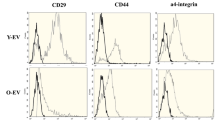
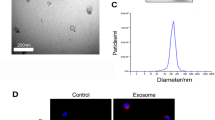
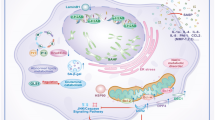
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a clinically common kidney disease. Age is an important factor that contributes to the susceptibility to AKI. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a promising therapy for AKI, and miRNAs in exosomes (Exos) derived from MSCs are an important aspect of MSC treatment. However, the therapeutic effect of miRNA from MSC-derived Exos on AKI and the related mechanism have not been fully clarified. Whether there is a relationship between the mechanisms of senescence for AKI susceptibility and the therapeutic effect of MSCs has not been studied. We compared the degree of cisplatin-induced AKI injury in young and elderly mice and investigated changes in the expression of p53 and markers of DNA damage and apoptosis, which are important in both senescence and AKI. Ageing mice exhibited increased expression of p53 and pro-apoptosis markers. Upregulation of the senescence-associated DNA damage/p53 pathway may be an important susceptibility factor for cisplatin-induced AKI. Treatment with MSCs can reduce the degree of DNA damage and suppress p53 expression and apoptosis. Upon screening for differentially expressed miRNAs, let-7b-5p levels were found to be lower in aged mice than in young mice, and MSC treatment increased let-7b-5p levels. The presence of let-7b-5p in MSC-derived Exos alleviates tubular epithelial cell apoptosis by inhibiting p53, which reduces DNA damage and apoptosis pathway activity. Let-7b-5p downregulation may lead to increased renal AKI susceptibility, thus indicating that this miRNA is a potential driver of the MSC treatment response in AKI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatt K, Mi QS, Dong Z (2011) microRNAs in kidneys: biogenesis, regulation, and pathophysiological roles. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300:F602-610
Che Q, Wang W, Duan P, Fang F, Liu C, Zhou T, Li H, Xiong C, Zhao K (2019) Downregulation of miR-322 promotes apoptosis of GC-2 cell by targeting Ddx3x. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology : RB&E 17:63
Chen Z, Su X, Shen Y, Jin Y, Luo T, Kim IM, Weintraub NL, Tang Y (2019) MiR322 mediates cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury via FBXW7/notch pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol 133:67–74
Docherty MH, O’Sullivan ED, Bonventre JV, Ferenbach DA (2019) Cellular senescence in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 30:726–736
Duan ZY, Liu JQ, Yin P, Li JJ, Cai GY, Chen XM (2018) Impact of aging on the risk of platinum-related renal toxicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev 69:243–253
Ferguson SW, Wang J, Lee CJ, Liu M, Neelamegham S, Canty JM, Nguyen J (2018) The microRNA Regulatory Landscape of MSC-Derived Exosomes: a Systems View 8:1419
Jiang M, Dong Z (2008) Regulation and pathological role of p53 in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:300–307
Kruiswijk F, Labuschagne CF, Vousden KH (2015) p53 in survival, death and metabolic health: a lifeguard with a licence to kill. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:393–405
Kuhlmann MK, Burkhardt G, Köhler H (1997) Insights into potential cellular mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity and their clinical application. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation : Official Publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association 12:2478–2480
Kumar M, Lu Z, Takwi AA, Chen W, Callander NS, Ramos KS, Young KH, Li Y (2011) Negative regulation of the tumor suppressor p53 gene by microRNAs. Oncogene 30:843–853
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013) The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153:1194–1217
Latcha S, Jaimes EA, Patil S, Glezerman IG, Mehta S, Flombaum CD (2016) Long-term renal outcomes after cisplatin treatment. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : CJASN 11:1173–1179
Liu Z, Wang S, Mi QS, Dong Z (2016) MicroRNAs in pathogenesis of acute kidney injury. Nephron 134:149–153
Marasa BS, Srikantan S, Martindale JL, Kim MM, Lee EK, Gorospe M, Abdelmohsen K (2010) MicroRNA profiling in human diploid fibroblasts uncovers miR-519 role in replicative senescence. Aging 2:333–343
Marcheque J, Bussolati B, Csete M, Perin L (2019) Concise reviews: stem cells and kidney regeneration: an update. Stem Cells Transl Med 8:82–92
Mehta RL, Cerdá J, Burdmann EA, Tonelli M, García-García G, Jha V, Susantitaphong P, Rocco M, Vanholder R, Sever MS, Cruz D, Jaber B, Lameire NH, Lombardi R, Lewington A, Feehally J, Finkelstein F, Levin N, Pannu N, Thomas B, Aronoff-Spencer E, Remuzzi G (2015) International Society of Nephrology’s 0by25 initiative for acute kidney injury (zero preventable deaths by 2025): a human rights case for nephrology. Lancet (London, England) 385:2616–2643
Meng X, Xue M, Xu P, Hu F, Sun B, Xiao Z (2017) MicroRNA profiling analysis revealed different cellular senescence mechanisms in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from different origin. Genomics 109:147–157
Mohd Ali N, Boo L, Yeap SK, Ky H, Satharasinghe DA, Liew WC, Ong HK, Cheong SK, Kamarul T (2016) Probable impact of age and hypoxia on proliferation and microRNA expression profile of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ 4:e1536
Munk R, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, Gorospe M, Abdelmohsen K (2017) Senescence-associated microRNAs. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 334:177–205
