Abstract
Background
Left lateral sectionectomy (LLS) is one of the most commonly performed minimally invasive liver resections. While laparoscopic (L)-LLS is a well-established technique, over traditional open resection, it remains controversial if robotic (R)-LLS provides any advantages of L-LLS.
Methods
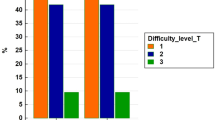
A post hoc analysis of 997 patients from 21 international centres undergoing L-LLS or R-LLS from 2006 to 2020 was conducted. A total of 886 cases (214 R-LLS, 672 L-LLS) met study criteria. 1:1 and 1:2 propensity score matched (PSM) comparison was performed between R-LLS & L-LLS. Further subset analysis by Iwate difficulty was also performed. Outcomes measured include operating time, blood loss, open conversion, readmission rates, morbidity and mortality.
Results
Comparison between R-LLS and L-LLS after PSM 1:2 demonstrated statistically significantly lower open conversion rate in R-LLS than L-LLS (0.6% versus 5%, p = 0.009) and median blood loss was also statistically significantly lower in R-LLS at 50 (80) versus 100 (170) in L-LLS (p = 0.011) after PSM 1:1 although there was no difference in the blood transfusion rate. Pringle manoeuvre was also found to be used more frequently in R-LLS, with 53(24.8%) cases versus to 84(12.5%) L-LLS cases (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in the other key perioperative outcomes such as operating time, length of stay, postoperative morbidity, major morbidity and 90-day mortality between both groups.
Conclusion
R-LLS was associated with similar key perioperative outcomes compared to L-LLS. It was also associated with significantly lower blood loss and open conversion rates compared to L-LLS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goh B, Lee SY, Teo JY, Kam JH, Jeyaraj PR, Cheow PC, Chow P, Ooi L, Chung A, Chan CY (2018) Changing trends and outcomes associated with the adoption of minimally invasive hepatectomy: a contemporary single-institution experience with 400 consecutive resections. Surg Endosc 32(11):4658–4665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6310-1
Goh B, Lee SY, Koh YX, Kam JH, Chan CY (2020) Minimally invasive major hepatectomies: a Southeast Asian single institution contemporary experience with its first 120 consecutive cases. ANZ J Surg 90(4):553–557. https://doi.org/10.1111/ans.15563
Salloum C, Lim C, Lahat E, Gavara CG, Levesque E, Compagnon P, Azoulay D (2017) Robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy: analysis of surgical outcomes and costs by a propensity score matched cohort study. World J Surg 41(2):516–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3736-2
Chin KM, Linn YL, Cheong CK, Koh YX, Teo JY, Chung A, Chan CY, Goh B (2022) Minimally invasive vs open major hepatectomies for liver malignancies: a propensity score-matched analysis. J Gastrointestinal Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-021-05226-4
Ocuin LM, Tsung A (2015) Robotic liver resection for malignancy: Current status, oncologic outcomes, comparison to laparoscopy, and future applications. J Surg Oncol 112(3):295–301. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.23901
Chua D, Syn N, Koh YX, Goh B (2021) Learning curves in minimally invasive hepatectomy: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Br J Surg 108(4):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjs/znaa118
Goh BK, Low TY, Teo JY, Lee SY, Chan CY, Chow PK, Chung AY, Ooi L (2020) Adoption of robotic liver, pancreatic and biliary surgery in singapore: a single institution experience with its first 100 consecutive cases. Ann Acad Med Singapore 49(10):742–748
Hu M, Liu Y, Li C, Wang G, Yin Z, Lau WY, Liu R (2019) Robotic versus laparoscopic liver resection in complex cases of left lateral sectionectomy. Int J Surg 67:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.05.008
Kim JK, Park JS, Han DH, Choi GH, Kim KS, Choi JS, Yoon DS (2016) Robotic versus laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy of liver. Surg Endosc 30(11):4756–4764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4803-3
