of solids using triangular meshes. J Comput Appl Math 223(9): 2112–2135
Thompson LL (2003) On optimal stabilized mitc4 plate bending elements for accurate frequency response analysis. Comput Struct 81: 995–1008
Liew KM, Wang J, Ng TY, Tan MJ (2004) Free vibration and buckling analyses of shear-deformable plates based on FSDT meshfree method. J Sound Vib 276: 997–1017
Lyly M, Stenberg R, Vihinen T (1993) A stable bilinear element for the Rissnerindlin plate model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 110: 343–357
Bischoff M, Bletzinger KU (2001) Stabilized dsg plate and shell elements. Trends in computational structural mechanics, CIMNE, Barcelona, Spain
Bonet J, Burton AJ (1998) A simple average nodal pressure tetrahedral element for incompressible and nearly incompressible dynamic explicit applications. Commun Numer Methods Eng 14: 437–449
Dohrmann CR, Heinstein MW, Jung J, Key SW, Witkowski WW (2000) Node-based uniform strain elements for three-node triangular and four-node tetrahedral meshes. Int J Numer Methods Eng 47: 1549–1568
Bonet J, Marriott H, Hassan O (2001) An averaged nodal deformation gradient linear tetrahedral element for large strain explicit dynamic applications. Commun Numer Methods Eng 17: 551–561
Pires FMA, Neto EAD, Padilla JLD (2004) An assessment of the average nodal volume formulation for the analysis of nearly incompressible solids under finite strains. Commun Numer Methods Eng 20: 569–583
Puso MA, Solberg J (2006) A stabilized nodally integrated tetrahedral. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 67: 841–867
Gee MW, Dohrmann CR, Key SW, Wall WA (2008) A uniform nodal strain tetrahedron with isochoric stabilization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 78: 429–443
Krysl P, Zhu B (2008) Locking-free continuum displacement finite elements with nodal integration International. J Numer Methods Eng 76: 1020–1043
Castellazzi G, Krysl P (2009) Displacement-based finite elements with nodal integration for Reissner–Mindlin plates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 80: 135–162
Zienkiewicz OC, Xu Z, Zeng LX, Samuelsson A, Wiberg NE (1993) Linked interpolation for Reissner–Mindlin plate elements: part I-a simple quadrilateral. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 3043–3056
Katili I (1993) A new discrete Kirchhoff–Mindlin element based on Mindlin-Reissner plate theory and assumed shear strain fields-part II: an extended DKQ element for thick-plate bending analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 1885–1908
Lee SJ (2004) Free vibration analysis of plates by using a four-node finite element formulated with assumed natural transverse shear strain. J Sound Vib 278: 657–684
Lee SJ, Han SE (2001) Free-vibration analysis of plates and shells with a nine-node assumed natural degenerated shell element. J Sound Vib 241: 605–633
Liew KM, Chen XL (2004) Buckling of rectangular Mindlin plates subjected to partial in-plane edge loads using the radial point interpolation method. Int J Solids Struct 41: 1677–1695
Karunasena W, Kitipornchai S, Al-bermani FGA (1996) Free vibration of cantilevered arbitrary triangular mindlin plates. Int J Mech Sci 38: 431–442
Morley LSD (1963) Skew plates and structures. Pergamon Press, NY
Abbassian F, Dawswell DJ, Knowles NC (1987) Free vibration benchmarks. Technical report Softback, 40 pp, Atkins Engineering Sciences, Glasgow, UK
Leissa AW (1969) Vibration of plates. NASA, SP-160. Washington, DC
Irie T, Yamada G, Aomura S (1980) Natural frequencies of mindlin circular plates. Appl Mech 47: 652–655
McGee OG, Leissa AW, Huang CS (1992) Vibrations of cantilevered skewed trapezodial and triangular plates with corner stress singularities. Mech Sci 34: 63–84
Timoshenko SP, Gere JM (1970) Theory of elastic stability, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kitipornchai S, Xiang Y, Wang CM, Liew KM (1993) Buckling of thick skew plates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 1299–1310
Tham LG, Szeto HY (1990) Buckling analysis of arbitrary shaped plates by spline finite strip method. Comput Struct 36: 729–735
Azhari M, Hoshdar S, Bradford MA (2000) On the use of bubble functions in the local buckling analysis of plate structures by the spline finite strip method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 48: 583–593
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen-Xuan, H., Rabczuk, T., Nguyen-Thanh, N. et al. A node-based smoothed finite element method with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner–Mindlin plates. Comput Mech 46, 679–701 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0509-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0509-x