Abstract
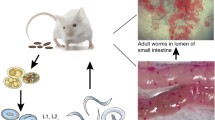
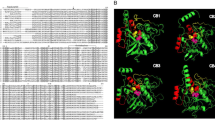
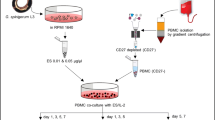
Excretory-secretory products (ESPs) of parasitic helminths are well known to exert immunostimulation and immunomodulation in hosts. Immune regulation plays a key role in anti-tumour therapy. The present study explored the anti-tumour effect of ESPs released by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. In Hepa1-6 mouse tumour models, ESPs significantly reduced tumour growth. Tumour-bearing mice treated with ESPs had significantly higher CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cell counts than those treated with Freund’s adjuvant. In vitro, human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells, human lung cancer A549 cells, and normal human liver HL-7702 cells were co-incubated with ESPs for 24 h and 48 h. ESPs significantly accelerated HepG2 apoptosis but had no inhibitory effect on the proliferation of A549 and HL-7702 cells. Apoptotic HepG2 cells displayed condensed nuclei, apoptotic bodies, and swollen endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Expression of the endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-related factors activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) and C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) in HepG2 cells increased with increasing ESP concentration and treatment time. Calreticulin (CRT) is a key effector protein of ESPs, and recombinant calreticulin (rCRT) was produced in BL21 Escherichia coli (E. coli). In contrast to ESPs, rCRT markedly reduced the proliferation of HepG2 cells. The expression levels of ATF6 and CHOP in HepG2 cells treated with 30 μg/mL rCRT significantly increased at 48 h. Notably, these findings synergistically suggest that ESPs and rCRT are promising candidates for anti-tumour immunotherapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article. All data are fully available without restriction.
References
Azhary JMK, Harada M, Takahashi N, Nose E, Kunitomi C, Koike H, Hirata T, Hirota Y, Koga K, Wada-Hiraike O, Fujii T, Osuga Y (2019) Endoplasmic reticulum stress activated by androgen enhances apoptosis of granulosa cells via induction of death receptor 5 in PCOS. Endocrinology 160:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2018-00675
Bell MC, Meier SE, Ingram AL, Abisambra JF (2016) PERK-opathies: an endoplasmic reticulum stress mechanism underlying neurodegeneration. Curr Alzheimer Res 13:150–163. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205013666151218145431
Boehm J, Orth T, Van Nguyen P, Söling HD (1994) Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with increased auto-antibody titers against calreticulin and grp94, but calreticulin is not the Ro/SS-A antigen. Eur J Clin Investig 24:248–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.1994.tb01082.x
Busch M, Große-Kreul J, Wirtz JJ, Beier M, Stephan H, Royer-Pokora B, Metz K, Dünker N (2017) Reduction of the tumorigenic potential of human retinoblastoma cell lines by TFF1 overexpression involves p53/caspase signaling and miR-18a regulation. Int J Cancer 141:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30768
Cao X, Fu Z, Zhang M, Han Y, Han Q, Lu K, Li H, Zhu C, Hong Y, Lin J (2016) Excretory/secretory proteome of 14-day schistosomula, Schistosoma japonicum. J Proteome 130:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2015.10.001
Crowe J, Lumb FE, Harnett MM, Harnett W (2017) Parasite excretory-secretory products and their effects on metabolic syndrome. Parasite Immunol 39. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12410
Dalton JP, Robinson MW, Mulcahy G, O'Neill SM, Donnelly S (2013) Immunomodulatory molecules of Fasciola hepatica: candidates for both vaccine and immunotherapeutic development. Vet Parasitol 195:272–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.04.008
Fang W, Xu S, Wang Y, Ni F, Zhang S, Liu J, Chen X, Luo D (2010) ES proteins analysis of Angiostrongylus cantonensis: products of the potential parasitism genes? Parasitol Res 106:1027–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1751-z
Ferreira I, Smyth D, Gaze S, Aziz A, Giacomin P, Ruyssers N, Artis D, Laha T, Navarro S, Loukas A, McSorley HJ (2013) Hookworm excretory/secretory products induce interleukin-4 (IL-4)+ IL-10+ CD4+ T cell responses and suppress pathology in a mouse model of colitis. Infect Immun 81:2104–2111. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00563-12
Furudate S, Fujimura T, Kambayashi Y, Kakizaki A, Hidaka T, Aiba S (2017) Immunomodulatory effect of imiquimod through CCL22 produced by tumor-associated macrophages in B16F10 melanomas. Anticancer Res 37:3461–3471. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11714
