Abstract
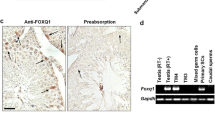
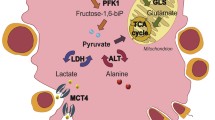
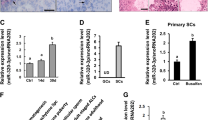
Sertoli cells (SCs) preferentially use glucose to convert to lactate. As an energy source, lactate is essential for survival of developed germ cells (GCs) due to its anti-apoptotic effect. Failure to maintain lactate metabolism homeostasis leads to infertility or germ cell apoptosis. Several Sertoli cell-expressed genes, such as Foxq1 and Gata4, have been identified as critical regulators for lactate synthesis, but the pathways that potentially modulate their expression remain ill defined. Although recent work from our collaborators pointed to an involvement of STIP1 homology and U-box–containing protein 1 (STUB1) in the modulation of Sertoli cell response to GCs-derived IL-1α, a true physiological function of STUB1 signaling in SCs has not been demonstrated. We therefore conditionally ablated Stub1 in SCs using Amh-Cre. Stub1 knockout males exhibited impaired fertility due to oligozoospermia and asthenospermia, possibly caused by lactate deficiency. Furthermore, by means of chromatin immunoprecipitation, in vivo ubiquitination, and luciferase reporter assays, we showed that STUB1 directed forkhead box Q1 (FOXQ1)-mediated transactivation of the lactate dehydrogenase A (Ldha) gene via K63-linked non-proteolytic polyubiquitination, thus facilitating lactate production in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)-stimulated SCs. In agreement, overexpression of LDHA by lentivirus infection effectively rescued the lactate production in TM4Stub1−/− cells. Our results collectively identify STUB1-mediated transactivation of FOXQ1 signaling as a post-translationally modified transcriptional regulatory network underlying nursery function in SCs, which may nutritionally contribute to Sertoli cell dysfunction of male infertility.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- SCs:
-
Sertoli cells
- GCs:
-
Germ cells
- BTB:
-
Blood–testis barrier
- GLUT1:
-
Glucose transporter 1
- LDHA:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase A
- MCT1:
-
Monocarboxylate transporter 1
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid
- FSH:
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- TH:
-
Thyroid hormone
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- IL-1α:
-
Interleukin 1α
- STUB1:
-
STIP1 homology and U-box–containing protein 1
- CHIP:
-
C terminus of HSP70-interacting protein
- ELK1:
-
ETS domain transcription factor Elk-1
- FOXQ1:
-
Forkhead box Q1
- CASA:
-
Computer-assisted semen analysis
- DMEM/F-12:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12
- FCS:
-
Fetal calf serum
- qPCR:
-
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- MDM2:
-
Murine double minute 2 homolog
References
Ballinger CA, Connell P, Wu Y, Hu Z, Thompson LJ, Yin LY, Patterson C (1999) Identification of CHIP, a novel tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein that interacts with heat shock proteins and negatively regulates chaperone functions. Mol Cell Biol 19:4535–4545
Boussouar F, Benahmed M (2004) Lactate and energy metabolism in male germ cells. Trends Endocrinol Metab 15:345–350
Brenkman AB, de Keizer PL, van den Broek NJ, Jochemsen AG, Burgering BM (2008) Mdm2 induces mono-ubiquitination of FOXO4. PLoS ONE 3:e2819
Cheng YC, Lin TY, Shieh SY (2013) Candidate tumor suppressor BTG3 maintains genomic stability by promoting Lys63-linked ubiquitination and activation of the checkpoint kinase CHK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5993–5998
Deng L, Jiang C, Chen L, Jin J, Wei J, Zhao L, Chen M, Pan W, Xu Y, Chu H, Wang X, Ge X, Li D, Liao L, Liu M, Li L, Wang P (2015) The ubiquitination of rag A GTPase by RNF152 negatively regulates mTORC1 activation. Mol Cell 58:804–818
