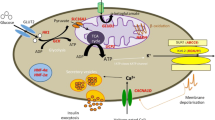
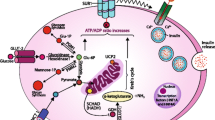
Abstract
Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia (HH) is a major cause of hypoglycaemia in the neonatal period, infancy and childhood. It is caused by unsuppressed insulin secretion in the setting of hypoglycaemia and carries a high risk of significant neurological sequelae, such as cognitive impairment. Genetic mutations have been implicated in the pathogenesis of the condition. Other causes include intra-uterine growth retardation, perinatal asphyxia, maternal diabetes mellitus and syndromes, such as Beckwith-Wiedemann. Based on the aetiology, the clinical presentation can range from absence of symptoms to the typical adrenergic symptoms and coma and even death. The diagnosis is based on biochemical findings and the gold-standard imaging technique is 18F-DOPA PET/CT scanning. Treatment options involve medications, such as diazoxide, nifedipine, glucagon and octreotide, as well as surgery. Novel treatment, such as long-acting octreotide, lanreotide and sirolimus, may be used as an alternative to pancreatectomy. Potential future medical treatments include exendin, a GLP-1 receptor antagonist, and glucagon infusion via a pump.
Conclusion: Advances in the fields of genetic testing, imaging techniques and medical treatment are beginning to provide novel insights into earlier detection, less invasive treatment approaches and fewer complications associated with the complex entity of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia.
What is Known: • HH is caused by dysregulated insulin release from the β cell due to genetic mutations and carries a risk for complications, such as neurocognitive impairment. 18F-DOPA PET/CT scanning is presented as the gold-standard imaging technique currently in children with hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. • Clinical presentation is heterogeneous and treatment options include medical therapy and pancreatectomy. | |
What is New: • 18F-DOPA PET/CT is indicated in suspected focal CHI due to paternal transmitted mutations in ABCC8 or KCNJ11. • Novel treatment options have been introduced, such as long-acting octreotide, lanreotide, sirolimus and selective nonpeptide somatostatin receptor subtype 5 (SSTR5) agonists. Future medical treatments include exendin, a GLP-1 antagonist, and glucagon infusion via a pump. However, all these options are off-label at present. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- EIF2S3:
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit gamma
- 18F-L-DOPA:
-
18-Fluoro-L-dihydroxyphenylalanine
- FOXA2:
-
Forkhead box A2
- GCK:
-
Glucokinase
- GH:
-
Growth hormone
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GLUT2:
-
Glucose transporter 2
- GLUD1:
-
Glutamate dehydrogenase 1
- HA:
-
Hyperammonia
- HADH:
-
3-hyrdoxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase
- HH:
-
Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia
- HI:
-
Hyperinsulinism
- HK1:
-
Hexokinase 1
- HNF1A:
-
Homeobox A
- HNF4:
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- KATP channels:
-
ATP-sensitive potassium channels
- Kir6.2:
-
Inward-rectifier potassium 6.2
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PGM1:
-
Phosphoglucomutase 1
- SLC16A1:
-
Solute carrier family 16 member 1
- SSTR:
-
Somatostatin receptor
- SUR1:
-
Sulfonylurea receptor 1
- TSH:
-
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
References
Ajala ON, Huffman DM, Ghobrial II (2016) Glucokinase mutation-a rare cause of recurrent hypoglycemia in adults: a case report and literature review. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect 6:32983
Amato LA, Quigley CA, Neville KA, Hameed S, Verge CF, Woodhead HJ, Walker JL (2015) Sirolimus treatment of severe congenital hyperinsulinism. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 2015:123
