Abstract
Background
The possible risk of colonic perforation during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for colorectal tumors is a barrier to wide application. This retrospective study was performed to evaluate the risk and the predictive factors for perforation during ESD procedure.
Methods
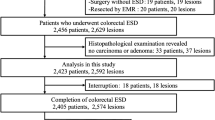
Between October 2006 and November 2010, a total of 499 consecutive patients (mean age 60.0 ± 11.3 years) who underwent ESD for large-sized (≥20 mm), nonpedunculated colorectal tumor were analyzed. First, incidence rate and clinical course of perforation were evaluated. Second, patient-related variables (age, sex, history of aspirin or antiplatelet agents, and comorbidity), endoscopic variables (tumor size, location, and type), procedure-related variables (experience of procedures, procedure time, and materials of submucosal injection), and pathologic diagnosis were analyzed.
Results
The mean size of the lesions was 28.9 mm. The overall en bloc resection rate was 95.0%. Perforation occurred in 37 out of 499 patients (7.4%). Thirty-four patients could be successfully treated conservatively. The type (laterally spreading tumor) and the location (right-sided colon) of the tumors, less experience of the procedure (<100 cases) in each endoscopist, and submucosal injection without hyaluronic acid were associated with higher frequency of perforation (all P < 0.05). On multivariate analysis, laterally spreading type of tumor [odds ratio (OR) 4.10, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.17–14.34] and submucosal injection with hyaluronic acid (OR 0.31, 95% CI 0.13–0.72) were independent predictive factors.
Conclusions
Perforation rate was 7.4%, and most cases could be successfully managed nonsurgically. In case of laterally spreading type of tumor, more caution is needed during submucosal dissection and long-lasting submucosal cushion is important for preventing perforation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saito Y, Fukuzawa M, Matsuda T, Fukunaga S, Sakamoto T, Uraoka T, Nakajima T, Ikehara H, Fu KI, Itoi T, Fujii T (2010) Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal tumors as determined by curative resection. Surg Endosc 24(2):343–352
Tanaka S, Haruma K, Oka S, Takahashi R, Kunihiro M, Kitadai Y, Yoshihara M, Shimamoto F, Chayama K (2001) Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm. Gastrointest Endosc 54(1):62–66
Tamegai Y, Saito Y, Masaki N, Hinohara C, Oshima T, Kogure E, Liu Y, Uemura N, Saito K (2007) Endoscopic submucosal dissection: a safe technique for colorectal tumors. Endoscopy 39(5):418–422
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Ono S, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2007) Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms in 200 consecutive cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(6):678–683 quiz 45
Tanaka S, Oka S, Kaneko I, Hirata M, Mouri R, Kanao H, Yoshida S, Chayama K (2007) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization. Gastrointest Endosc 66(1):100–107
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, Emura F, Ikehara H, Mashimo Y, Kikuchi T, Fu KI, Sano Y, Saito D (2007) Endoscopic treatment of large superficial colorectal tumors: a case series of 200 endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 66(5):966–973
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Yamaguchi Y, Hotta K, Sakamoto N, Ikematsu H, Fukuzawa M, Kobayashi N, Nasu J, Michida T, Yoshida S, Ikehara H, Otake Y, Nakajima T, Matsuda T, Saito D (2010) A prospective, multicenter study of 1111 colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72(6):1217–1225
Isomoto H, Nishiyama H, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda E, Ishii H, Ikeda K, Ohnita K, Nakao K, Kohno S, Shikuwa S (2009) Clinicopathological factors associated with clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy 41(8):679–683
Tanaka S, Oka S, Chayama K (2008) Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection: present status and future perspective, including its differentiation from endoscopic mucosal resection. J Gastroenterol 43(9):641–651
