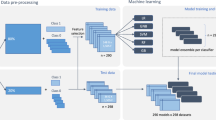
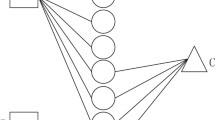
Abstract
Recent transcriptomics and bioinformatics studies have shown that ncRNAs can affect chromosome structure and gene transcription, participate in the epigenetic regulation, and take part in diseases such as tumorigenesis. Biologists have found that most ncRNAs usually work by interacting with the corresponding RNA-binding proteins. Therefore, ncRNA-protein interaction is a very popular study in both the biological and medical fields. However, due to the limitations of manual experiments in the laboratory, machine-learning methods for predicting ncRNA-protein interactions are increasingly favored by the researchers. In this review, we summarize several machine learning predictive models of ncRNA-protein interactions over the past few years, and briefly describe the characteristics of these machine learning models. In order to optimize the performance of machine learning models to better predict ncRNA-protein interactions, we give some promising future computational directions at the end.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ncRNA:
-
Non-coding RNA
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- tRNA:
-
Transfer RNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- snRNA:
-
Small nuclear RNA
- lncRNAs:
-
Long non coding RNAs
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- RF:
-
Random forest
- LOOCV:
-
Leave-one-out cross validation
- K-CV:
-
K-Fold Cross Validation
- ROC:
-
Receiver operator characteristics
- AUC:
-
The area under ROC curve
- PPSNs:
-
Protein–protein similarity networks
- SNF:
-
Similarity network fusion
- XGB:
-
Extreme gradient enhancement
- SAN:
-
Stacking autoencoder networks
- PSSM:
-
Position-specific scoring matrix
- SVD:
-
Singular value decomposition
- PZM:
-
Pseudo-Zernike moment
- PCC:
-
Pearson correlation coefficient
- GBDT:
-
Gradient boosting decision tree
- Extra tree:
-
Extremely randomized trees
- LMs:
-
Legendre moments
- PWM:
-
Position weight matrix
References
Adelman K, Egan E (2017) Non-coding RNA: more uses for genomic junk. Nature 543:183–185
Ahmad S, Sarai A (2005) PSSM-based prediction of DNA binding sites in proteins. BMC Bioinform 6:33
Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS, Slack FJ (2018) Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 18:5–18
Barros RC, Basgalupp MP, de Carvalho AC, Freitas AA (2013) Automatic design of decision-tree algorithms with evolutionary algorithms. Evol Comput 21:659–684
Bastanlar Y, Ozuysal M (2014) Introduction to machine learning. Methods Mol Biol 1107:105–128
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242
Blumensath T (2016) Directional clustering through matrix factorization. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27:2095–2107
Chartrand G, Cheng PM, Vorontsov E, Drozdzal M, Turcotte S, Pal CJ, Kadoury S, Tang A (2017) Deep learning: a primer for radiologists. Radiographics 37:2113–2131
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. ACM SIGKDD Int Conf Knowl Discov Data Min 16:785–794
Chen X, Yan CC, Zhang X, You ZH (2017) Long non-coding RNAs and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Brief Bioinform 18:558–576
Chen X, Wang L, Qu J, Guan NN, Li JQ (2018a) Predicting miRNA-disease association based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics 34:4256–4265
Chen X, Yin J, Qu J, Huang L (2018b) MDHGI: matrix decomposition and heterogeneous graph inference for miRNA-disease association prediction. PLoS Comput Biol 14:e1006418–e1006418
Chen X, Xie D, Zhao Q, You Z-H (2019a) MicroRNAs and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Brief Bioinform 20:515–539
Chen X, Zhu CC, Yin J (2019b) Ensemble of decision tree reveals potential miRNA-disease associations. PLoS Comput Biol 15:e1007209
Chhabra R (2015) miRNA and methylation: a multifaceted liaison. ChemBioChem 16:195–203
