Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the prognostic value of gross tumor volume (GTV) in early-stage extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTCL) treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and explore the interactive effect of GTV and radiotherapy (RT) dose on locoregional recurrence (LRR).
Methods
The data of 319 early-stage ENKTCL patients who underwent IMRT were reviewed retrospectively. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and locoregional control (LRC) were estimated using Kaplan–Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards regression was performed to identify independent risk factors for survival outcomes. Penalized spline regression was used to flexibly model the association of continuous predictors (GTV and RT dose) with mortality, progression, and relapse.
Results
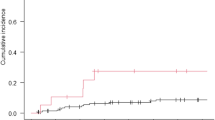
The 5-year OS, PFS, and LRC for the entire cohort were 72.9, 64.4, and 89.9%, respectively. The risks of disease mortality, progression, and recurrence increased steadily with increasing GTV. Patients with GTV < 35 mL had significantly higher 5-year OS (83.0% vs. 59.4%; P < 0.001), PFS (76.7% vs. 48.4%; P < 0.001), and lower 5-year cumulative LRR rate (4.9% vs. 14.5%; P = 0.004), than patients with GTV ≥ 35 mL. The risk of LRR was low with RT doses of 50-56 Gy, independent of GTV. For patients with GTV ≥ 35 mL, dose ≥ 56 Gy was not associated with decreased LRR.
Conclusion
Larger GTV is associated with worse survival and higher LRR in early-stage ENKTCL patients treated with IMRT. A dose of 50–56 Gy may be appropriate to achieve lower risk of LRR, regardless of GTV.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data avaliability
Research data are not available at this time.
References
Alaggio R, Amador C, Anagnostopoulos I, Attygalle AD, Araujo IBDO, Berti E, et al. (2022) The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia. 36:1720–1748
Baumann M, Krause M, Hill R (2008) Exploring the role of cancer stem cells in radioresistance. Nat Rev Cancer 8:545–554. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2419
Bi XW, Li YX, Fang H, Jin J, Wang WH, Wang SL et al (2013) High-dose and extended-field intensity modulated radiation therapy for early-stage NK/T-cell lymphoma of Waldeyer’s ring: dosimetric analysis and clinical outcome. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:1086–1093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.08.040
Bradley AJ, Carrington BM, Lawrance JA, Ryder WD, Radford JA (1999) Assessment and significance of mediastinal bulk in Hodgkin’s disease: comparison between computed tomography and chest radiography. J Clin Oncol 17:2493–2498. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1999.17.8.2493
Chen SY, Yang Y, Qi SN, Wang Y, Hu C, He X et al (2021) Validation of nomogram-revised risk index and comparison with other models for extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma in the modern chemotherapy era: indication for prognostication and clinical decision-making. Leukemia 35:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0791-3
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E et al (2014) Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol 32:3059–3068. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.54.8800
Cheung MM, Chan JK, Lau WH, Ngan RK, Foo WW (2002) Early stage nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: clinical outcome, prognostic factors, and the effect of treatment modality. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 54:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(02)02916-4
Deng XW, Wu JX, Wu T, Zhu SY, Shi M, Su H et al (2018) Radiotherapy is essential after complete response to asparaginase-containing chemotherapy in early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma: a multicenter study from the China Lymphoma collaborative Group (CLCG). Radiother Oncol 129:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.04.026
Huang H, Zhu J, Yao M, Kim TM, Yoon DH, Cho SG et al (2021) Daratumumab monotherapy for patients with relapsed or refractory natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: an open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 2 study. J Hematol Oncol 14:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-01020-y
Huang MJ, Jiang Y, Liu WP, Li ZP, Li M, Zhou L et al (2008) Early or up-front radiotherapy improved survival of localized extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type in the upper aerodigestive tract. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.05.073
Isobe K, Uno T, Tamaru J, Kawakami H, Ueno N, Wakita H et al (2006) Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: the significance of radiotherapeutic parameters. Cancer 106:609–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.21656
Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Jaccard A, Chng WJ, Lim ST, Hong H et al (2016) A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 17:389–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00533-1
Koom WS, Chung EJ, Yang WI, Shim SJ, Suh CO, Roh JK et al (2004) Angiocentric T-cell and NK/T-cell lymphomas: radiotherapeutic viewpoints. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1127–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.12.006
Kwong YL, Kim SJ, Tse E, Oh SY, Kwak JY, Eom HS et al (2018) Sequential chemotherapy/radiotherapy was comparable with concurrent chemoradiotherapy for stage I/II NK/T-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol 29:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx684
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH et al (2006) Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 24:612–618. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.04.1384
Li YX, Yao B, Jin J, Wang WH, Liu YP, Song YW et al (2006) Radiotherapy as primary treatment for stage IE and IIE nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 24:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.03.2573
Liu W, Li Y, Zhu H, Pei Q, Tan F, Song X et al (2021) The relationship between primary gross tumor volume and tumor response of locally advanced rectal cancer: pGTV as a more accurate tumor size indicator. J Invest Surg 34:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941939.2019.1615153
Pfreundschuh M, Ho AD, Cavallin-Stahl E, Wolf M, Pettengell R, Vasova I et al (2008) Prognostic significance of maximum tumour (bulk) diameter in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma treated with CHOP-like chemotherapy with or without rituximab: an exploratory analysis of the MabThera international trial group (MInT) study. Lancet Oncol 9:435–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70078-0
