Abstract
Introduction
Endoscopic plication offers an alternative to surgical fundoplication for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluate outcomes following endoscopic plication compared to laparoscopic fundoplication.
Methods and procedures
Systematic search of MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science was conducted in September 2022. Study followed PRISMA guidelines. Studies comparing endoscopic plication to laparoscopic fundoplication with n > 5 were included. Primary outcome was PPI cessation, with secondary outcomes including complications, procedure duration, length of stay, change in lower esophageal sphincter (LES) tone, and DeMeester score.
Results
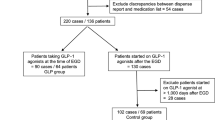
We reviewed 1544 studies, with five included comparing 105 (46.1%) patients receiving endoscopic plication (ENDO) to 123 (53.9%) undergoing laparoscopic fundoplication (LAP). Average patient age was 47.6 years, with those undergoing plication being younger (46.4 ENDO vs 48.5 LAP). BMI (26.6 kg/m2 ENDO vs 26.2 kg/m2 LAP), and proportion of females (42.9% ENDO vs 37.4% LAP) were similar. Patients undergoing laparoscopic procedures had worse baseline LES pressure (12.8 mmHg ENDO vs 9.0 mmHg LAP) and lower preoperative DeMeester scores (34.6 ENDO vs. 34.1 LAP). The primary outcome demonstrated that 89.2% of patients undergoing laparoscopic fundoplication discontinued PPI compared to 69.4% for those receiving plication. Meta-analysis revealed that plication had significantly reduced odds of PPI discontinuation (OR 0.27, studies = 3, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.64, P = 0.003, I2 = 0%). Secondary outcomes demonstrated that odds of complications (OR 1.46, studies = 4, 95% CI 0.34 to 6.32, P = 0.62, I2 = 0%), length of stay (MD − 1.37, studies = 3, 95% CI − 3.48 to 0.73, P = 0.20, I2 = 94%), and procedure durations were similar (MD 0.78, studies = 3, 95% CI − 39.70 to 41.26, P = 0.97, I2 = 98%).
Conclusions
This is the first meta-analysis comparing endoscopic plication to laparoscopic fundoplication. Results demonstrate greater likelihood of PPI discontinuation with laparoscopic fundoplication with similar post-procedural risk.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richter JE, Rubenstein JH (2018) Presentation and epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 154(2):267–276. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.045
Katz PO, Dunbar KB, Schnoll-Sussman FH, Greer KB, Yadlapati R, Spechler SJ (2022) ACG clinical guideline for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol ACG 117(1):27. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001538
Marchese M, Spada C, Costamagna G (2006) Endoluminal fundoplication. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 15(6):356–365. https://doi.org/10.1080/13645700601040594
Bell RCW (2015) Randomized controlled trial of transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. proton pump inhibitors for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 110(11):1621–1623. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2015.324
Kahrilas P, Hunter J, Bell R et al (2014) Transoral fundoplication provides better GERD symptom control than PPIs in patients with troublesome regurgitation: a multicenter sham-controlled randomized clinical trial. Am J Gastroenterol 109:S13–S13
Kaindlstorfer A, Koch OO, Antoniou SA, Asche KU, Granderath FA, Pointner R (2013) A randomized trial on endoscopic full-thickness gastroplication versus laparoscopic antireflux surgery in GERD patients without hiatal hernias. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 23(2):212–222. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLE.0b013e3182827f79
Trad KS, Barnes WE, Simoni G et al (2015) Transoral incisionless fundoplication effective in eliminating GERD symptoms in partial responders to proton pump inhibitor therapy at 6 months: the TEMPO Randomized Clinical Trial. Surg Innov 22(1):26–40. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350614526788
Lee DP, Chang KJ (2022) Endoscopic management of GERD. Dig Dis Sci 67(5):1455–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-022-07390-2
Rinsma NF, Smeets FG, Bruls DW et al (2014) Effect of transoral incisionless fundoplication on reflux mechanisms. Surg Endosc 28(3):941–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3250-7
Chen D, Barber C, McLoughlin P, Thavaneswaran P, Jamieson GG, Maddern GJ (2009) Systematic review of endoscopic treatments for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 96(2):128–136. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.6440
Falk GW, Fennerty MB, Rothstein RI (2006) AGA institute technical review on the use of endoscopic therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 131(4):1315–1336. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.019
Galmiche JP, Bruley des Varannes S (2003) Endoluminal therapies for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet Lond Engl. 361(9363):1119–1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)12889-9
Swain CP, Mills TN (1986) An endoscopic sewing machine. Gastrointest Endosc 32(1):36–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5107(86)71727-6
Richter JE, Kumar A, Lipka S, Miladinovic B, Velanovich V (2018) Efficacy of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication vs transoral incisionless fundoplication or proton pump inhibitors in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 154(5):1298-1308.e7. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.12.021