Ni F, Zhao H, Cui H, Wu Z, Chen L, Hu Z, Guo C, Liu Y, Chen Z, Wang X, Chen D, Wei H, Wang S (2015) MicroRNA-362-5p promotes tumor growth and metastasis by targeting CYLD in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 356:809–818
Pabla N, Huang S, Mi QS, Daniel R, Dong Z (2008) ATR-Chk2 signaling in p53 activation and DNA damage response during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 283:6572–6583
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Müller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408:86–89
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403:901–906
Saleh LM, Wang W, Herman SE, Saba NS, Anastas V, Barber E, Corrigan-Cummins M, Farooqui M, Sun C, Sarasua SM, Zhao Z, Abousamra NK, Elbaz O, Abdelghaffar HA, Wiestner A, Calvo KR (2017) Ibrutinib downregulates a subset of miRNA leading to upregulation of tumor suppressors and inhibition of cell proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 31:340–349
Srivastava SP, Hedayat AF, Kanasaki K, Goodwin JE (2019) microRNA crosstalk influences epithelial-to-mesenchymal, endothelial-to-mesenchymal, and macrophage-to-mesenchymal transitions in the kidney. Front Pharmacol 10:904
Tang C, Ma Z, Zhu J, Liu Z, Liu Y, Liu Y, Cai J, Dong Z (2019) P53 in kidney injury and repair: mechanism and therapeutic potentials. Pharmacol Ther 195:5–12
Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E (2009) Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol 9:581–593
Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S (2002) Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol 2:569–579
Ti D, Hao H, Tong C, Liu J, Dong L, Zheng J, Zhao Y, Liu H, Fu X, Han W (2015) LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med 13:308
Toledano H, D’Alterio C, Czech B, Levine E, Jones DL (2012) The let-7-Imp axis regulates ageing of the Drosophila testis stem-cell niche. Nature 485:605–610
Tsai SH, Huang PH, Tsai HY, Hsu YJ, Chen YW, Wang JC, Chen YH, Lin SJ (2019) Roles of the hypoximir microRNA-424/322 in acute hypoxia and hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular leakage. FASEB Journal : Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 33:12565–12575
Ullah M, Ng NN, Concepcion W, Thakor AS (2020) Emerging role of stem cell-derived extracellular microRNAs in age-associated human diseases and in different therapies of longevity. Ageing Res Rev 57:100979
Wang B, Jha JC, Hagiwara S, McClelland AD, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Thomas MC, Cooper ME, Kantharidis P (2014a) Transforming growth factor-β1-mediated renal fibrosis is dependent on the regulation of transforming growth factor receptor 1 expression by let-7b. Kidney Int 85:352–361
Wang B, Yao K, Huuskes BM, Shen HH, Zhuang J, Godson C, Brennan EP, Wilkinson-Berka JL, Wise AF, Ricardo SD (2016) Mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous microRNA-let7c via exosomes to attenuate renal fibrosis. Molecular Therapy : the Journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 24:1290–1301
Wang X, Bonventre JV, Parrish AR (2014b) The aging kidney: increased susceptibility to nephrotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 15:15358–15376
Wei Q, Mi QS, Dong Z (2013) The regulation and function of microRNAs in kidney diseases. IUBMB Life 65:602–614
Xu F, Pang L, Cai X, Liu X, Yuan S, Fan X, Jiang B, Zhang X, Dou Y, Gorospe M, Wang W (2014) let-7-repressesed Shc translation delays replicative senescence. Aging Cell 13:185–192
Yan M, Tang C, Ma Z, Huang S, Dong Z (2016) DNA damage response in nephrotoxic and ischemic kidney injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 313:104–108
Yang L, Xing G, Wang L, Wu Y, Li S, Xu G, He Q, Chen J, Chen M, Liu X, Zhu Z, Yang L, Lian X, Ding F, Li Y, Wang H, Wang J, Wang R, Mei C, Xu J, Li R, Cao J, Zhang L, Wang Y, Xu J, Bao B, Liu B, Chen H, Li S, Zha Y, Luo Q, Chen D, Shen Y, Liao Y, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhang K, Liu L, Mao P, Guo C, Li J, Wang Z, Bai S, Shi S, Wang Y, Wang J, Liu Z, Wang F, Huang D, Wang S, Ge S, Shen Q, Zhang P, Wu L, Pan M, Zou X, Zhu P, Zhao J, Zhou M, Yang L, Hu W, Wang J, Liu B, Zhang T, Han J, Wen T, Zhao M, Wang H (2015) Acute kidney injury in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet (London, England) 386:1465–1471
Yang P, Ni F, Deng RQ, Qiang G, Zhao H, Yang MZ, Wang XY, Xu YZ, Chen L, Chen DL, Chen ZJ, Kan LX, Wang SY (2015b) MiR-362-5p promotes the malignancy of chronic myelocytic leukaemia via down-regulation of GADD45α. Mol Cancer 14:190
Yun CW, Lee SH (2019) Potential and therapeutic efficacy of cell-based therapy using mesenchymal stem cells for acute/chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 20:1619
Zou Y, Chiu H, Zinovyeva A, Ambros V, Chuang CF, Chang C (2013) Developmental decline in neuronal regeneration by the progressive change of two intrinsic timers. Science (New York, NY) 340:372–376
Zuk A, Bonventre JV (2016) Acute kidney injury. Annu Rev Med 67:293–307
Funding
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0108803) and the Science and Technology Project of Beijing (D181100000118004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee for the Use of Animals of PLA General Hospital.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, SY., Xu, Y., Hong, Q. et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via let-7b-5p. Cell Tissue Res 392, 517–533 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03729-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03729-3