Antwi K, Fani M, Heye T, Nicolas G, Rottenburger C, Kaul F, Merkle E, Zech CJ, Boll D, Vogt DR, Gloor B, Christ E, Wild D (2018) Comparison of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) PET/CT, SPECT/CT and 3T MRI for the localization of occult insulinomas: evaluation of diagnostic accuracy in a prospective crossover imaging study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45:2318–2327
Arnoux JB, Verkarre V, Saint-Martin C, Montravers F, Brassier A, Valayannopoulos V, Brunelle F, Fournet JC, Robert JJ, Aigrain Y, Bellanné-Chantelot C, de Lonlay P (2011) Congenital hyperinsulinism: current trends in diagnosis and therapy. Orphanet J Rare Dis 6:63
Ashcroft FM, Harrison DE, Ashcroft SJ (1984) Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic β-cells. Nature 312:446–448
Avatapalle HB, Banerjee I, Shah S, Pryce M, Nicholson J, Rigby L, Caine L, Didi M, Skae M, Ehtisham S et al (2013) Abnormal neurodevelopmental outcomes are common in children with transient congenital hyperinsulinism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:60
Aynsley-Green A, Hussain K, Hall J, Saudubray JM, Nihoul-Fékété C, De Lonlay-Debeney P, Brunelle F, Otonkoski T, Thornton P, Lindley KJ (2000) Practical management of hyperinsulinism in infancy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 82:F98–F107
Banerjee I, Avatapalle B, Padidela R, Stevens A, Cosgrove K, Clayton P, Dunne M (2013) Integrating genetic and imaging investigations into the clinical management of congenital hyperinsulinism. Clin Endocrinol 78:803–813
Baş F, Darendeliler F, Demirkol D, Bundak R, Saka N, Günöz H (1999) Successful therapy with calcium channel blocker (nifedipine) in persistent neonatal hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 12:873–878
Beltrand J, Caquard M, Arnoux J-B, Laborde K, Velho G, Verkarre V, Rahier J, Brunelle F, Nihoul-Fekete C, Saudubray JM, Robert JJ, de Lonlay P (2012) Glucose metabolism in 105 children and adolescents after pancreatectomy for congenital hyperinsulinism. Diabetes Care 35:198–203
Blomberg BA, Moghbel MC, Saboury B, Stanley CA, Alavi A (2013) The value of radiologic interventions and 18F-DOPA PET in diagnosing and localizing focal congenital hyperinsulinism: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Imaging Biol 15:97–105
Bruninig GJ (1990) Recent advances in hyperinsulinism and the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Pediatr 2:758–765
Calabria AC, Li C, Gallagher PR, Stanley CA, De León DD (2012) GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin-(9-39) elevates fasting blood glucose levels in congenital hyperinsulinism owing to inactivating mutations in the ATP-sensitive K+ channel. Diabetes 61:2585–2591
Cartier EA, Conti LR, Vandenberg CA, Shyng SL (2001) Defective trafficking and function of KATP channels caused by a sulfonylurea receptor 1 mutation associated with persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. PNAS 98:2882–2887
Christesen HB, Tribble ND, Molven A, Siddiqui J, Sandal T, Brusgaard K, Ellard S, Njolstad PR, Alm J, Brock Jacobsen B et al (2008) Activating glucokinase (GCK) mutations as a cause of medically responsive congenital hyperinsulinism: prevalence in children and characterisation of a novel GCK mutation. Eur J Endocrinol 159:27–34
de Lonlay P, Cornier-Daire V, Amiel J, Touati G, Goldenberg A, Fournet JC, Brunelle F, Nihoul-Fekete C, Rahier J, Junien C, Robert JJ, Saudubreay JM (2002) Facial appearance in persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycaemia. Am J Med Genet 111:130–133
Dehdashtian M (2014) Reversible pulmonary hypertension in an infant treated with diazoxide. APJMT 3:84–86
Demirbilek H, Hussain K (2017) Congenital hyperinsulinism: diagnosis and treatment update. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 9:69–87