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group TP (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283(15):2008–2012. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Haddaway NR, Collins AM, Coughlin D, Kirk S (2015) The role of Google Scholar in evidence reviews and its applicability to grey literature searching. PLoS One 10(9):e0138237. https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.proxy.queensu.ca/26379270/. Accessed 3 Feb 2023
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73(9):712–716. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
Khan W, Khan M, Alradwan H, Williams R, Simunovic N, Ayeni OR (2015) Utility of intra-articular hip injections for femoroacetabular impingement: a systematic review. Orthop J Sports Med 3(9):2325967115601030. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967115601030
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366:14898. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T (2014) Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol 14(1):135. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
Higgins JPT (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Danalioglu A, Cipe G, Toydemir T et al (2014) Endoscopic stapling in comparison to laparoscopic fundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Endosc 26(1):37–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.12081
Mahmood Z, Byrne PJ, McMahon BP et al (2006) Comparison of transesophageal endoscopic plication (TEP) with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication (LNF) in the treatment of uncomplicated reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 101(3):431–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00534.x
Frazzoni M, Conigliaro R, Manta R, Melotti G (2011) Reflux parameters as modified by EsophyX or laparoscopic fundoplication in refractory GERD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34(1):67–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04677.x
Ramai D, Shapiro A, Barakat M et al (2022) Adverse events associated with transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) for chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease: a MAUDE database analysis. Surg Endosc 36(7):4956–4959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08851-x
Toomey P, Teta A, Patel K, Ross S, Sukharamwala P, Rosemurgy AS (2014) Transoral incisionless fundoplication: is it as safe and efficacious as a Nissen or Toupet fundoplication? Am Surg 80(9):860–867
Imhann F, Bonder MJ, Vich Vila A et al (2016) Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 65(5):740–748. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310376
Masclee GMC, Coloma PM, Kuipers EJ, Sturkenboom MCJM (2015) Increased risk of microscopic colitis with use of proton pump inhibitors and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol ACG 110(5):749. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2015.119
Reimer C (2013) Safety of long-term PPI therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 27(3):443–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2013.06.001
Tran-Duy A, Spaetgens B, Hoes AW, de Wit NJ, Stehouwer CDA (2016) Use of proton pump inhibitors and risks of fundic gland polyps and gastric cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(12):1706-1719.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2016.05.018
Wassenaar EB, Oelschlager BK (2010) Effect of medical and surgical treatment of Barrett’s metaplasia. World J Gastroenterol WJG 16(30):3773–3779. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i30.3773
Achem AC, Achem SR, Stark ME, DeVault KR (2003) Failure of esophageal peristalsis in older patients: association with esophageal acid exposure. Am J Gastroenterol 98(1):35–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07188.x
Lee J, Anggiansah A, Anggiansah R, Young A, Wong T, Fox M (2007) Effects of age on the gastroesophageal junction, esophageal motility, and reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(12):1392–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2007.08.011
Ter RB, Johnston BT, Castell DO (1998) Influence of age and gender on gastroesophageal reflux in symptomatic patients. Dis Esophagus 11(2):106–108. https://doi.org/10.1093/dote/11.2.106
Furnée EJB, Broeders JAJL, Draaisma WA et al (2010) Symptomatic and objective results of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication after failed EndoCinch gastroplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(9):1118–1122. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0b013e328338c1f8
Perry KA, Linn JG, Eakin JL, Onders RP, Velanovich V, Melvin WS (2013) Transoral incisionless fundoplication does not significantly increase morbidity of subsequent laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 23(5):456–458. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2012.0525
Funding
No funding to be disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Alexander Hajjar, Kevin Verhoeff, Uzair Jogiat, Valentin Mocanu, Daniel W. Birch, Noah J. Switzer, Clarence Wong, and Shahzeer Karmali have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was exempt from ethics review.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hajjar, A., Verhoeff, K., Jogiat, U. et al. Endoscopic plication compared to laparoscopic fundoplication in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 37, 5791–5806 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10202-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10202-x