Qi SN, Xu LM, Yuan ZY, Wu T, Zhu SY, Shi M et al (2019) Effect of primary tumor invasion on treatment and survival in extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma in the modern chemotherapy era: a multicenter study from the China Lymphoma collaborative group (CLCG). Leuk Lymphoma 60:2669–2678. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2019.1602265
Qi SN, Yang Y, Zhang YJ, Huang HQ, Wang Y, He X et al (2020) Risk-based, response-adapted therapy for early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma in the modern chemotherapy era: a China Lymphoma collaborative group study. Am J Hematol 95:1047–1056. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25878
Qi SN, Li YX, Specht L, Oguchi M, Tsang R, Ng A et al (2021) Modern radiation therapy for extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma: risk-adapted therapy, target volume, and dose guidelines from the International Lymphoma radiation oncology group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 110:1064–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.02.011
Reymen B, Van Loon J, van Baardwijk A, Wanders R, Borger J, Dingemans AM et al (2013) Total gross tumor volume is an independent prognostic factor in patients treated with selective nodal irradiation for stage I to III small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:1319–1324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.10.003
Sze WM, Lee AW, Yau TK, Yeung RM, Lau KY, Leung SK et al (2004) Primary tumor volume of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: prognostic significance for local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.10.027
Vargo JA, Patel A, Glaser SM, Balasubramani GK, Farah RJ, Marks SM et al (2017) The impact of the omission or inadequate dosing of radiotherapy in extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, in the United States. Cancer 123:3176–3185. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30697
Wang H, Li YX, Wang WH, Jin J, Dai JR, Wang SL et al (2012) Mild toxicity and favorable prognosis of high-dose and extended involved-field intensity-modulated radiotherapy for patients with early-stage nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:1115–1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.039
Wu RY, Liu K, Wang WH, Jin J, Song YW, Wang SL et al (2017) Patterns of primary tumor invasion and regional lymph node spread based on magnetic resonance imaging in early-stage nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: implications for clinical target volume definition and prognostic significance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 97:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.09.013
Wu T, Yang Y, Zhu SY, Shi M, Su H, Wang Y et al (2018) Risk-adapted survival benefit of IMRT in early-stage NKTCL: a multicenter study from the China Lymphoma Collaborative Group. Blood Adv 2:2369–2377. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2018021311
Yahalom J, Illidge T, Specht L, Hoppe RT, Li YX, Tsang R et al (2015) Modern radiation therapy for extranodal lymphomas: field and dose guidelines from the International Lymphoma radiation oncology group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 92:11–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.01.009
Yamaguchi M, Suzuki R, Oguchi M, Asano N, Amaki J, Akiba T et al (2017) Treatments and outcomes of patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma diagnosed between 2000 and 2013: a cooperative study in Japan. J Clin Oncol 35:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.68.1619
Yang Y, Zhang YJ, Zhu Y, Cao JZ, Yuan ZY, Xu LM et al (2015a) Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in previously untreated patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a multicenter study. Leukemia 29:1571–1577. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.44
Yang Y, Zhu Y, Cao JZ, Zhang YJ, Xu LM, Yuan ZY et al (2015b) Risk-adapted therapy for early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma: analysis from a multicenter study. Blood 126:1424–1432. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-04-639336
Yang Y, Cao JZ, Lan SM, Wu JX, Wu T, Zhu SY et al (2017) Association of improved locoregional control with prolonged survival in early-stage extranodal nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. JAMA Oncol 3:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5094
Zheng X, He X, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhang LL, Qu BL et al (2021) Association of improved overall survival with decreased distant metastasis following asparaginase-based chemotherapy and radiotherapy for intermediate- and high-risk early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma: a CLCG study. ESMO Open 6:100206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100206
Acknowledgements
The present work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970185), and the National Key Research and Development of China (2020AAA0109504).
Funding
The present work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970185), and the National Key Research and Development of China (2020AAA0109504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YXL and SNQ: contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by YMZ, XL, YY, SLW, HF, YWS, YPL, JJ, NL, NNL, HJ, YT, BC, WWZ, YRZ, KM, JRD and MD. Data analysis were performed by YMZ, SNQ and YXL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YMZ and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. SNQ and YXL: made critical revision of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the institutional review board of National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) and Peking Union Medical College (PUMC), China.
Consent to participate
The need for informed consent was waived in view of the retrospective nature of the study.
Consent for publication
The need for informed consent was waived in view of the retrospective nature of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, YM., Liu, X., Yang, Y. et al. Effects of gross tumor volume and radiation dose on survival and locoregional recurrence in early-stage extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 5219–5230 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04472-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04472-6