Dunne MJ, Kane C, Shepherd RM, Sanchez JA, James RF, Johnson PR, Aynsley- Green A, Lu S, Clement JP IV, Lindley KJ et al (1997) Familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy and mutations in the sulfonylurea receptor. N Engl J Med 336:703–706
Durmaz E, Flanagan SE, Parlak M, Ellard S, Akcurin S, Bircan I (2014) A combination of nifedipine and octreotide treatment in an hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemic infant. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 6:119–121
Eichmann D, Hufnagel M, Quick P, Santer R (1999) Treatment of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia with nifedipine. Eur J Pediatr 158:204–206
Flanagan SE, Kapoor RR, Hussain K (2011) Genetics of congenital hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Semin Pediatr Surg 20:13–17
Fournet JC, Junien C (2003) The genetics of neonatal hyperinsulinism. Horm Res 59:30–34
Glaser B, Hirsch HJ, Landau H (1993) Persistent hyper-insulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy: long-term octreotide treatment without pancreatectomy. J Pediatr 123:644–650
Glaser B, Thornton PS, Otonkoski T, Junien C (2000) The genetics of neonatal hyperinsulinism. Arch Dis Child 82:79–86
Gregory LC, Ferreira CB, Young-Baird SK, Williams HJ, Harakalova M, van Haaften G, Rahman SA, Gaston-Massuet C, Kelberman D, GOSgene, Qasim W, Camper SA, Dever TE, Shah P, Iain C.A.F., Robinson ICAF, Dattani MT (2019) Impaired EIF2S3 function associated with a novel phenotype of X-linked hypopituitarism with glucose dysregulation. EBioMedicine 42:470–480
Güemes M, Shah P, Silvera S, Morgan K, Gilbert C, Hinchey L, Hussain K (2017) Assessment of nifedipine therapy in hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia due to mutations in the ABCC8 gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102:822–830
Gutgold A, Gutgold DJ, Glaser B, Szalat A (2017) Diagnosis of ABCC8 congenital hyperinsulinism of infancy in a 20-year-old man evaluated for factitious hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102:345–349
Herrera A, Vajravelu ME, Givler S, Mitteer L, Avitabile CM, Lord K, De Leon DD (2018) Prevalence of adverse events in children with congenital hyperinsulinism treated with diazoxide. JCEM 103:4365–4372
Hussain K, Aynsley-Green A (2003) Hyperinsulinism in infancy: understanding the pathophysiology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:1312–1317
Hussain K, Thornton PS, Otonkoski T, Aynsley-Green A (2004) Severe transient neonatal hyperinsulinism associated with hyperlactataemia in non-asphyxiated infants. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 17:203–209
Hussain K, Aynsley-Green A, Stanley CA (2004) Medications used in the treatment of hypoglycemia due to congenital hyperinsulinism of infancy (HI). Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 2:163–167
Hussain K, Clayton PT, Krywawych S, Chatziandreou I, Mills P, Ginbey DW, Geboers AJ, Berger R, van den Berg IE, Eaton S (2005) Hyperinsulinism of infancy associated with a novel splice site mutation in the SCHAD gene. J Pediatr 146:706–708
Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Clement JP 4th, Namba N, Inazawa J, Gonzalez G, Aguilar- Bryan L, Seino S, Bryan J (1995) Reconstitution of KATP: an inward rectifier subunit plus the sulphonylurea receptor. Science 270:1166–1170
Kane C, Shepherd RM, Squires PE, Johnson PR, James RF, Milla PJ, Aynsley-Green A, Lindley KJ, Dune MJ (1996) Loss of functional KATP channels in pancreatic β-cells causes persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. Nat Med 2:1344–1347
Kapoor RR, Locke J, Colclough K, Wales J, Conn JJ, Hattersley AT, Ellard S, Hussain K (2008) Persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia and maturity-onset diabetes of the young due to heterozygous HNF4A mutations. Diabetes 57:1659–1663
