Abstract
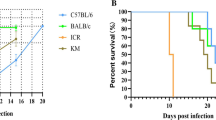
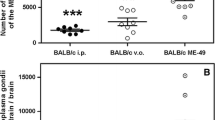
Studies with murine infection models have shown that immunity to the protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium involves T-cells and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) activity. The present study was performed to compare the course of infection of Cryptosporidium muris in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) congeneic strains of mice and examine the relationship between susceptibility to infection and production of T-cell cytokines. In experiments with BALB mice, the BALB/c strain (H-2 d) produced significantly fewer oocysts and recovered from infection sooner than the BALB/B (H-2 b) or BALB/K (H-2 k) strains. BALB/B X BALB/c F1 hybrid mice were found to express the more susceptible phenotype of the BALB/B parent strain, indicating that the gene(s) in the H-2 locus conferring increased susceptibility to C. muris infection was dominant. At different times during infection of the resistant BALB/c strain and the susceptible BALB/B strain, splenocytes were cultured with soluble parasite antigen and measurements were made of production of a number of T-cell cytokines. Similar patterns of increasing levels of IFN-γ and interleukin 2 (IL-2) were observed in both the resistant and susceptible strains during the patent stage of infection, indicating that production of these type 1 T-helper-cell (TH1) cytokines (i.e. involved in cell-mediated responses) correlated with the development of immunity. This also suggested that the increased susceptibility of BALB/B mice was not associated with a defective TH1 cytokine response. In the study of TH2 cytokines (involved in induction of an antibody response), low levels of IL-10 were detected during infection of BALB/c and BALB/B mice. In contrast, although IL-4 was released by splenocytes of both strains, significantly larger amounts were obtained from cells of the susceptible BALB/B mice in the early stages of infection. Thus, the H-2-dependent variation in susceptibility to infection between these BALB strains correlated with a difference in the pattern of IL-4 secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 July 1996 / Accepted: 15 September 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davami, M., Bancroft, G. & McDonald, V. Cryptosporidium infection in major histocompatibility complex congeneic strains of mice: variation in susceptibility and the role of T-cell cytokine responses. Parasitol Res 83, 257–263 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050243
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050243