Abstract
Purpose
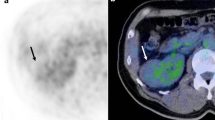
This study investigated the clinical usefulness of F-18 fluorodeoxylucose (FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) for postoperative surveillance in the RCC patients in terms of detectability of recurrence and radiation exposure.
Methods
Three-hundred-and-forty- three RCC patients who underwent surgery and postoperative surveillance were retrospectively included. Conditional recurrent free survival (CRFS) was investigated and diagnostic performance of conventional imaging (CI) which include abdominopelvic CT or/and chest CT was compared to the FDG PET/CT.
Results
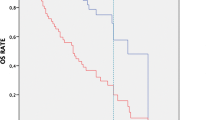
At a median follow-up of 4.3 years (0.5–13.0 years), thirty-nine patients (11.4%) developed recurrence. CRFS of the patients increased over time with greater increment in advanced stage. The sensitivity, specificity, positive-predictive value, negative-predictive value, and accuracy of FDG PET/CT were 92.3%, 97%, 80%, 99.0%, and 96.5% in detecting recurrence, while those values for CI were 89.7%, 97.7%, 83.3%, 98.7%, and 96.8%, respectively. There were no significant differences in these values between FDG PET/CT and CI (McNemar test, p = 0.581). The average radiation dose from FDG PET/CT was around 16.9 ± 3.08 mSv at each follow-up time point. For early stage patients, the average radiation dose from CI was around 26.5 ± 8.57 mSv at each follow-up time point, while this was about 33.0 ± 9.76 mSv for advanced stage patients.
Conclusion
FDG PET/CT exhibited good diagnostic performance in asymptomatic RCC patients after surgery, of a level comparable to that of CI, but with a lower radiation dose.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
The 2007 recommendations of the international commission on radiological protection. (2007) ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP 37:1–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icrp.2007.10.003
Bhatia S (2015) Genetic variation as a modifier of association between therapeutic exposure and subsequent malignant neoplasms in cancer survivors. Cancer 121:648–663. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29096
Chen JL, Appelbaum DE, Kocherginsky M, Cowey CL, Rathmell WK, McDermott DF, Stadler WM (2013) FDG-PET as a predictive biomarker for therapy with everolimus in metastatic renal cell cancer . Cancer Med 2:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.102
Donat SM et al (2013) Follow-up for clinically localized renal neoplasms: AUA guideline. J Urol 190:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2013.04.121
Fuccio C et al (2014) Restaging clear cell renal carcinoma with 18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med 39:e320-324. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000000382
Hendee WR, O’Connor MK (2012) Radiation risks of medical imaging: separating fact from fantasy. Radiology 264:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12112678
Icrp (2008) Radiation dose to patients from radiopharmaceuticals. Addendum 3 to ICRP Publication 53. ICRP Publication 106. Approved by the Commission in October 2007. Ann ICRP 38:1–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icrp.2008.08.003
Jang J et al (2016) Radiation doses of various CT protocols: a multicenter longitudinal observation study. J Korean Med Sci 31(Suppl 1):S24-31. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S1.S24
Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS (2003) Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am 30:843–852
Jewett M (2012) Management of kidney cancer: canadian kidney cancer forum consensus update. Can Urol Assoc J 6:16–22. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.11273
Kim EH, Strope SA (2015) Postoperative surveillance imaging for patients undergoing nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol 33:499–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.08.008
Kumar R, Shandal V, Shamim SA, Jeph S, Singh H, Malhotra A (2010) Role of FDG PET-CT in recurrent renal cell carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun 31:844–850. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNM.0b013e32833d6882
Kwon HW et al (2016) Radiation dose from whole-body f-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography: nationwide survey in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 31(Suppl 1):S69-74. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S1.S69
Lin YK, Gettle L, Raman JD (2013) Significant variability in 10-year cumulative radiation exposure incurred on different surveillance regimens after surgery for pT1 renal cancers: yet another reason to standardize protocols? BJU Int 111:891–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11531.x
Lipsky MJ, Shapiro EY, Hruby GW, McKiernan JM (2013) Diagnostic radiation exposure during surveillance in patients with pT1a renal cell carcinoma. Urology 81:1190–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2012.08.056
Ljungberg B et al (2015) EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur Urol 67:913–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.01.005
Martinez R, de Llano S, Jimenez-Vicioso A, Mahmood S, Carreras-Delgado JL (2010) Clinical impact of (18)F-FDG PET in management of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Rev Esp Med Nucl 29:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.remn.2009.11.008
Mizuno T et al (2015) Clinically significant association between the maximum standardized uptake value on 18F-FDG PET and expression of phosphorylated Akt and S6 kinase for prediction of the biological characteristics of renal cell cancer. BMC Cancer 15:1097. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1097-0
Motzer RJ et al (2015) Kidney cancer, version 3.2015. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 13:151–159
Nakaigawa N et al (2015) FDG PET/CT as a prognostic biomarker in the era of molecular-targeting therapies: max SUVmax predicts survival of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 16:67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2097-4
Nakatani K, Nakamoto Y, Saga T, Higashi T, Togashi K (2011) The potential clinical value of FDG-PET for recurrent renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 79:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.11.019
Nakhoda Z, Torigian DA, Saboury B, Hofheinz F, Alavi A (2013) Assessment of the diagnostic performance of (18)F-FDG-PET/CT for detection and characterization of solid renal malignancies Hell. J Nucl Med 16:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1967/s002449910067
Ozulker T, Ozulker F, Ozbek E, Ozpacaci T (2011) A prospective diagnostic accuracy study of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the evaluation of indeterminate renal masses. Nucl Med Commun 32:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNM.0b013e3283442e3b
Pantuck AJ, Zisman A, Belldegrun AS (2001) The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 166:1611–1623
Park JW, Jo MK, Lee HM (2009) Significance of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/computed tomography for the postoperative surveillance of advanced renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 103:615–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08150.x
Park YH, Baik KD, Lee YJ, Ku JH, Kim HH, Kwak C (2012) Late recurrence of renal cell carcinoma >5 years after surgery: clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis. BJU Int 110:E553-558. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11246.x
Rohren EM, Turkington TG, Coleman RE (2004) Clinical applications of PET in oncology. Radiology 231:305–332. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2312021185
Shuryak I, Sachs RK, Brenner DJ (2010) Cancer risks after radiation exposure in middle age. J Natl Cancer Inst 102:1628–1636. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djq346
Siegel RL, Miller KD (2016) Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21332
Takahashi M et al (2015) Preoperative evaluation of renal cell carcinoma by using 18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med 40:936–940. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000000875
Ueno D et al (2012) Early assessment by FDG-PET/CT of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors is predictive of disease course. BMC Cancer 12:162. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-162
Wang HY, Ding HJ, Chen JH, Chao CH, Lu YY, Lin WY, Kao CH (2012) Meta-analysis of the diagnostic performance of [18F]FDG-PET and PET/CT in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 12:464–474. https://doi.org/10.1102/1470-7330.2012.0042
Williamson TJ, Pearson JR, Ischia J, Bolton DM, Lawrentschuk N (2016) Guideline of guidelines: follow-up after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 117:555–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13384
Funding
Funding information is not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Lee, HY. & Lee, S. Role of F-18 FDG PET/CT in the follow-up of asymptomatic renal cell carcinoma patients for postoperative surveillance: based on conditional survival analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 215–224 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03688-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03688-2