Abstract
Background and aim
According to previous reports, GTPase of immunity-associated protein 6 (GIMAP6) is essential for autophagy. However, it is unclear how GIMAP6 affects the development and tumor immunity of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Methods
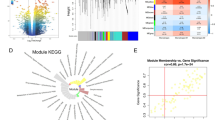
In the present study, the role of GIMAP6 in vivo and in vitro was examined using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, western blotting, and Cell Counting Kit-8, colony formation and Transwell assays. Datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas and Genotype-Tissue Expression databases were thoroughly analyzed using R software. A nomogram was created using GIMAP6 and prognostic characteristics. Gene Ontology, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis were applied to explore the potential mechanism of GIMAP6 in lung cancer. The link between GIMAP6 and the immunological landscape was studied using single-cell RNA sequencing datasets from Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) 2.0 and Tumor Immune Single-cell Hub.
Results
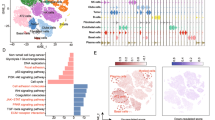
Patients with high GIMAP6 expression had improved overall and disease-specific survival compared with those patients with low GIMAP6 expression. According to the receiver operating characteristic and calibration curve, the nomogram based on T stage, N stage and GIMAP6 had predictive value for prognosis. According to functional enrichment analysis, GIMAP6 was primarily involved in T-cell receptor signaling pathway, chemokine signaling pathway, cytokine and cytokine receptor interaction. GIMAP6 was shown to be favorably linked with the infiltration of immune cells and immune-related molecules, including cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4, programmed death-ligand 1, and T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains, by single-cell sequencing and TIMER2.0 analysis. The role of GIMAP6 in lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion, migration and immunity was experimentally verified.
Conclusion
These findings confirmed that GIMAP6 was an effective prognostic molecule that was involved in the regulation of the immune microenvironment of LUAD, and may become a predictor for the efficacy of immunotherapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC, Debnath J (2019) Targeting autophagy in cancer: recent advances and future directions. Cancer Discov 9(9):1167–1181
Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V, Fearon DF, Merad M, Coussens LM, Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Hedrick CC et al (2018) Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med 24(5):541–550
Cheng Y, Wang C, Wang H, Zhang Z, Yang X, Dong Y, Ma L, Luo J (2022) Combination of an autophagy inhibitor with immunoadjuvants and an anti-PD-L1 antibody in multifunctional nanoparticles for enhanced breast cancer immunotherapy. BMC Med 20(1):411
Datta P, Webb LM, Avdo I, Pascall J, Butcher GW (2017) Survival of mature T cells in the periphery is intrinsically dependent on GIMAP1 in mice. Eur J Immunol 47(1):84–93
Drilon A, Bergagnini I, Delasos L, Sabari J, Woo KM, Plodkowski A, Wang L, Hellmann MD, Joubert P, Sima CS et al (2016) Clinical outcomes with pemetrexed-based systemic therapies in RET-rearranged lung cancers. Ann Oncol 27(7):1286–1291
Evan GI, Vousden KH (2001) Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature 411(6835):342–348
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ, Powell SF et al (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378(22):2078–2092
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N, Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L et al (2015) Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372(21):2018–2028
Gettinger SN, Choi J, Mani N, Sanmamed MF, Datar I, Sowell R, Du VY, Kaftan E, Goldberg S, Dong W et al (2018) A dormant TIL phenotype defines non-small cell lung carcinomas sensitive to immune checkpoint blockers. Nat Commun 9(1):3196
Haq S, Wang H, Grondin J, Banskota S, Marshall JK, Khan II, Chauhan U, Cote F, Kwon YH, Philpott D et al (2021) Disruption of autophagy by increased 5-HT alters gut microbiota and enhances susceptibility to experimental colitis and Crohn’s disease. Sci Adv 7(45):eabi6442
Heinonen MT, Kanduri K, Lähdesmäki HJ, Lahesmaa R, Henttinen TA (2015) Tubulin- and actin-associating GIMAP4 is required for IFN-γ secretion during Th cell differentiation. Immunol Cell Biol 93(2):158–166
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD, Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger SN et al (2014) Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515(7528):563–567
Hu F, Song D, Yan Y, Huang C, Shen C, Lan J, Chen Y, Liu A, Wu Q, Sun L et al (2021) IL-6 regulates autophagy and chemotherapy resistance by promoting BECN1 phosphorylation. Nat Commun 12(1):3651
Huang Z, Zhang W, Gao C, Ji B, Chi X, Zheng W, Wang HL (2016) Dysregulation of GTPase IMAP family members in hepatocellular cancer. Mol Med Rep 14(5):4119–4123
Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, Fu W, Gaw BL, Harvey JD, Henrikson HJ, Lu D, Pennini A, Xu R et al (2022) Cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life years for 29 cancer groups from 2010 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. JAMA Oncol 8(3):420–444
Li ZL, Zhang HL, Huang Y, Huang JH, Sun P, Zhou NN, Chen YH, Mai J, Wang Y, Yu Y et al (2020) Autophagy deficiency promotes triple-negative breast cancer resistance to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity by blocking tenascin-C degradation. Nat Commun 11(1):3806
Ligeon LA, Pena-Francesch M, Vanoaica LD, Núñez NG, Talwar D, Dick TP, Münz C (2021) Oxidation inhibits autophagy protein deconjugation from phagosomes to sustain MHC class II restricted antigen presentation. Nat Commun 12(1):1508
Limoges MA, Cloutier M, Nandi M, Ilangumaran S, Ramanathan S (2021) The GIMAP family proteins: an incomplete puzzle. Front Immunol 12:679739
Nakagawa K, Garon EB, Seto T, Nishio M, Ponce Aix S, Paz-Ares L, Chiu CH, Park K, Novello S, Nadal E et al (2019) Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 20(12):1655–1669
Nitta T, Takahama Y (2007) The lymphocyte guard-IANs: regulation of lymphocyte survival by IAN/GIMAP family proteins. Trends Immunol 28(2):58–65
Pardoll DM (2012) The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12(4):252–264
Pascall JC, Webb LMC, Eskelinen EL, Innocentin S, Attaf-Bouabdallah N, Butcher GW (2018) GIMAP6 is required for T cell maintenance and efficient autophagy in mice. PLoS One 13(5):e0196504
Patterson AR, Endale M, Lampe K, Aksoylar HI, Flagg A, Woodgett JR, Hildeman D, Jordan MB, Singh H, Kucuk Z et al (2018) Gimap5-dependent inactivation of GSK3β is required for CD4(+) T cell homeostasis and prevention of immune pathology. Nat Commun 9(1):430
Qiao Y, Choi JE, Tien JC, Simko SA, Rajendiran T, Vo JN, Delekta AD, Wang L, Xiao L, Hodge NB et al (2021) Autophagy inhibition by targeting PIKfyve potentiates response to immune checkpoint blockade in prostate cancer. Nat Cancer 2:978–993
Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, Zhou C, Reungwetwattana T, Cheng Y, Chewaskulyong B et al (2020) Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med 382(1):41–50
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe S et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375(19):1823–1833
Sarode P, Zheng X, Giotopoulou GA, Weigert A, Kuenne C, Günther S, Friedrich A, Gattenlöhner S, Stiewe T, Brüne B et al (2020) Reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages by targeting β-catenin/FOSL2/ARID5A signaling: a potential treatment of lung cancer. Sci Adv 6(23):eaaz6105
Schnell S, Démollière C, van den Berk P, Jacobs H (2006) Gimap4 accelerates T-cell death. Blood 108(2):591–599
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 70(1):7–30
Taube JM, Anders RA, Young GD, Xu H, Sharma R, McMiller TL, Chen S, Klein AP, Pardoll DM, Topalian SL et al (2012) Colocalization of inflammatory response with B7–h1 expression in human melanocytic lesions supports an adaptive resistance mechanism of immune escape. Sci Transl Med 4(127):127ra137
Velcheti V, Schalper KA, Carvajal DE, Anagnostou VK, Syrigos KN, Sznol M, Herbst RS, Gettinger SN, Chen L, Rimm DL (2014) Programmed death ligand-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lab Invest 94(1):107–116
Wong VW, Saunders AE, Hutchings A, Pascall JC, Carter C, Bright NA, Walker SA, Ktistakis NT, Butcher GW (2010) The autoimmunity-related GIMAP5 GTPase is a lysosome-associated protein. Self Nonself 1(3):259–268
Wu F, Wang L, Zhou C (2021) Lung cancer in China: current and prospect. Curr Opin Oncol 33(1):40–46
Yao Y, Du Jiang P, Chao BN, Cagdas D, Kubo S, Balasubramaniyam A, Zhang Y, Shadur B, NaserEddin A, Folio LR et al (2022) GIMAP6 regulates autophagy, immune competence, and inflammation in mice and humans. J Exp Med. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20201405
Zeng D, Li M, Zhou R, Zhang J, Sun H, Shi M, Bin J, Liao Y, Rao J, Liao W (2019) Tumor microenvironment characterization in gastric cancer identifies prognostic and immunotherapeutically relevant gene signatures. Cancer Immunol Res 7(5):737–750
Acknowledgements
We thank Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital for providing us with pathological specimens.
Funding
This present research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (to Richeng Jiang) (No. 82172620).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XC and ZL: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, writing-original draft. XC and JZ: software, validation, formal analysis. XW and JZ: software, validation, formal analysis. XC and QW: investigation, resources. XC, ZL, XW, JZ, QW, and KC: investigation, resources. RJ and XW: supervision. ZL: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the institutional Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin, China (approval number was bc2022263).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Li, Z., Wang, X. et al. Investigation and verification of GIMAP6 as a robust biomarker for prognosis and tumor immunity in lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 11041–11055 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04980-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04980-z