Dong Y, Yang C, Pan F (2021) Post-translational regulations of Foxp3 in Treg cells and their therapeutic applications. Front Immunol 12:626172
Dong YS, Hou WG, Li Y, Liu DB, Hao GZ, Zhang HF, Li JC, Zhao J, Zhang S, Liang GB, Li W (2016) Unexpected requirement for a binding partner of the syntaxin family in phagocytosis by murine testicular Sertoli cells. Cell Death Differ 23:787–800
Gao G, Zhao Y, Wang K, Wang F (2021) Sodium vitamin C transporter 2 orchestrates lactate metabolism in mouse Sertoli cells. J Mol Endocrinol 66:157–170
Garcia TX, Farmaha JK, Kow S, Hofmann MC (2014) RBPJ in mouse Sertoli cells is required for proper regulation of the testis stem cell niche. Development 141:4468–4478
Goldbraikh D, Neufeld D, Eid-Mutlak Y, Lasry I, Gilda JE, Parnis A, Cohen S (2020) USP1 deubiquitinates Akt to inhibit PI3K-Akt-FoxO signaling in muscle during prolonged starvation. EMBO Rep 21:e48791
Gualtieri AF, Mazzone GL, Rey RA, Schteingart HF (2009) FSH and bFGF stimulate the production of glutathione in cultured rat Sertoli cells. Int J Androl 32:218–225
Guo Y, Li Q, Zhao G, Zhang J, Yuan H, Feng T, Ou D, Gu R, Li S, Li K, Lin P (2021) Loss of TRIM31 promotes breast cancer progression through regulating K48- and K63-linked ubiquitination of p53. Cell Death Dis 12:945
He K, Qu H, Wang H, Zhang S, Qian XH, Li W (2016) Regulated and functional expression of the corepressor MTA3 in rodent testis. Endocrinology 157:4400–4410
Huang H, Tindall DJ (2011) Regulation of FOXO protein stability via ubiquitination and proteasome degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:1961–1964
Jin X, Zhang S, Ding T, Zhao P, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Li W (2020) Testicular Lmcd1 regulates phagocytosis by Sertoli cells through modulation of NFAT1/Txlna signaling pathway. Aging Cell 19:e13217
Jungmann RA, Huang D, Tian D (1998) Regulation of LDH-A gene expression by transcriptional and posttranscriptional signal transduction mechanisms. J Exp Zool 282:188–195
Kodani N, Nakae J (2020) Tissue-specific metabolic regulation of FOXO-binding protein: FOXO Does not act alone. Cells 9
Kulathu Y, Komander D (2012) Atypical ubiquitylation - the unexplored world of polyubiquitin beyond Lys48 and Lys63 linkages. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:508–523
Li T, Zheng C, Han WJ, Chen ZZ (2022a) Regulation of STUB1 expression and its biological significance in mouse Sertoli cells. Syst Biol Reprod Med 68:298–313
Li T, Zheng C, Han WJ, Chen ZZ (2022b) Regulation of STUB1 expression and its biological significance in mouse Sertoli cells. Syst Biol Reprod Med 1–15
Lim P, Robson M, Spaliviero J, McTavish KJ, Jimenez M, Zajac JD, Handelsman DJ, Allan CM (2009) Sertoli cell androgen receptor DNA binding domain is essential for the completion of spermatogenesis. Endocrinology 150:4755–4765
Liu C, Lou W, Yang JC, Liu L, Armstrong CM, Lombard AP, Zhao R, Noel ODV, Tepper CG, Chen HW, Dall’Era M, Evans CP, Gao AC, (2018) Proteostasis by STUB1/HSP70 complex controls sensitivity to androgen receptor targeted therapy in advanced prostate cancer. Nat Commun 9:4700
Liu F, Chen ZZ, Zhao J, Zhang YQ, Ma J, Li W (2022) T2DM-elicited oxidative stress represses MTA3 expression in mouse Leydig cells. Reproduction 163:267–280
Liu Z, Yuan M, Meng X, Bie H, Yao S (2021) Identification of testicular Foxq1 as a critical modulator of lactate metabolism in mouse Sertoli cells. Histochem Cell Biol 156:227–237
Mascaro M, Lages I, Meroni G (2022) Microtubular TRIM36 E3 ubiquitin ligase in embryonic development and spermatogenesis. Cells 11
Melo LH, Melo RMC, Luz RK, Bazzoli N, Rizzo E (2019) Expression of Vasa, Nanos2 and Sox9 during initial testicular development in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) submitted to sex reversal. Reprod Fertil Dev 31:1637–1646