Kapoor RR, James C, Flanagan SE, Ellard S, Eaton S, Hussain K (2009) 3-Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency and hyper-insulinemic hypoglycemia: characterization of a novel mutation and severe dietary protein sensitivity. JCEM 94:2221–2225
Kapoor RR, Flanagan SE, James C, Shield J, Ellard S, Hussain K (2009) Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. Arch Dis Child 94:450–457
Khawash P, Hussain K, Flanagan SE, Chatterjee S, Basak D (2015) Nifedipine in congenital Hyperinsulinism - a case report. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 7:151–154
Laje P, States LJ, Zhuang H, Becker SA, Palladino AA, Stanley CA, Adzick NC (2013) Accuracy of PET/CT scan in the diagnosis of the focal form of congenital hyperinsulinism. J Pediatr Surg 48:388–393
Le Quan Sang KH, Arnoux JB, mamoune A, Saint-Martin C, Bellanne-Chantelot C, Valayannopoulos V, Brassier A, Kayirangwa H, Barbier V, Broissand C, Fabreguettes JR, Charron B, Thalabard JC, de Lonlay P (2012) Successful treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism with long-acting release octreotide. Eur J Endocrinol 166:333–339
Li C, Chen P, Palladino A, Narayan S, Russell LK, Sayed S, Xiong G, Chen J, Stokes D, Butt YM, Jones PM, Collins HW, Cohen NA, Cohen AS, Nissim I, Smith TJ, Strauss AW, Matschinsky FM, Bennett MJ, Stanley CA (2010) Mechanism of hyperinsulinism in short-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency involves activation of glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 285:31806–31818
Lord K, De León DD (2013) Monogenic hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia: current insights into the pathogenesis and management. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 2013:3
Ludwig A, Enke S, Heindorf J, Empting S, Meissner T, Mohnike K (2018) Formal neurocognitive testing in 60 patients with congenital hyperinsulinism. Horm Res Paediatr 89:1–6
Matsuo M, Trapp S, Tanizawa Y, Kioka N, Amachi T, Oka Y, Ashcroft FM, Ueda K (2000) Functional analysis of a mutant sulfonylurea receptor, SUR1-R1420C, that is responsible for persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. J Biol Chem 275:41184–41191
Mazor-Aronovitch K, Gillis D, Lobel D, Hirsch HJ, Pinhas-Hamiel O, Modan-Moses D, Glaser B, Landau H (2007) Long-term neurodevelopmental outcome in conservatively treated congenital hyperinsulinism. Eur J Endocrinol 157:491–497
Mohnike K, Blankenstein O, Pfuetzner A, Potzsch S, Schober E, Steiner S, Hardy OT, Grimberg A, van Waarde WM (2008) Long-term non-surgical therapy of severe persistent congenital hyperinsulinism with glucagon. Horm Res 70:59–64
Nestorowicz A, Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Schoor KP, Wilson BA, Glaser B, Landau H, Stanley CA, Thornton PS, Seino S, Permutt MA (1997) A nonsense mutation in the inward rectifier potassium channel gene, Kir6.2, is associated with familial hyperinsulinism. Diabetes 46:1743–1748
Neylon OM, Moran MM, Pellicano A, Nightingale M, O’Connell MA (2013) Successful subcutaneous glucagon use for persistent hypoglycaemia in congenital hyperinsulinism. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 26:1157–1161
Otonkoski T, Kaminen N, Ustinov J, Lapatto R, Meissner T, Mayatepek E, Kere J, Sipila I (2003) Physical exercise-induced hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia is an autosomal-dominant trait characterized by abnormal pyruvate-induced insulin release. Diabetes 52:199–204
Otonkoski T, Näntö-Salonen K, Seppänen M, Veijola R, Huopio H, Hussain K, Tapanainen P, Eskola O, Parkkola R, Ekstrom K et al (2006) Noninvasive diagnosis of focal hyperinsulinism of infancy with [18F]-DOPA positron emission tomography. Diabetes 55:13–18