Gahoi S, Singh S, Gautam B (2019) Genome-wide identification and comprehensive analysis of excretory/secretory proteins in nematodes provide potential drug targets for parasite control. Genomics 111:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.03.007
Guasconi L, Chiapello LS, Masih DT (2015) Fasciola hepatica excretory-secretory products induce CD4+T cell anergy via selective up-regulation of PD-L2 expression on macrophages in a Dectin-1 dependent way. Immunobiology 220:934–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2015.02.001
Hadj Abdallah N, Baulies A, Bouhlel A, Bejaoui M, Zaouali MA, Ben Mimouna S, Messaoudi I, Fernandez-Checa JC, García Ruiz C, Ben Abdennebi H (2018) Zinc mitigates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by modulating oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy. J Cell Physiol 233:8677–8690. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26747
Hernández-Ancheyta L, Salinas-Tobón MDR, Cifuentes-Goches JC, Hernández-Sánchez J (2018) Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae excretory-secretory products induce changes in cytoskeletal and myogenic transcription factors in primary myoblast cultures. Int J Parasitol 48:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2017.10.002
Huby F, Nano JL, Mallet S, Hoste H (1999) Effects of the excretory/secretory products of Trichostrongylus colubriformis on the growth of different cell lines. Int J Parasitol 29:697–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(99)00014-4
Ilic N, Gruden-Movsesijan A, Sofronic-Milosavljevic L (2012) Trichinella spiralis: shaping the immune response. Immunol Res 52:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-012-8287-5
Lindo JF, Waugh C, Hall J, Cunningham-Myrie C, Ashley D, Eberhard ML, Sullivan JJ, Bishop HS, Robinson DG, Holtz T, Robinson RD (2002) Enzootic Angiostrongylus cantonensis in rats and snails after an outbreak of human eosinophilic meningitis, Jamaica. Emerg Infect Dis 8:324–326. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0803.010316
Luo J, Yu L, Xie G, Li D, Su M, Zhao X, Du L (2017) Study on the mitochondrial apoptosis pathways of small cell lung cancer H446 cells induced by Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae ESPs. Parasitology 144:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182016002535
Ma Y, Brewer JW, Diehl JA, Hendershot LM (2002) Two distinct stress signaling pathways converge upon the CHOP promoter during the mammalian unfolded protein response. J Mol Biol 318:1351–1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00234-6
Miura K, Fukumoto S, Dirgahayu P, Hirai K (2001) Excretory/secretory products from plerocercoids of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei suppress gene expressions and production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or lipoteichoic acid. Int J Parasitol 31:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00149-1
Park S, Lim W, Bazer FW, Song G (2017) Naringenin induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress by regulating MAPK and AKT signal transduction pathways in endometriosis cells. Mol Hum Reprod 23:842–854. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gax057
Pritchard DI, Leggett KV, Rogan MT, McKean PG, Brown A (1991) Necator americanus secretory acetylcholinesterase and its purification from excretory-secretory products by affinity chromatography. Parasite Immunol 13:187–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3024.1991.tb00274.x
Radovic I, Gruden-Movsesijan A, Ilic N, Cvetkovic J, Mojsilovic S, Devic M, Sofronic-Milosavljevic L (2015) Immunomodulatory effects of Trichinella spiralis-derived excretory-secretory antigens. Immunol Res 61:312–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8626-4
Ramírez G, Valck C, Aguilar L, Kemmerling U, López-Muñoz R, Cabrera G, Morello A, Ferreira J, Maya JD, Galanti N, Ferreira A (2012) Roles of Trypanosoma cruzi calreticulin in parasite-host interactions and in tumor growth. Mol Immunol 52:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2012.05.006
Ren Z, Chen S, Qing T, Xuan J, Couch L, Yu D, Ning B, Shi L, Guo L (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and MAPK signaling pathway activation underlie leflunomide-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells. Toxicology 392:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2017.10.002
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M (2008) Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 133:775–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.009
Sim S, Park G-M, Yong T-S (2003) Cloning and characterization of Clonorchis sinensis myoglobin using immune sera against excretory-secretory antigens. Parasitol Res 91:338–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0869-7