Miki K (2007) Energy metabolism and sperm function. Soc Reprod Fertil Suppl 65:309–325
Min JN, Whaley RA, Sharpless NE, Lockyer P, Portbury AL, Patterson C (2008) CHIP deficiency decreases longevity, with accelerated aging phenotypes accompanied by altered protein quality control. Mol Cell Biol 28:4018–4025
Nehar D, Mauduit C, Boussouar F, Benahmed M (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated lactate production is linked to lactate dehydrogenase A expression and activity increase in porcine cultured Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 138:1964–1971
Nehar D, Mauduit C, Boussouar F, Benahmed M (1998) Interleukin 1alpha stimulates lactate dehydrogenase A expression and lactate production in cultured porcine sertoli cells. Biol Reprod 59:1425–1432
Rato L, Alves MG, Socorro S, Duarte AI, Cavaco JE, Oliveira PF (2012) Metabolic regulation is important for spermatogenesis. Nat Rev Urol 9:330–338
Riera MF, Meroni SB, Schteingart HF, Pellizzari EH, Cigorraga SB (2002) Regulation of lactate production and glucose transport as well as of glucose transporter 1 and lactate dehydrogenase A mRNA levels by basic fibroblast growth factor in rat Sertoli cells. J Endocrinol 173:335–343
Rutter J, Reick M, Wu LC, McKnight SL (2001) Regulation of clock and NPAS2 DNA binding by the redox state of NAD cofactors. Science 293:510–514
Schisler JC, Rubel CE, Zhang C, Lockyer P, Cyr DM, Patterson C (2013) CHIP protects against cardiac pressure overload through regulation of AMPK. J Clin Invest 123:3588–3599
Seo J, Lee EW, Sung H, Seong D, Dondelinger Y, Shin J, Jeong M, Lee HK, Kim JH, Han SY, Lee C, Seong JK, Vandenabeele P, Song J (2016) CHIP controls necroptosis through ubiquitylation- and lysosome-dependent degradation of RIPK3. Nat Cell Biol 18:291–302
Shang Y, He J, Wang Y, Feng Q, Zhang Y, Guo J, Li J, Li S, Yan G, Ren F, Shi Y, Xu J, Zeps N, Zhai Y, He D, Chang Z (2017) CHIP/Stub1 regulates the Warburg effect by promoting degradation of PKM2 in ovarian carcinoma. Oncogene 36:4191–4200
Shang Y, Zhao X, Xu X, Xin H, Li X, Zhai Y, He D, Jia B, Chen W, Chang Z (2009) CHIP functions an E3 ubiquitin ligase of Runx1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:242–246
Shi CH, Schisler JC, Rubel CE, Tan S, Song B, McDonough H, Xu L, Portbury AL, Mao CY, True C, Wang RH, Wang QZ, Sun SL, Seminara SB, Patterson C, Xu YM (2014a) Ataxia and hypogonadism caused by the loss of ubiquitin ligase activity of the U box protein CHIP. Hum Mol Genet 23:1013–1024
Shi M, Cui J, Du J, Wei D, Jia Z, Zhang J, Zhu Z, Gao Y, Xie K (2014b) A novel KLF4/LDHA signaling pathway regulates aerobic glycolysis in and progression of pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20:4370–4380
Shim H, Dolde C, Lewis BC, Wu CS, Dang G, Jungmann RA, Dalla-Favera R, Dang CV (1997) c-Myc transactivation of LDH-A: implications for tumor metabolism and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6658–6663
Sun H, Yang B, Zhu C, Liu R, Wang H, Li W (2013) Presence of metastasis-associated protein 1 in Sertoli cells is required for proper contact between Sertoli cells and adjacent germ cells. Urology 81:66–73
Ullah K, Chen S, Lu J, Wang X, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Long Y, Hu Z, Xu G (2020) The E3 ubiquitin ligase STUB1 attenuates cell senescence by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of the core circadian regulator BMAL1. J Biol Chem 295:4696–4708
Valvona CJ, Fillmore HL, Nunn PB, Pilkington GJ (2016) The regulation and function of lactate dehydrogenase A: therapeutic potential in brain tumor. Brain Pathol 26:3–17
