Abstract
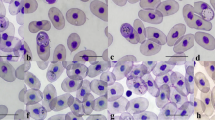
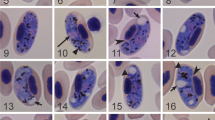
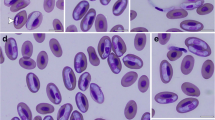
A severely underweight alligator snapping turtle Macrochelys temminckii Troost in Harlan, 1835, was found near Tyler, Texas, and taken to the Caldwell Zoo. Blood films were submitted to Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, for morphological and molecular identification of haemogregarine-like inclusions in the red blood cells. Intraerythrocytic Haemogregarina sp. forms were found on microscopic examination at a parasitemia of <1 %. The morphology and morphometric data for the forms indicate similarity to Haemogregarina macrochelysi n. sp. Telford et al., 2009, previously reported in alligator snapping turtles in Florida and Georgia, but two characteristic stage forms were not shared between H. macrochelysi n. sp. and the parasite found in this report. The haemogregarine 18S ribosomal RNA gene (1555-bp fragment) was amplified and cloned, and five clones sequenced. The sequences were deposited in the NCBI GenBank database. All five showed ∼96 % identity to Haemogregarina balli Paterson and Desser, 1976, Hepatozoon sp., and Hemolivia stellata Petit et al., 1990. A 774-bp segment shared 98-99 % identity with the corresponding Haemogregarina sp. rDNA sequence (KR006985) from Caspian turtles (Mauremys caspica McDowell, 1964) in Iran. A neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree generated from aligned sequences from the clones, 26 hematozoa, Adelina dimidiata Schneider, 1875, and Cryptosporidium serpentis Levine, 1980, revealed the cloned sequences clustered on their own branch within the Haemogregarina spp. clade. No genetic data are available for H. macrochelysi n. sp. at this time, so it remains unclear if this parasite in a Texas alligator snapping turtle is conspecific with H. macrochelysi n. sp.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acholonu A (1974) Haemogregarina pseudemydisn. sp. (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae) and Pirhemocyton chelonarumn n. sp. in turtles from Louisiana. J Protozool 21(5):659–664
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller EW, Myers DJ, Lipman (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Barta JR, Ogedengbe JD, Martin DS, Smith TG (2012) Phylogenetic position of the adeleorinid coccidia (Myzozoa, Apicomplexa, Coccidia, Eucoccidiorida, Adeleorina) inferred using 18S rDNA sequences. J Eukaryot Microbiol 59(2):171–180
Boundy J, Kennedy C (2006) Trapping survey results for the alligator snapping turtle (Macrochelys temminckii) in southeastern Louisiana, with comments on exploitation. Chelonian Conserv Biol 5(1):3–9
Cook CA, Smit NJ, Davies AJ (2009) A redescription of Haemogregarina fitzsimonsi Dias, 1953 and some comments on Haemogregarina parvula Dias, 1953 (Adeleorina: Haemogregarinidae) from southern African tortoises (Cryptodira: Testudinidae), with new host data and distribution records. Folia Parasitol 56(3):173–179
Criado-Fornelio A, Ruas JL, Casado N, Farias NAR, Soares MP, Müller G, Brum JGW, Berne MEA, Buling-Saraña A, Barba-Carretero JC (2006) New molecular data on mammalian Hepatozoon species (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) from Brazil and Spain. J Parasitol 92(1):93–99
Davis A, Sterrett S (2011) Prevalence of haemogregarine parasites in three freshwater turtle species in a population in northeast Georgia, USA. Int J Zool Res 7(2):156–163
Dvořáková N, Kvičerová J, Hostovský M, Široký P (2015) Haemogregarines of freshwater turtles from Southeast Asia with a description of Haemogregarina sacaliae n. sp. and a redescription of Haemogregarina pellegrini Laveran and Pettit, 1910. Parasitology 142(06):816–826
Dvořáková N, Kvičerová J, Papoušek I, Javanbakht H, Tiar G, Kami H, Široký P (2014) Haemogregarines from western Palaearctic freshwater turtles (genera Emys, Mauremys) are conspecific with Haemogregarina stepanowi Danilewsky, 1885. Parasitology 141(04):522–530
Edney JM (1949) Haemogregarina stepanowi Danilewsky (1885) in middle Tennessee turtles. J Tenn Acad Sci 24(3):220–223
Ernst CH, Lovich JE (2009) Turtles of the United States and Canada. JHU Press, Baltimore
Ewert MA (1976) Nests, nesting and aerial basking of Macroclemys under natural conditions, and comparisons with Chelydra (Testudines: Chelydridae). Herpetologica 32:150–156
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Kopečná J, Jirků M, Oborník M, Tokarev YS, Lukeš J, Modrý D (2006) Phylogenetic analysis of coccidian parasites from invertebrates: search for missing links. Protist 157(2):173–183
Kvičerová J et al (2014) Hemolivia and Hepatozoon: haemogregarines with tangled evolutionary relationships. Protist 165(5):688–700
Levine ND (1982) Some corrections in haemogregarine (Apicomplexa: Protozoa) nomenclature. J Protozool 29(4):601–603
Lv Z, Wu Z, Zhang L, Ji P, Cai Y, Luo S, Wang H, Li H (2015) Genome mining offers a new starting point for parasitology research. Parasitol Res 114(2):399–409