Sofronic-Milosavljevic LJ, Radovic I, Ilic N, Majstorovic I, Cvetkovic J, Gruden-Movsesijan A (2013) Application of dendritic cells stimulated with Trichinella spiralis excretory-secretory antigens alleviates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Med Microbiol Immunol 202:239–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-012-0286-6
Techasoponmani R, Sirisinha S (1980) Use of excretory and secretory products from adult female worms to immunize rats and mice against Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Parasitology 80:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000000925
Valanparambil RM, Segura M, Tam M, Jardim A, Geary TG, Stevenson MM (2014) Production and analysis of immunomodulatory excretory-secretory products from the mouse gastrointestinal nematode Heligmosomoides polygyrus bakeri. Nat Protoc 9:2740–2754. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2014.184
Viseshakul N, Dechkhajorn W, Benjathummarak S, Nuamtanong S, Maneerat Y (2017) Excretory-secretory product of third-stage Gnathostoma spinigerum larvae induces apoptosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Parasitol Res 116:2783–2794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5589-5
Vitta A, Dekumyoy P, Komalamisra C, Kalambaheti T, Yoshino TP (2016) Cloning and expression of a 16-kDa recombinant protein from Angiostrongylus cantonensis for use in immunoblot diagnosis of human angiostrongyliasis. Parasitol Res 115:4115–4122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5184-1
Wang T, Ma G, Ang C-S, Korhonen PK, Koehler AV, Young ND, Nie S, Williamson NA, Gasser RB (2019) High throughput LC-MS/MS-based proteomic analysis of excretory-secretory products from short-term in vitro culture of Haemonchus contortus. J Proteome 204:103375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2019.05.003
Yadav S, Prakash J, Saxena JK (2018) Metal binding study of calreticulin: an immunomodulatory protein of human filarial parasite Brugia malayi. Int J Biol Macromol 117:1157–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.011
Yang X, Li Z, He H, Cheng M, Liu Q, Zhang D, Chen J, Wu X, He A, Zheng X, Wu Y, Wu Z, Zhan X (2013) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of a putative activation-associated secreted protein from Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Parasitol Res 112:781–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3198-x
Yang L, Wang B, Qiu L, Wan B, Yang Y, Liu M, Wang F, Fang Q, Stanley DW, Ye G (2019) Functional characterization of a venom protein calreticulin in the ectoparasitoid. Insects 11:29–43. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11010029
Yong H-S, Song S-L, Eamsobhana P, Goh S-Y, Lim P-E (2015) Complete mitochondrial genome reveals genetic diversity of Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Nematoda: Angiostrongylidae). Acta Trop 152:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2015.09.001
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang X, Batchvarova N, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H, Stevens JL, Ron D (1998) CHOP is implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev 12:982–995. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.12.7.982
Zumaquero-Ríos J-L, García-Juarez J, de-la-Rosa-Arana J-L, Marcet R, Sarracent-Pérez J (2012) Trichinella spiralis: monoclonal antibody against the muscular larvae for the detection of circulating and fecal antigens in experimentally infected rats. Exp Parasitol 132:444–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2012.09.016
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Education Department of Hainan Province for the financial support and Academician Workstation for material support. The authors express the deep appreciation to Ms. Sijing Li for English language editing.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Hainan Medical University (No. HY2015-08) and the Education Department of Hainan Province (Hnky2017ZD-15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yajun Lu designed the study, analysed the data, and wrote the manuscript. Yajun Lu, Yuxiao Yang, and Siqi Yang performed the experiments. Qianfeng Xia revised the draft report. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committees of Hainan Medical University.
Consent to participate
All participants provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Julia Walochnik
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Yang, Y., Yang, S. et al. Immunomodulatory action of excretory-secretory products of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in a mouse tumour model. Parasitol Res 119, 3705–3718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06872-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06872-4