Czarnecki WM, Podlewska S, Bojarski AJ (2015) Extremely randomized machine learning methods for compound activity prediction. Molecules 20:20107–20117
Ding Y, Tang J, Guo F (2019) Identification of drug-side effect association via multiple information integration with centered kernel alignment. Neurocomputing 325:211–224
Esteller M (2011) Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12:861–874
Ge E, Yang Y, Gang M, Fan C, Zhao Q (2020) Predicting human disease-associated circRNAs based on locality-constrained linear coding. Genomics 112:1335–1342
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O, Carey BW, Cassady JP, Cabili MN, Jaenisch R, Mikkelsen TS, Jacks T, Hacohen N, Bernstein BE, Kellis M, Regev A, Rinn JL, Lander ES (2009) Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 458:223–227
Hombach S, Kretz M (2016) Non-coding RNAs: classification, biology and functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol 937:3–17
Hu H, Zhang L, Ai H, Zhang H, Fan Y, Zhao Q, Liu H (2018) HLPI-Ensemble: prediction of human lncRNA-protein interactions based on ensemble strategy. RNA Biol 15:797–806
Kondo Y, Shinjo K, Katsushima K (2017) Long non-coding RNAs as an epigenetic regulator in human cancers. Cancer Sci 108:1927–1933
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436–444
Li ZW, You ZH, Chen X, Gui J, Nie R (2016) Highly accurate prediction of protein–protein interactions via incorporating evolutionary information and physicochemical characteristics. Int J Mol Sci 17:1396
Liu H, Ren G, Chen H, Liu Q, Yang Y, Zhao Q (2020) Predicting lncRNA–miRNA interactions based on logistic matrix factorization with neighborhood regularized. Knowl Based Syst 191:105261
Liu H, Ren G, Hu H, Zhang L, Ai H, Zhang W, Zhao Q (2017) LPI-NRLMF: lncRNA-protein interaction prediction by neighborhood regularized logistic matrix factorization. Oncotarget 8:103975–103984
Mattick JS, Makunin IV (2006) Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet 15(Spec No 1):R17–29
Muppirala UK, Honavar VG, Dobbs D (2011) Predicting RNA-protein interactions using only sequence information. BMC Bioinform 12:489
Nedaie A, Najafi AA (2018) Support vector machine with Dirichlet feature mapping. Neural Netw 98:87–101
Pan X, Fan YX, Yan J, Shen HB (2016) IPMiner: hidden ncRNA-protein interaction sequential pattern mining with stacked autoencoder for accurate computational prediction. BMC Genom 17:582
Peschansky VJ, Wahlestedt C (2014) Non-coding RNAs as direct and indirect modulators of epigenetic regulation. Epigenetics 9:3–12
Ruths T, Ruths D, Nakhleh L (2009) GS2: an efficiently computable measure of GO-based similarity of gene sets. Bioinformatics 25:1178–1184
Shen C, Ding Y, Tang J, Jiang L, Guo F (2019) LPI-KTASLP: prediction of lncRNA-protein interaction by semi-supervised link learning with multivariate information. IEEE Access 7:13486–13496
Smith TF, Waterman MS (1981) Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol 147:195–197
Su R, Liu X, Wei L, Zou Q (2019) Deep-Resp-Forest: a deep forest model to predict anti-cancer drug response. Methods 166:91–102
Vareka L, Mautner P (2017) Stacked autoencoders for the P300 component detection. Front Neurosci 11:302
Wang B, Mezlini AM, Demir F, Fiume M, Tu Z, Brudno M, Haibe-Kains B, Goldenberg A (2014) Similarity network fusion for aggregating data types on a genomic scale. Nat Methods 11:333–337
Wei JW, Huang K, Yang C, Kang CS (2017) Non-coding RNAs as regulators in epigenetics (Review). Oncol Rep 37:3–9
Xiao Y, Zhang J, Deng L (2017) Prediction of lncRNA-protein interactions using HeteSim scores based on heterogeneous networks. Sci Rep 7:3664
Yang F, Zhang H, Mei Y, Wu M (2014) Reciprocal regulation of HIF-1alpha and lincRNA-p21 modulates the Warburg effect. Mol Cell 53:88–100
