Abstract
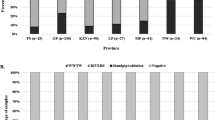
The phylum Microsporidia includes obligate intracellular parasites that can infect humans and various animals. To date, 17 different species within the phylum have been reported to infect humans. Among them, Enterocytozoon bieneusi (E. bieneusi) is one of the most frequently detected species in humans. Identification of E. bieneusi as well as its genotypes in humans and animals is important to reveal their role in transmission to each other. Cats are blamed as the source of E. bieneusi transmission to humans. In this study, we aimed to genotype 170 E. bieneusi positive samples isolated from stool of stray cats living in İzmir province of Türkiye. According to the results, 47 samples were amplified by nested PCR protocol targeting ITS region and successfully sequenced. The phylogenetic analysis showed the presence of zoonotic genotype D and type IV in stray cats, which are also frequently detected in humans. Among the E. bieneusi genotypes detected, the prevalence of type IV (93.6%; 44/47) was very high compared to genotype D. Overall, the identification of zoonotic genotypes of E. bieneusi supports that stray cats can play an important role in the transmission of E. bieneusi to humans in İzmir.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Accession numbers given by NCBI for E. bieneusi isolates detected in this study (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) are OR159312 and OR159313.
References
Agholi M, Hatam GR, Motazedian MH (2013) Microsporidia and coccidia as causes of persistence diarrhea among liver transplant children: incidence rate and species/genotypes. Pediatr Infect Dis J 32(2):185–187
Altekar G, Dwarkadas S, Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2004) Parallel metropolis-coupled Markov chain Monte Carlo for Bayesian phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics 20:407–415
Buckholt MA, Lee JH, Tzipori S (2002) Prevalence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in swine: an 18-month survey at a slaughterhouse in Massachusetts. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2595–2599
Cotte L, Rabodonirina M, Chapuis F, Bailly F, Bissuel F, Raynal C, Gelas P, Persat F, Piens MA, Trepo C (1999) Waterborne outbreak of intestinal microsporidiosis in persons with and without human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis 180(6):2003–2008. https://doi.org/10.1086/315112
Dengjel B, Zahler M, Hermanns W, Heinritzi K, Spillmann T, Thomschke A, Löscher T, Gothe R, Rinder H (2001) Zoonotic potential of Enterocytozoon bieneusi. J Clin Microbiol 39(12):4495–4499. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.39.12.4495-4499.2001
ErkuntAlak S, Can H, DeğirmenciDöşkaya A, Sürgeç E, Güvendi M, Ün C, Döşkaya M, Gürüz AY, Karakavuk M (2023) Molecular prevalence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in stray cats of İzmir. Türkiye. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 100:102037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2023.102037
Han B, Weiss LM (2017) Microsporidia: obligate intracellular pathogens within the fungal kingdom. Microbiology spectrum 5(2):10–1128. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0018-2016
Karim MR, Dong H, Yu F, Jian F, Zhang L, Wang R, Zhang S, Rume FI, Ning C, Xiao L (2014) Genetic diversity in Enterocytozoon bieneusi isolates from dogs and cats in China: host specificity and public health implications. J Clin Microbiol 52(9):3297–3302. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01352-14
Kumar SS (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Li W, Xiao L (2020) Ecological and public health significance of Enterocytozoon bieneusi. One health (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 12:100209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2020.100209
Li W, Feng Y, Zhang L, Xiao L (2019) Potential impacts of host specificity on zoonotic or interspecies transmission of Enterocytozoon bieneusi. Infect Genet Evol 75:104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2019.104033
Li W, Feng Y, Santin M (2019) Host specificity of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and public health implications. Trends Parasitol 35(6):436–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2019.04.004
