Abstract
Purpose
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor caused by melanocytes and associated with high mortality rates. This study aims to investigate the specific mechanism of ZWZ-3 in melanoma proliferation and metastasis.
Methods
RNA sequencing was performed to identify the effect of ZWZ-3 on gene expression. siRNA was used to inhibit BIRC5 gene expression in the B16F10 cell line. A zebrafish tumor model was used to assess the therapeutic effect of ZWZ-3 in vivo. Mechanistic insights into the inhibition of tumor metastasis by ZWZ-3 were obtained through analysis of tumor tissue sections in mice.
Results
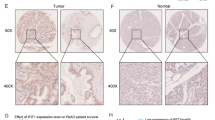
Our findings demonstrated that ZWZ-3 suppressed melanoma cell proliferation and migration. We performed RNA sequencing in melanoma cells after the treatment with ZWZ-3 and found that Birc5, which is closely associated with tumor metastasis, was significantly down-regulated. Bioinformatics analysis and the immuno-histochemical results of tissue chips for melanoma further confirmed the high expression of BIRC5 in melanoma and its effect on disease progression. Moreover, Birc5 knock-down significantly inhibited melanoma cell proliferation and metastasis, which was correlated with the β-catenin/HIF-1α/VEGF/MMPs pathway. Additionally, ZWZ-3 significantly inhibited tumor growth in the zebrafish tumor model without any evident side effects. Histological and immuno-histochemical analyses revealed that ZWZ-3 inhibited tumor cell metastasis by down-regulating HIF-1α, VEGF, and MMP9.
Conclusion
Our findings revealed that ZWZ-3 could downregulate BIRC5 and inhibit melanoma proliferation and metastasis through the β-catenin/HIF-1α/VEGF/MMPs pathway. Therefore, BIRC5 represents a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of melanoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable requests.
References
Altieri DC (2008) Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 8:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2293
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3:917–921. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0897-917
Connolly DT (1991) Vascular permeability factor: a unique regulator of blood vessel function. J Cell Biochem 47:219–223. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.240470306
Davis LE, Shalin SC, Tackett AJ (2019) Current state of melanoma diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Biol Ther 20:1366–1379. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2019.1640032
de Castro JG, Puglisi F, de Azambuja E, El SN, Awada A (2006) Angiogenesis and cancer: a cross-talk between basic science and clinical trials (the “do ut des” paradigm). Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 59:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2006.02.007
Dimitrov-Markov S, Perales-Paton J, Bockorny B, Dopazo A, Munoz M, Banos N, Bonilla V, Menendez C, Duran Y, Huang L, Perea S, Muthuswamy SK, Al-Shahrour F, Lopez-Casas PP, Hidalgo M (2020) Discovery of new targets to control metastasis in pancreatic cancer by single-cell transcriptomics analysis of circulating tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther 19:1751–1760. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-1166
Dvorak HF (2002) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol 20:4368–4380. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2002.10.088
Fernandez JG, Rodriguez DA, Valenzuela M, Calderon C, Urzua U, Munroe D, Rosas C, Lemus D, Diaz N, Wright MC, Leyton L, Tapia JC, Quest AF (2014) Survivin expression promotes VEGF-induced tumor angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt enhanced beta-catenin/Tcf-Lef dependent transcription. Mol Cancer 13:209. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-209
Foda HD, Zucker S (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Drug Discov Today 6:478–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1359-6446(01)01752-4
Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR, Sondak VK, Long GV, Ross MI, Lazar AJ, Faries MB, Kirkwood JM, McArthur GA, Haydu LE, Eggermont A, Flaherty KT, Balch CM, Thompson JF (2017) Melanoma staging: evidence-based changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin 67:472–492. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21409
Hanna SC, Krishnan B, Bailey ST, Moschos SJ, Kuan PF, Shimamura T, Osborne LD, Siegel MB, Duncan LM, O’Brien ER, Superfine R, Miller CR, Simon MC, Wong KK, Kim WY (2013) HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha independently activate SRC to promote melanoma metastases. J Clin Invest 123:2078–2093. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI66715
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1027. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.06.081
Hwang HW, Baxter LL, Loftus SK, Cronin JC, Trivedi NS, Borate B, Pavan WJ (2014) Distinct microRNA expression signatures are associated with melanoma subtypes and are regulated by HIF1A. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 27:777–787. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcmr.12255
Khosravi SP, Fernandez PI (2008) Tumoral angiogenesis: review of the literature. Cancer Invest 26:104–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357900701662509
Kraus C, Liehr T, Hulsken J, Behrens J, Birchmeier W, Grzeschik KH, Ballhausen WG (1994) Localization of the human beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1) to 3p21: a region implicated in tumor development. Genomics 23:272–274. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1994.1493
Leight JL, Tokuda EY, Jones CE, Lin AJ, Anseth KS (2015) Multifunctional bioscaffolds for 3D culture of melanoma cells reveal increased MMP activity and migration with BRAF kinase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:5366–5371. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1505662112
