Abstract
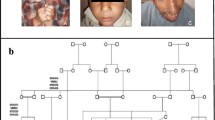
We report a consanguineous Pakistani family with seven affected individuals showing a syndromic form of congenital microcephaly. Clinical features of affected individuals include congenital microcephaly with sharply slopping forehead, moderate to severe mental retardation, anonychia congenita, and digital malformations. By screening human genome with microsatellite markers, this autosomal recessive condition was mapped to a 25.2 cM interval between markers D18S1150 and D18S1100 on chromosome 18p11.22–q12.3. However, the region of continuous homozygosity between markers D18S1150 and D18S997 spanning 15.33 cM, probably define the most likely candidate region for this condition. This region encompasses a physical distance of 12.03 Mb. The highest two-point LOD score of 3.03 was obtained with a marker D18S1104 and multipoint score reached a maximum of 3.43 with several markers. Six candidate genes, CEP76, ESCO1, SEH1L, TUBB6, ZNF519, and PTPN2 were sequenced, and were found to be negative for functional sequence variants.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002) Merlin: rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30:97–101
Andersen JS, Wilkinson CJ, Mayor T, Mortensen P, Nigg EA, Mann M (2003) Proteomic characterization of the human centrosome by protein correlation profiling. Nature 426:570–574
Bellows AM, Kenna MA, Cassimeris L, Skibbens RV (2003) Human EFO1p exhibits acetyltransferase activity and is a unique combination of linker histone and Ctf7p/Eco1p chromatid cohesion establishment domains. Nucleic Acids Res 31:6334–6343
Borglum AD, Balslev T, Haagerup A, Birkebaek N, Binderup H, Kruse TA, Hertz JM (2001) A new locus for Seckel syndrome on chromosome 18p11.31-q11.2. Eur J Hum Genet 9:753–757
Campbell GR, Pasquier E, Watkins J, Bourgarel-Rey V, Peyrot V, Esquieu D, Barbier P, de Mareuil J, Braguer D, Kaleebu P, Yirrell DL, Loret EP (2004) The glutamine-rich region of the HIV-1 Tat protein is involved in T-cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:48197–48204
Cottingham R, Indury RM, Schaffer AA (1993) Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet 53:252–263
Cronshaw JM, Krutchinsky AN, Zhang W, Chait BT, Matunis MJ (2002) Proteomic analysis of the mammalian nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol 158:915–927
Filippi G (1985) Unusual facial appearance, microcephaly, growth and mental retardation, and syndactyly. A new syndrome? Am J Med Genet 22:821–824
Goodship J, Gill H, Carter J, Jackson A, Splitt M, Wright M (2000) Autozygosity mapping of a seckel syndrome locus to chromosome 3q22. 1-q24. Am J Hum Genet 67:498–503
Gudbjartsson DF, Thorvaldsson T, Kong A, Gunnarsson G, Ingolfsdottir A (2005) Allegro version 2. Nat Genet 37:1015–1016
Gul A, Hassan MJ, Mahmood S, Chen W, Rahmani S, Naseer MI, Dellefave L, Muhammad N, Rafiq MA, Ansar M, Chishti MS, Ali G, Siddique T, Ahmad W (2006a) Genetic studies of autosomal recessive primary microcephaly in 33 Pakistani families: novel sequence variants in ASPM gene. Neurogenetics 7:105–110
Gul A, Hassan MJ, Hussain S, Raza SI, Chishti MS, Ahmad W (2006b) A novel deletion mutation in CENPJ gene in a Pakistani family with autosomal recessive primary microcephaly. J Hum Genet 51:760–764
Hou F, Zou H (2005) Two human orthologues of Eco1/Ctf7 acetyltransferases are both required for proper sister-chromatid cohesion. Mol Biol Cell 16:3908–3918
International Human Genome Sequence Consortium (2001) Initial sequence and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860–921
Johnson CV, Cool DE, Glaccum MB, Green N, Fischer EH, Bruskin A, Hill DE, Lawrence JB (1993) Isolation and mapping of human T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase sequences: localization of genes and pseudogenes discriminated using fluorescence hybridization with genomic versus cDNA probes. Genomics 16:619–629
Kilinç MO, Ninis VN, Ugur SA, Tüysüz B, Seven M, Balci S, Goodship J, Tolun A (2003) Is the novel SCKL3 at 14q23 the predominant Seckel locus? Eur J Hum Genet 11:851–857
Kong X, Murphy K, Raj T, He C, White PS, Matise TC (2004) A combined linkage-physical map of the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 75:1143–1148
Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, Fisk CJ, Li N, Smolyar A, Hill DE, Barabási AL, Vidal M, Zoghbi HY (2006) A protein–protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration. Cell 125:801–814
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE (1998) PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 63:259–266
O’Driscoll M, Jackson AP, Jeggo PA (2006) A causal link between impaired damage response and microcephaly. Cell cycle 5:2339–2344
O’Driscoll M, Ruiz-Perez VL, Woods CG, Jeggo PA, Goodship JA (2003) A splicing mutation affecting expression of ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein (ATR) results in Seckel syndrome. Nat Genet 33:497–501
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, NJ, pp 365–386
Sharif S, Donnai D (2004) Filippi syndrome: two cases with ectodermal features, expanding the phenotype. Clin Dysmorphol 13:221–226
Sobel E, Lange K (1996) Descent graphs in pedigree analysis: applications to haplotyping, location scores, and marker sharing statistics. Am J Hum Genet 58:1323–1337
Weeks DE, Sobel E, O’Connell JR, Lange K (1995) Computer programs for multilocus haplotyping of general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet 56:1506–1507
Woods CG, Bond J, Enard W (2005) Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (MCPH): a review of clinical, molecular, and evolutionary findings. Am J Hum Genet 76:717–728
Woods CG, Crouchman M, Huson SM (1992) Three sibs with phalangeal anomalies, microcephaly, severe mental retardation, and neurological abnormalities. J Med Genet 29:500–502
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the members of the family for their cooperation. The work presented was funded by the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan. Muhammad Jawad Hassan was supported by an indigenous PhD fellowship from HEC, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M.J., Chishti, M.S., Jamal, S.M. et al. A syndromic form of autosomal recessive congenital microcephaly (Jawad syndrome) maps to chromosome 18p11.22–q11.2. Hum Genet 123, 77–82 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0452-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0452-x