Matos O, Lobo ML, Xiao L (2012) Epidemiology of Enterocytozoon bieneusi infection in humans. J Parasitol Res 2012:981424. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/981424
Mirjalali H, Mirhendi H, Meamar AR, Mohebali M, Askari Z, Mirsamadi ES, Rezaeian M (2015) Genotyping and molecular analysis of Enterocytozoon bieneusi isolated from immunocompromised patients in Iran. Infect Genet Evol 36:244–249
Mori H, Mahittikorn A, Thammasonthijarern N, Chaisiri K, Rojekittikhun W, Sukthana Y (2013) Presence of zoonotic Enterocytozoon bieneusi in cats in a temple in central Thailand. Vet Parasitol 197(3–4):696–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.07.025
Pekmezci D, Pekmezci GZ, Yildirim A, Duzlu O, Inci A (2019) Molecular detection of zoonotic microsporidia in domestic cats in Turkey: a preliminary study. Acta Parasitol 64(1):13–18. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-018-00003-x
Piekarska J, Kicia M, Wesołowska M, Kopacz Ż, Gorczykowski M, Szczepankiewicz B, Kváč M, Sak B (2017) Zoonotic microsporidia in dogs and cats in Poland. Vet Parasitol 246:108–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.09.011
Pirestani M, Sadraei J, Forouzandeh M (2013) Molecular characterization and genotyping of human related microsporidia in free-ranging and captive pigeons of Tehran. Iran Infect Genet Evol 20:495–499
Rabaud C, Georges E, Guedenet JC, Allamagny E, May T, Canton P (1999) Infestation disséminée à Enterocytozoon bieneusi chez un patient infecté par le VIH [Disseminated infestation of Enterocytozooon bieneusi a an HIV-infected patient]. Pathol Biol (paris) 47(5):576–578
Rambaut A (2018) FigTree v.1.4.4. [accessed 25 October 2020]. http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/.
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2. efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61(3):539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Santín M, Fayer R (2011) Microsporidiosis: Enterocytozoon bieneusi in domesticated and wild animals. Res Vet Sci 90:363–371
Santín M, Trout JM, Vecino JA, Dubey JP, Fayer R (2006) Cryptosporidium, Giardia and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in cats from Bogota (Colombia) and genotyping of isolates. Vet Parasitol 141(3–4):334–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.06.004
Sodqi M, Brazille P, Gonzalez-Canali G, Cornet M, Piketty C, Weiss L (2004) Unusual pulmonary Enterocytozoon bieneusi microsporidiosis in an AIDS patient: case report and review. Scand J Infect Dis 36(3):230–231
Verweij JJ, Ten Hove R, Brienen EA, van Lieshout L (2007) Multiplex detection of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Encephalitozoon spp. in fecal samples using real-time PCR. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 57(2):163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2006.08.009
Wang H, Lin X, Sun Y, Qi N, Lv M, Xiao W, Chen Y, Xiang R, Sun M, Zhang L (2020) Occurrence, risk factors and genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in dogs and cats in Guangzhou, southern China: high genotype diversity and zoonotic concern. BMC Vet Res 16(1):201. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-020-02421-4
Yildirim Y, Al S, Duzlu O, Onmaz NE, Onder Z, Yetismis G, Hizlisoy H, Gonulalan Z, Yildirim A (2020) Enterocytozoon bieneusi in raw milk of cattle, sheep and water buffalo in Turkey: Genotype distributions and zoonotic concerns. Int J Food Microbiol 334:108828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108828
Zhang Y, Koehler AV, Wang T, Cunliffe D, Gasser RB (2019) Enterocytozoon bieneusi genotypes in cats and dogs in Victoria. Australia BMC Microbiol 19(1):183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: HC. Performed the experiments: ES, MG, MK, SEA, ADD. Analyzed the data: HC, ADD, MD, CÜ, AYY. Wrote the paper: HC, MD. Reviewed and edited the paper: CÜ, HC, MD. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Ege University (Permit number: 2022–100).
Consent to participate and consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Section Editor: Lihua Xiao.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sürgeç, E., Güvendi, M., Karakavuk, M. et al. Genotyping of Enterocytozoon bieneusi isolates detected in stray cats of İzmir, Türkiye. Parasitol Res 122, 2729–2735 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-023-07974-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-023-07974-5