Lin TY, Chan HH, Chen SH, Sarvagalla S, Chen PS, Coumar MS, Cheng SM, Chang YC, Lin CH, Leung E, Cheung C (2020) BIRC5/Survivin is a novel ATG12-ATG5 conjugate interactor and an autophagy-induced DNA damage suppressor in human cancer and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Autophagy 16:1296–1313. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1671643
Liu Z, Wang H, Sun C, He Y, Xia T, Wang J, Xiong X, Zhang Q, Yang S, Liu L (2022) ZWZ-3, a fluorescent probe targeting mitochondria for melanoma imaging and therapy. Front Pharmacol 13:829684. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.829684
Mareel M, Oliveira MJ, Madani I (2009) Cancer invasion and metastasis: interacting ecosystems. Virchows Arch 454:599–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-009-0784-0
McCrea PD, Turck CW, Gumbiner B (1991) A homolog of the armadillo protein in Drosophila (plakoglobin) associated with E-cadherin. Science 254:1359–1361. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1962194
McKenzie JA, Grossman D (2012) Role of the apoptotic and mitotic regulator survivin in melanoma. Anticancer Res 32:397–404
O’Grady A, Dunne C, O’Kelly P, Murphy GM, Leader M, Kay E (2007) Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2 in non-melanoma skin cancer: implications for tumour progression. Histopathology 51:793–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02885.x
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1911
Pittayapruek P, Meephansan J, Prapapan O, Komine M, Ohtsuki M (2016) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 17:868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060868
Quan T, Qin Z, Xia W, Shao Y, Voorhees JJ, Fisher GJ (2009) Matrix-degrading metalloproteinases in photoaging. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 14:20–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/jidsymp.2009.8
Resnik E (1997) beta-Catenin—one player, two games. Nat Genet 16:9–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0597-9
Riggleman B, Schedl P, Wieschaus E (1990) Spatial expression of the Drosophila segment polarity gene armadillo is post-transcriptionally regulated by wingless. Cell 63:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90451-j
Rotte A, Martinka M, Li G (2012) MMP2 expression is a prognostic marker for primary melanoma patients. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 35:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-012-0080-x
Sun B, Zhang D, Zhang S, Zhang W, Guo H, Zhao X (2007) Hypoxia influences vasculogenic mimicry channel formation and tumor invasion-related protein expression in melanoma. Cancer Lett 249:188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2006.08.016
Tang Q, Efe G, Chiarella AM, Leung J, Chen M, Yamazoe T, Su Z, Pitarresi JR, Li J, Islam M, Karakasheva T, Klein-Szanto AJ, Pan S, Hu J, Natsugoe S, Gu W, Stanger BZ, Wong KK, Diehl JA, Bass AJ, Nakagawa H, Murphy ME, Rustgi AK (2021) Mutant p53 regulates Survivin to foster lung metastasis. Genes Dev 35:528–541. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.340505.120
Targen S, Konu O (2021) Zebrafish xenotransplantation models for studying gene function and drug treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer 52:1248–1265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-021-00782-z
Vallee A, Guillevin R, Vallee JN (2018) Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in gliomas. Rev Neurosci 29:71–91. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2017-0032
van Rooijen E, Fazio M, Zon LI (2017) From fish bowl to bedside: the power of zebrafish to unravel melanoma pathogenesis and discover new therapeutics. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 30:402–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcmr.12592
Wang N, Huang X, Cheng J (2022) BIRC5 promotes cancer progression and predicts prognosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. PeerJ 10:e12871. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12871
Wheatley SP, Altieri DC (2019) Survivin at a glance. J Cell Sci 132:s223826. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.223826
Yen JH, Chio WT, Chuang CJ, Yang HL, Huang ST (2022) Improved wound healing by naringin associated with MMP and the VEGF pathway. Molecules 27:1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051695
Zhao Y, Liu S, Li S, Zhang G, Tian A, Wan Y (2022) BIRC5 regulates inflammatory tumor microenvironment-induced aggravation of penile cancer development in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 22:448. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09500-9
Acknowledgements
We thank Bullet Edits Limited for the linguistic editing and proofreading of the manuscript. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82003716), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2022YFS0631), Luzhou Science and Technology Projects (2022‐JYJ‐141), Southwest Medical University School‐level Project Fund (2022QN044).
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82003716), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2022YFS0631), Luzhou Science and Technology Projects (2022‐JYJ‐141), Southwest Medical University School‐level Project Fund (2022QN044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QH and LL designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. YH and JX analyzed the data. QH, JW and TX performed the experiments. CL and XX conceived and supervised the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The protocol of this research has been approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University (No. KY2023049).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, Q., He, Y., Li, C. et al. Downregulated BIRC5 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of melanoma through the β-catenin/HIF-1α/VEGF/MMPs pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 16797–16809 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05425-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05425-3