Yi HC, You ZH, Huang DS, Li X, Jiang TH, Li LP (2018) A deep learning framework for robust and accurate prediction of ncRNA-protein interactions using evolutionary information. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 11:337–344
Yi HC, You ZH, Wang MN, Guo ZH, Wang YB, Zhou JR (2020) RPI-SE: a stacking ensemble learning framework for ncRNA-protein interactions prediction using sequence information. Bio Inform 21:60
Yi Y, Zhao Y, Li C, Zhang L, Huang H, Li Y, Liu L, Hou P, Cui T, Tan P, Hu Y, Zhang T, Huang Y, Li X, Yu J, Wang D (2017) RAID v2.0: an updated resource of RNA-associated interactions across organisms. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D115–D118
Yuan J, Wu W, Xie C, Zhao G, Zhao Y, Chen R (2014) NPInter v2.0: an updated database of ncRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D104–D108
Zeng X, Liao Y, Liu Y, Zou Q (2017) Prediction and validation of disease genes using HeteSim scores. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 14:687–695
Zhan ZH, Jia LN, Zhou Y, Li LP, Yi HC (2019) BGFE: a deep learning model for ncRNA-protein interaction predictions based on improved sequence information. Int J Mol Sci 20(4):978
Zhang H, Shu H, Coatrieux G, Zhu J, Wu QM, Zhang Y, Zhu H, Luo L (2011) Affine Legendre moment invariants for image watermarking robust to geometric distortions. IEEE Trans Image Process 20:2189–2199
Zhang L, Ai HX, Li SM, Qi MY, Zhao J, Zhao Q, Liu HS (2017) Virtual screening approach to identifying influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitors using molecular docking combined with machine-learning-based scoring function. Oncotarget 8:83142–83154
Zhang T, Wang M, Xi J, Li A (2018) LPGNMF: predicting long non-coding RNA and protein interaction using graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 17:189–197
Zhao Q, Liang D, Hu H, Ren G, Liu H (2018a) RWLPAP: random walk for lncRNA-protein associations prediction. Protein Pept Lett 25:830–837
Zhao Q, Yu H, Ming Z, Hu H, Ren G, Liu H (2018b) The bipartite network projection-recommended algorithm for predicting long non-coding RNA-protein interactions. Mol Therapy Nucleic Acids 13:464–471
Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Hu H, Ren G, Zhang W, Liu H (2018c) IRWNRLPI: integrating random walk and neighborhood regularized logistic matrix factorization for lncRNA-protein interaction prediction. Frontiers Genet 9:239–239
Zhao Q, Yang Y, Ren G, Ge E, Fan C (2019) Integrating bipartite network projection and KATZ measure to identify novel CircRNA-disease associations. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 18:578–584
Zheng X, Wang Y, Tian K, Zhou J, Guan J, Luo L, Zhou S (2017) Fusing multiple protein-protein similarity networks to effectively predict lncRNA-protein interactions. BMC Bioinform 18:420
Zhou YK, Shen ZA, Yu H, Luo T, Gao Y, Du PF (2020) Predicting lncRNA-protein interactions with miRNAs as mediators in a heterogeneous network model. Front Genet 10:1341
Zitnik M, Nguyen F, Wang B, Leskovec J, Goldenberg A, Hoffman MM (2019) Machine learning for integrating data in biology and medicine: principles, practice, and opportunities. Inf Fusion 50:71–91
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11805091.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ designed and conceived the project. LZ, JS and QZ wrote the manuscript. MZ designed the figures and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conficts of interest and in particular: Lin Zhong declares that she has no confict of interest, Meiqin Zhen declares that she has no confict of interest, Jianqiang Sun declares that he has no confict of interest, Qi Zhao declares that he has no confict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, L., Zhen, M., Sun, J. et al. Recent advances on the machine learning methods in predicting ncRNA-protein interactions. Mol Genet Genomics 296, 243–258 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01727-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01727-0