Schlemper RJ, Riddell RH, Kato Y, Borchard F, Cooper HS, Dawsey SM, Dixon MF, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Flejou JF, Geboes K, Hattori T, Hirota T, Itabashi M, Iwafuchi M, Iwashita A, Kim YI, Kirchner T, Klimpfinger M, Koike M, Lauwers GY, Lewin KJ, Oberhuber G, Offner F, Price AB, Rubio CA, Shimizu M, Shimoda T, Sipponen P, Solcia E, Stolte M, Watanabe H, Yamabe H (2000) The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Gut 47(2):251–255
Taku K, Sano Y, Fu KI, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Uraoka T, Yoshino T, Yamaguchi Y, Fujita M, Hattori S, Ishikawa T, Saito D, Fujii T, Kaneko E, Yoshida S (2007) Iatrogenic perforation associated with therapeutic colonoscopy: a multicenter study in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(9):1409–1414
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Nakamura M, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Ono S, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2006) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for rectal epithelial neoplasia. Endoscopy 38(5):493–497
Muto M, Miyamoto S, Hosokawa A, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Yoshida S, Endo Y, Hosokawa K, Saito D, Shim CS, Gossner L (2005) Endoscopic mucosal resection in the stomach using the insulated-tip needle-knife. Endoscopy 37(2):178–182
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Ono S, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2006) Successful nonsurgical management of perforation complicating endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy 38(10):1001–1006
Toyanaga T, Man IM, Ivanov D, Sanuki T, Morita Y, Kutsumi H, Inokuchi H, Azuma T (2008) The results and limitations of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors. Acta Chir Iugosl 55(3):17–23
Jeong G, Lee JH, Yu MK, Moon W, Rhee PL, Paik SW, Rhee JC, Kim JJ (2006) Non-surgical management of microperforation induced by EMR of the stomach. Dig Liver Dis 38(8):605–608
Yoshida N, Wakabayashi N, Kanemasa K, Sumida Y, Hasegawa D, Inoue K, Morimoto Y, Kashiwa A, Konishi H, Yagi N, Naito Y, Yanagisawa A, Yoshikawa T (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors: technical difficulties and rate of perforation. Endoscopy 41(9):758–761
Matsumoto A, Tanaka S, Oba S, Kanao H, Oka S, Yoshihara M, Chayama K (2010) Outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors accompanied by fibrosis. Scand J Gastroenterol 45(11):1329–1337
Yamamoto H, Kawata H, Sunada K, Satoh K, Kaneko Y, Ido K, Sugano K (2002) Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc 56(4):507–512
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kashimura K, Mizushima Y, Oka M, Enomoto S, Kakushima N, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Iguchi M, Shimizu Y, Ichinose M, Omata M (2004) Comparison of various submucosal injection solutions for maintaining mucosal elevation during endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy 36(7):579–583
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kashimura K, Matsuura T, Nakamura M, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Ono S, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y, Oka M, Ichinose M, Omata M (2005) Tissue damage of different submucosal injection solutions for EMR. Gastrointest Endosc 62(6):933–942
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Nakamura M, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Ono S, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2006) Successful outcomes of a novel endoscopic treatment for GI tumors: endoscopic submucosal dissection with a mixture of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and sugar. Gastrointest Endosc 63(2):243–249
Kita H, Yamamoto H, Miyata T, Sunada K, Iwamoto M, Yano T, Yoshizawa M, Hanatsuka K, Arashiro M, Omata T, Sugano K (2007) Endoscopic submucosal dissection using sodium hyaluronate, a new technique for en bloc resection of a large superficial tumor in the colon. Inflammopharmacology 15(3):129–131
Disclosures
Authors Eun-Jung Lee, Jae Bum Lee, Yong Sung Choi, Suk Hee Lee, Doo Han Lee, Do Sun Kim, and Eui Gon Youk have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, EJ., Lee, J.B., Choi, Y.S. et al. Clinical risk factors for perforation during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for large-sized, nonpedunculated colorectal tumors. Surg Endosc 26, 1587–1594 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-011-2075-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-011-2075-5