Otonkoski T, Jiao H, Kaminen-Ahola N, Tapia-Paez I, Ullah MS, Parton LE, Schuit F, Quintens R, Sipila I, Mayatepek E et al (2007) Physical exercise-induced hypoglycemia caused by failed silencing of monocarboxylate transporter 1 in pancreatic β cells. Am J Hum Genet 81:467–474
Palladino AA, Bennett MJ, Stanley CA (2008) Hyperinsulinism in infancy and childhood: when an insulin level is not always enough. Clin Chem 54:256–263
Pallet N, Legendre C (2013) Adverse events associated with mTOR inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Saf 12:177–186
Pierro A, Nah SA (2011) Surgical management of congenital hyperinsulinism of infancy. Semin Pediatr Surg 20:50–53
Pinney SE, MacMullen C, Becker S, Lin YW, Hanna C, Thornton P, Ganguly A, Shyng SL, Stanley CA (2008) Clinical characteristics and biochemical mechanisms of congenital hyperinsulinism associated with dominant KATP channel mutations. J Clin Invest 118:2877–2886
Rahier J, Guiot Y, Sempoux C (2000) Persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia of infancy: a heterogeneous syndrome unrelated to nesidioblastosis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 82:F108–F112
Rahman SA, Nessa A, Hussain K (2015) Molecular mechanisms of congenital hyperinsulinism. J Mol Endocrinol 54:119–129
Rico-Bautista E, Kusnetzow AK, Fowler ΜΑ, Athanacio J, Kredel TA, Zhao J, Wang S, Markinson S, Fei Zhu Y, Struthers RS, Betz SF, Crinetics Pharmaceuticals, San Diego, CA (2019) Selective nonpeptide somatostatin receptor subtype 5 (sst5) agonists suppress induced insulin secretion in pancreatic islets from both rats and healthy human donors. Presented in Endo 2019
Rozenkova K, Malikova J, Nessa A, Dusatkova L, Bjørkhaug L, Obermannova B, Dusatkova P, Kytnarova J, Aukrust I, Najmi LA, Rypackova B, Sumnik Z, Lebl J, Njølstad PR, Hussain K, Pruhova S (2015) High incidence of heterozygous ABCC8 and HNF1A mutations in Czech patients with congenital hyperinsulinism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:E1540–E1549
Sakakibara A, Hashimoto Y, Kawakita R, Hosokawa Y, Nagahara K, Hasegawa Y, Hoshino S, Nagasaka H, Yorifuji T (2018) Diagnosis of congenital hyperinsulinism: biochemical profiles during hypoglycaemia. Pediatr Diabetes 19:259–264
Salomon-Estebanez M, Flanagan SE, Ellard S, Rigby L, Bowden L, Mohamed Z, Nicholson J, Skae M, Hall C, Craigie R, Padidela R, Murphy N, Randell T, Cosgrove KE, Dunne MJ, Banerjee I (2016) Conservatively treated Congenital Hyperinsulinism (CHI) due to K-ATP channel gene mutations: reducing severity over time. Orphanet J Rare Dis 11:163
Sayed S, Langdon DR, Odili S, Chen P, Buettger C, Schiffman AB, Suchi M, Taub R, Grimsby J, Matschinsky FM, Stanley CA (2009) Extremes of clinical and enzymatic phenotypes in children with hyperinsulinism caused by glucokinase activating mutations. Diabetes 58:1419–1427
Senniappan S, Alexandrescu S, Tatevian N, Shah P, Arya V, Flanagan S, Ellard S, Rampling D, Ashworth M, Brown R et al (2014) Sirolimus therapy in infants with severe hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med 370:1131–1137
Shah P, Rahman SA, McElroy S, Gilbert C, Morgan K, Hinchey L, Senniappan S, Levy H, Amin R, Hussain K (2015) Use of long-acting Somatostatin analogue (Lanreotide) in an adolescent with Diazoxide-responsive congenital Hyperinsulinism and its psychological impact. Horm Res Paediatr 84:355–360
Shah P, Rahman SA, Demirbilek H, Güemes M, Hussain K (2016) Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia in children and adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 5:729–742
Shanbag P, Pathak A, Vaidya M, Shahid SK (2002) Persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy-successful therapy with nifedipine. Indian J Pediatr 69:271–272