Hajibandeh S, Hajibandeh S, Dosis A, Qayum MK, Hassan K, Kausar A, Satyadas T (2022) Level 2a evidence comparing robotic versus laparoscopic left lateral hepatic sectionectomy: a meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 407(2):479–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02366-8
Montalti R, Scuderi V, Patriti A, Vivarelli M, Troisi RI (2016) Robotic versus laparoscopic resections of posterosuperior segments of the liver: a propensity score-matched comparison. Surg Endosc 30(3):1004–1013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4284-9
Kadam P, Sutcliffe RP, Scatton O, Sucandy I, Kingham TP, Liu R, Choi GH, Syn NL, Gastaca M, Choi SH, Chiow A, Marino MV, Efanov M, Lee JH, Chong CC, Tang CN, Cheung TT, Pratschke J, Wang X, Campos RR, International Robotic and Laparoscopic Liver Resection Study Group Investigators (2022) An international multicenter propensity-score matched and coarsened-exact matched analysis comparing robotic versus laparoscopic partial liver resections of the anterolateral segments. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhbp.1149
Chong CC, Fuks D, Lee KF, Zhao JJ, Choi GH, Sucandy I, Chiow A, Marino MV, Gastaca M, Wang X, Lee JH, Efanov M, Kingham TP, D’Hondt M, Troisi RI, Choi SH, Sutcliffe RP, Chan CY, Lai E, Park JO, International Robotic and Laparoscopic Liver Resection study group investigators (2022) Propensity Score-Matched Analysis Comparing Robotic and Laparoscopic Right and Extended Right Hepatectomy. JAMA Surg. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2022.0161
Yang HY, Choi GH, Chin KM, Choi SH, Syn NL, Cheung TT, Chiow A, Sucandy I, Marino MV, Prieto M, Chong CC, Lee JH, Efanov M, Kingham TP, Sutcliffe RP, Troisi RI, Pratschke J, Wang X, D’Hondt M, Tang CN, International Robotic and Laparoscopic Liver Resection Study Group Investigators (2022) Robotic and laparoscopic right anterior sectionectomy and central hepatectomy: multicentre propensity score-matched analysis. Br J Surg 109(4):311–314. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjs/znab463
Chiow A, Fuks D, Choi GH, Syn N, Sucandy I, Marino MV, Prieto M, Chong CC, Lee JH, Efanov M, Kingham TP, Choi SH, Sutcliffe RP, Troisi RI, Pratschke J, Cheung TT, Wang X, Liu R, D’Hondt M, Chan CY, International Robotic and Laparoscopic Liver Resection Study Group collaborators (2021) International multicentre propensity score-matched analysis comparing robotic versus laparoscopic right posterior sectionectomy. Br J Surg 108(12):1513–1520. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjs/znab321
Lee MK 4th, Gao F, Strasberg SM (2015) Perceived complexity of various liver resections: results of a survey of experts with development of a complexity score and classification. J Am Coll Surg 220(1):64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.09.017
Liu Z, Ding H, Xiong X, Huang Y (2018) Laparoscopic left lateral hepatic sectionectomy was expected to be the standard for the treatment of left hepatic lobe lesions: a meta-analysis. Medicine 97(7):e9835. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000009835
Rao A, Rao G, Ahmed I (2011) Laparoscopic left lateral liver resection should be a standard operation. Surg Endosc 25(5):1603–1610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1459-2
Buell JF, Cherqui D, Geller DA, O’Rourke N, Iannitti D, Dagher I, Koffron AJ, Thomas M, Gayet B, Han HS, Wakabayashi G, Belli G, Kaneko H, Ker CG, Scatton O, Laurent A, Abdalla EK, Chaudhury P, Dutson E, Gamblin C, World Consensus Conference on Laparoscopic Surgery (2009) The international position on laparoscopic liver surgery: The Louisville Statement, 2008. Ann Surg 250(5):825–830. https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0b013e3181b3b2d8
Chang S, Laurent A, Tayar C, Karoui M, Cherqui D (2007) Laparoscopy as a routine approach for left lateral sectionectomy. Br J Surg 94(1):58–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.5562
Strasberg SM (2005) Nomenclature of hepatic anatomy and resections: a review of the Brisbane 2000 system. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 12(5):351–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-005-0999-7
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae
Ban D, Tanabe M, Ito H, Otsuka Y, Nitta H, Abe Y, Hasegawa Y, Katagiri T, Takagi C, Itano O, Kaneko H, Wakabayashi G (2014) A novel difficulty scoring system for laparoscopic liver resection. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21(10):745–753. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhbp.166
Tanaka S, Kawaguchi Y, Kubo S, Kanazawa A, Takeda Y, Hirokawa F, Nitta H, Nakajima T, Kaizu T, Kaibori M, Kojima T, Otsuka Y, Fuks D, Hasegawa K, Kokudo N, Kaneko H, Gayet B, Wakabayashi G (2019) Validation of index-based IWATE criteria as an improved difficulty scoring system for laparoscopic liver resection. Surgery 165(4):731–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2018.10.012
Austin PC (2011) An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivar Behav Res 46(3):399–424. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2011.568786
Montalti R, Berardi G, Patriti A, Vivarelli M, Troisi RI (2015) Outcomes of robotic vs laparoscopic hepatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 21(27):8441–8451. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8441
Daskalaki D, Gonzalez-Heredia R, Brown M, Bianco FM, Tzvetanov I, Davis M, Kim J, Benedetti E, Giulianotti PC (2017) Financial impact of the robotic approach in liver surgery: a comparative study of clinical outcomes and costs between the robotic and open technique in a single institution. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 27(4):375–382. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2016.0576
Acknowledgements
Collaborators for the International robotic and laparoscopic liver resection study group investigators: Chung-Yip Chan (Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary and Transplant Surgery, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore), Celine De Meyere (Department of Digestive and Hepatobiliary/Pancreatic Surgery, Groeninge Hospital, Kortrijk, Belgium), Diana Salimgereeva (Department of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery, Moscow Clinical Scientific Center, Moscow, Russia), Ruslan Alikhanov (Department of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery, Moscow Clinical Scientific Center, Moscow, Russia), Lip-Seng Lee (Hepatopancreatobiliary Unit, Department of Surgery, Changi General Hospital, Singapore), Jae Young Jang (Department of General Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea), Roberto Montalti (Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, Division of HPB, Minimally Invasive and Robotic Surgery, Federico II University Hospital Naples, Naples, Italy).
Funding
Dr T. P. Kingham was partially supported by the US National Cancer Institute MSKCC Core Grant number P30 CA008747 for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Dr Brian Goh has received travel grants and honorarium from Johnson and Johnson, Olympus and Transmedic the local distributor for the Da Vinci Robot. Dr Marco Marino is a consultant for CAVA robotics LLC. Johann Pratschke reports a research grant from Intuitive Surgical Deutschland GmbH and personal fees or non-financial support from Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, AFS Medical, Astellas, CHG Meridian, Chiesi, Falk Foundation, La Fource Group, Merck, Neovii, NOGGO, pharma-consult Peterson, and Promedicis. Moritz Schmelzle reports personal fees or other support outside of the submitted work from Merck, Bayer, ERBE, Amgen, Johnson & Johnson, Takeda, Olympus, Medtronic, Intuitive. Drs Chong Y, Prieto M, Gastaca M, Choi SH, Sucandy I, Chiow AK, Wang X, Efanov M, Schotte H, D’Hondt M, Choi GH, Krenzien F, Kingham TP, Giglio M, Troisi RI, Lee JH, Lai EC, Tang CN, Fuks D, D’Silva M, Han HS, Kadam P, Sutcliffe RP, Lee KF, Chong CC, Cheung TT, Liu Q and Liu R have no conflicts of interests and financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
International robotic and laparoscopic liver resection study group investigators are listed in acknowledgement section.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, Y., Prieto, M., Gastaca, M. et al. An international multicentre propensity score matched analysis comparing between robotic versus laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy. Surg Endosc 37, 3439–3448 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09790-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09790-x