Maia JP, Harris DJ, Carranza S, Gómez-Díaz E (2014) A comparison of multiple methods for estimating parasitemia of hemogregarine hemoparasites (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) and its application for studying infection in natural populations. PLoS ONE 9(4):e95010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095010
McAllister CT (2015) Hematozoa (Apicomplexa: Haemogregarinidae, Hepatozoidae) from two turtles (Testudines: Chelydridae, Emydidae) and two snakes (Ophidia: Colubridae, Viperidae) in southeastern Oklahoma. Proc Okla Acad Sci 95:119–124
McAllister CT, Upton SJ, Trauth SE (1995) Hemogregarines (Apicomplexa) and Falcaustra chelydrae (Nematoda) in an alligator snapping turtle, Macroclemys temminckii (Reptilia: Testudines), from Arkansas. J Helminthol Soc Wash 62(1):74–77
Merino S, Vásquez RA, Martínez J, Celis-Diez JL, Gutiérrez-Jiménez L, Ippi S, Sánchez-Monsalvez I, Martínez-De La Puente J (2009) Molecular characterization of an ancient Hepatozoon species parasitizing the ‘living fossil’marsupial ‘Monito del Monte’Dromiciops gliroides from Chile. Biol J Linnean Soc 98(3):568–576
Paterson WB, Desser SS (1976) Observations on Haemogregarina balli sp. n. from the common snapping turtle, Chelydra serpentina. J Protozool 23(2):294–301. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb03775.x
Perkins SL, Keller AK (2001) Phylogeny of nuclear small subunit rRNA genes of hemogregarines amplified with specific primers. J Parasitol 87(4):870–876
Petit G, Landau I, Baccam D, Lainson R (1990) Description et cycle biologique d’ Hemolivia stellata n.g., n.sp., hémogrégarinede crapauds Brésiliens. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 65:3–15
Powell R, Conant R, Collins JT (2016) Peterson field guide to reptiles and amphibians: eastern and central North America, 4th edn. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Boston
Rakhshandehroo E, Sharifiyazdi H, Ahmadi A (2016) Morphological and molecular characterisation of Haemogregarina sp. (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Haemogregarinidae) from the blood of the Caspian freshwater turtle Mauremys caspica (Gmelin) (Geoemydidae) in Iran. Syst Parasitol 93(5):517–524
Siddall ME, Desser SS (1991) Merogonic development of Haemogregarina balli (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Haemogregarinidae) in the leech Placobdella ornata (Glossiphoniidae), its transmission to a chelonian intermediate host and phylogenetic implications. J Parasitol 77(3):426–436. doi:10.2307/3283131
Siddall ME, Desser SS (1992) Prevalence and intensity of Haemogregarina balli (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Haemogregarinidae) in three turtle species from Ontario, with observations on intraerythrocytic development. Can J Surg 70(1):123–128. doi:10.1139/z92-018
Sloboda M, Kamler M, Bulantová J, Votýpka J, Modrý D (2007) A new species of Hepatozoon (Apicomplexa: Adeleorina) from Python regius (Serpentes: Pythonidae) and its experimental transmission by a mosquito vector. J Parasitol 93(5):1189–1198
Smith TG (1996) The genus Hepatozoon (Apicomplexa: Adeleina). J Parasitol 82:565–585
Strohlein DA, Christensen BM (1984) Haemogregarina sp. (Apicomplexa: Sporozoea) in aquatic turtles from Murphy’s Pond, Kentucky. T Am Microsc Soc 103(1):98–101. doi:10.2307/3226539
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, Version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Telford SR Jr (2009) Hemoparasites of the reptilia: color atlas and text. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Telford SR Jr, Norton TM, Moler PE, Jensen JB (2009) A new Haemogregarina species of the alligator snapping turtle, Macrochelys temminckii (Testudines: Chelydridae), in Georgia and Florida that produces macromeronts in circulating erythrocytes. J Parasitol 95(1):208–214
Troost G (1835) In: Harlan R (ed) Medical and physical researches; or, Original memoires in medicine, surgery, physiology, geology, zoology, and comparative anatomy. L.R. Bailey, Philadelphia
Wang CC, Hopkins SH (1965) Haemogregarina and Haemoproteus (Protozoa, Sporozoa) in blood of Texas freshwater turtles. J Parasitol 51:682–683
Xiao L, Escalante L, Yang C, Sulaiman I, Escalante AA, Montali RJ, Fayer R, Lal AA (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of Cryptosporidium parasites based on the small-subunit rRNA gene locus. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(4):1578–1583
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Caldwell Zoo in Tyler, Texas, for providing this sample for characterization. We thank Ann Buchanan, DVM, and Casey Plummer at the Caldwell Zoo in particular for communicating with us regarding this case. We thank Dr. Thomas M. Craig in the Department of Veterinary Pathobiology, College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University, for the helpful contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhaboubi, A.R., Pollard, D.A. & Holman, P.J. Molecular and morphological characterization of a haemogregarine in the alligator snapping turtle, Macrochelys temminckii (Testudines: Chelydridae). Parasitol Res 116, 207–215 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5280-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5280-2