Skae M, Avatapalle HB, Banerjee I, Rigby L, Vail A, Foster P, Charalambous C, Bowden L, Padidela R, Patel L, Ehthsham S, Cosgrove KE, Dunne MJ, Clayton P (2014) Reduced glycemic variability in diazoxide-responsive children with congenital hyperinsulinism using supplemental omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids; a pilot trial with MaxEPAR. Front Endocrinol 5:31
Stanley CA (2004) Hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia syndrome: insights into the regulatory role of glutamate dehydrogenase in ammonia metabolism. Mol Genet Metab 81:S45–S51
Stanley CA (2016) Perspective on the genetics and diagnosis of congenital hyperinsulinism disorders. JCEM 101:815–826
Suprasongsin C, Suthutvoravut U, Mahachoklertwattana P, Preeyasombat C (1999) Combined raw cornstarch and nifedipine as an additional treatment in persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. J Med Assoc Thail 82:S39–S42
Szymanowski M, Estebanez MS, Padidela R, Han B, Mosinska K, Stevens A, Damaj L, Pihan-Le Bars F, Lascouts E, Reynaud R et al (2016) mTOR inhibitors for the treatment of severe congenital hyperinsulinism: perspectives on limited therapeutic success. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:4719–4729
Thomas PM, Cote GJ, Wohllk N, Haddad B, Mathew PM, Rabl W, Aguilar-Bryan L, Gagel RF, Bryan J (1995) Mutations in the sulfonylurea receptor gene in familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. Science 268:426–429
Thomas P, Ye Y, Lightner E (1996) Mutation of the pancreatic islet inward rectifier Kir6.2 also leads to familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. Hum Mol Genet 5:1809–1812
Thornton PS, Alter CA, Katz LE, Baker L, Stanley CA (1993) Short- and long-term use of octreotide in the treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism. J Pediatr 123:637–643
Timlin MR, Black AB, Delaney HM, Matos RI, Percival CS (2017) Development of pulmonary hypertension during treatment with diazoxide: a case series and literature review. Pediatr Cardiol 38:1247–1250
Tornehave D, Kristensen P, Rorner J, Knudsen LB, Heller RS (2008) Expression of the GLP-1 receptor in mouse, rat, and human pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem 56:841–851
Verkarre V, Fournet JC, de Lonlay P, Gross-Morand MS, Devillers M, Rahier J, Brunelle F, Robert JJ, Nihoul-Fekete C, Saudubray JM et al (1998) Paternal mutation of the sulfonylurea receptor (SUR1) gene and maternal loss of 11p15 imprinted genes lead to persistent hyperinsulinism in focal adenomatous hyperplasia. J Clin Invest 102:1286–1291
Welters A, Lerch C, Kummer S, Marquard J, Salgin B, Mayatepek E, Meissner T (2015) Long-term medical treatment in congenital hyperinsulinism: a descriptive analysis in a large cohort of patients from different clinical centers. Orphanet J Rare Dis 10:150
Welters A, Meissner T, Grulich-Henn J, Frohlich-Reiterer E, Warncke K, Mohnike K, Blankenstein O, Menzel U, Datz N, Bollow E, Holl RW (2017) Characterization of diabetes following pancreatic surgery in patients with congenital hyperinsulinism. Orphanet J Rare Dis 13:230
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Oppliger W, Hall MN (2005) Molecular organization of target of rapamycin complex 2. J Biol Chem 280:30697–30704
Yang SB, Lee HY, Rapamycin DM, Tien AC, Rowson-Baldwin A, Shu YY, Jan YN, Jan LY (2012) Rapamycin induces glucose intolerance in mice by reducing islet mass, insulin content, and insulin sensitivity. J Mol Med (Berl) 90:575–585
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Communicated by Peter de Winter
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostopoulou, E., Shah, P. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia—an overview of a complex clinical condition. Eur J Pediatr 178, 1151–1160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-019-03414-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-019-03414-8