Wang A, Yang M, Liang R, Zhu F, Liu X, Han Y, Lin R, Wang X, Li D, Li H, Yuan X, Zhao H, Li B (2020) Mouse double minute 2 homolog-mediated ubiquitination facilitates forkhead box P3 stability and positively modulates human regulatory T cell function. Front Immunol 11:1087
Wang YT, Liu TY, Shen CH, Lin SY, Hung CC, Hsu LC, Chen GC (2022) K48/K63-linked polyubiquitination of ATG9A by TRAF6 E3 ligase regulates oxidative stress-induced autophagy. Cell Rep 38:110354
Xiong H, Chen Z, Zhao J, Li W, Zhang S (2021) TNF-alpha/ENO1 signaling facilitates testicular phagocytosis by directly activating Elmo1 gene expression in mouse Sertoli cells. FEBS J
Xu S, Fan L, Jeon HY, Zhang F, Cui X, Mickle MB, Peng G, Hussain A, Fazli L, Gleave ME, Dong X, Qi J (2020) p300-mediated acetylation of histone demethylase JMJD1A prevents its degradation by ubiquitin ligase STUB1 and enhances its activity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 80:3074–3087
Xu W, Marcu M, Yuan X, Mimnaugh E, Patterson C, Neckers L (2002) Chaperone-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP mediates a degradative pathway for c-ErbB2/Neu. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12847–12852
Yadav SK, Pandey A, Kumar L, Devi A, Kushwaha B, Vishvkarma R, Maikhuri JP, Rajender S, Gupta G (2018) The thermo-sensitive gene expression signatures of spermatogenesis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 16:56
Yamazaki D, Miyata H, Funato Y, Fujihara Y, Ikawa M, Miki H (2016) The Mg2+ transporter CNNM4 regulates sperm Ca2+ homeostasis and is essential for reproduction. J Cell Sci 129:1940–1949
Yang F, Cheng Y, An JY, Kwon YT, Eckardt S, Leu NA, McLaughlin KJ, Wang PJ (2010) The ubiquitin ligase Ubr2, a recognition E3 component of the N-end rule pathway, stabilizes Tex19.1 during spermatogenesis. PLoS One 5:e14017
Yin Y, Lin C, Kim ST, Roig I, Chen H, Liu L, Veith GM, Jin RU, Keeney S, Jasin M, Moley K, Zhou P, Ma L (2011) The E3 ubiquitin ligase Cullin 4A regulates meiotic progression in mouse spermatogenesis. Dev Biol 356:51–62
Zhang LL, Ma J, Yang B, Zhao J, Yan BY, Zhang YQ, Li W (2018) Interference with lactate metabolism by mmu-miR-320-3p via negatively regulating GLUT3 signaling in mouse Sertoli cells. Cell Death Dis 9:964
Zhang S, Li W, Zhu C, Wang X, Li Z, Zhang J, Zhao J, Hu J, Li T, Zhang Y (2012) Sertoli cell-specific expression of metastasis-associated protein 2 (MTA2) is required for transcriptional regulation of the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR) gene during spermatogenesis. J Biol Chem 287:40471–40483
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Tao Li (Reproductive Center, Baoji Maternal and Child Health Hospital, China) for enthusiastic discussion concerning the potential role of STUB1 in Sertoli cells and excellent scientific support.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81901510), and from Research Incubation Fund of Xi’an People’s Hospital (Xi’an NO.4 Hospital) (No. ZD-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design: AR. Study conduct: YY, MY, LM, ZH, and SP. Data collection: YY, MY, LM, ZH, SP, and AR. Data analysis: YY and AR. Data interpretation: YY and AR. Contribution of reagents: AR. Drafting and submission of manuscript: YY and AR.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (permission number XJTU1AF2018LSK-224). All procedures in studies involving animals were performed in accordance with the ethical standards recommended by Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Eighth Edition).
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Ma, Y., Li, M. et al. STUB1 directs FOXQ1-mediated transactivation of Ldha gene and facilitates lactate production in mouse Sertoli cells. Cell Tissue Res 392, 565–579 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03705-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03705-x