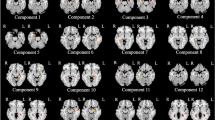
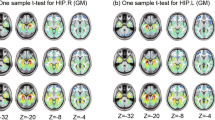
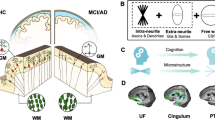
Abstract
The hippocampal networks support multiple cognitive functions and may have biological roles and functions in pathological cognitive aging (PCA) and its associated diseases, which have not been explored. In the current study, a total of 116 older adults with 39 normal controls (NC) (mean age: 52.3 ± 13.64 years; 16 females), 39 mild cognitive impairment (MCI) (mean age: 68.15 ± 9.28 years, 14 females), and 38 dementia (mean age: 73.82 ± 8.06 years, 8 females) were included. The within-hippocampal subfields and the cortico-hippocampal circuits were assessed via a micro-structural similarity network approach using T1w/T2w ratio and regional gray matter tissue probability maps, respectively. An analysis of covariance was conducted to identify between-group differences in structural similarities among hippocampal subfields. The partial correlation analyses were performed to associate changes in micro-structural similarities with cognitive performance in the three groups, controlling the effect of age, sex, education, and cerebral small-vessel disease. Compared with the NC, an altered T1w/T2w ratio similarity between left CA3 and left subiculum was observed in the mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia. The left CA3 was the most impaired region correlated with deteriorated cognitive performance. Using these regions as seeds for GM similarity comparisons between hippocampal subfields and cortical regions, group differences were observed primarily between the left subiculum and several cortical regions. By utilizing T1w/T2w ratio as a proxy measure for myelin content, our data suggest that the imbalanced synaptic weights within hippocampal CA3 provide a substrate to explain the abnormal firing characteristics of hippocampal neurons in PCA. Furthermore, our work depicts specific brain structural characteristics of normal and pathological cognitive aging and suggests a potential mechanism for cognitive aging heterogeneity.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting our findings are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alexander-Bloch A, Raznahan A, Bullmore E, Giedd J (2013) The convergence of maturational change and structural covariance in human cortical networks. J Neurosci 33(7):2889–2899
Barbas H (2015) General cortical and special prefrontal connections: principles from structure to function. Annu Rev Neurosci 38:269–289
Bettio LE, Rajendran L, Gil-Mohapel J (2017) The effects of aging in the hippocampus and cognitive decline. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 79:66–86
Buss EW, Corbett NJ, Roberts JG, Ybarra N, Musial TF, Simkin D, Molina-Campos E, Oh K-J, Nielsen LL, Ayala GD (2021) Cognitive aging is associated with redistribution of synaptic weights in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118(8):e1921481118
Butz M, Lehmann K, Dammasch IE, Teuchert-Noodt G (2006) A theoretical network model to analyse neurogenesis and synaptogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Neural Netw 19(10):1490–1505
Dalton MA, Zeidman P, McCormick C, Maguire EA (2018) Differentiable processing of objects, associations, and scenes within the hippocampus. J Neurosci 38(38):8146–8159. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0263-18.2018
Du C, Chen Y, Chen K, Zhang Z (2021) Disrupted anterior and posterior hippocampal structural networks correlate impaired verbal memory and spatial memory in different subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Eur J Neurol 28(12):3955–3964
Evans AC (2013) Networks of anatomical covariance. Neuroimage 80:489–504
Fang XT, Toyonaga T, Hillmer AT, Matuskey D, Holmes SE, Radhakrishnan R, Mecca AP, van Dyck CH, D’Souza DC, Esterlis I (2021) Identifying brain networks in synaptic density PET (11C-UCB-J) with independent component analysis. Neuroimage 237:118167
Fu Z, Zhao M, He Y, Wang X, Lu J, Li S, Li X, Kang G, Han Y, Li S (2021) Divergent connectivity changes in gray matter structural covariance networks in subjective cognitive decline, amnestic mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci 13:686598
Ganzetti M, Wenderoth N, Mantini D (2014) Whole brain myelin mapping using T1-and T2-weighted MR imaging data. Front Hum Neurosci 8:671
Ganzetti M, Wenderoth N, Mantini D (2015) Mapping pathological changes in brain structure by combining T1-and T2-weighted MR imaging data. Neuroradiology 57:917–928
Ge R, Kot P, Liu X, Lang DJ, Wang JZ, Honer WG, Vila-Rodriguez F (2019) Parcellation of the human hippocampus based on gray matter volume covariance: Replicable results on healthy young adults. Hum Brain Mapp 40(13):3738–3752
Glasser MF, Coalson TS, Robinson EC, Hacker CD, Harwell J, Yacoub E, Ugurbil K, Andersson J, Beckmann CF, Jenkinson M, Smith SM, Van Essen DC (2016) A multi-modal parcellation of human cerebral cortex. Nature 536(7615):171–178. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18933
Glasser MF, Van Essen DC (2011a) Mapping human cortical areas in vivo based on myelin content as revealed by T1- and T2-weighted MRI. J Neurosci 31(32):11597–11616. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2180-11.2011
Glasser MF, Van Essen DC (2011b) Mapping human cortical areas in vivo based on myelin content as revealed by T1-and T2-weighted MRI. J Neurosci 31(32):11597–11616
Gonuguntla V, Yang E, Guan Y, Koo BB, Kim JH (2022) Brain signatures based on structural MRI: Classification for MCI, PMCI, and AD. Hum Brain Mapp
Hainmueller T, Bartos M (2020) Dentate gyrus circuits for encoding, retrieval and discrimination of episodic memories. Nat Rev Neurosci 21(3):153–168
Huang CC, Rolls ET, Feng J, Lin CP (2022) An extended human connectome project multimodal parcellation atlas of the human cortex and subcortical areas. Brain Struct Funct 227:763–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-021-02421-6
Iglesias JE, Augustinack JC, Nguyen K, Player CM, Player A, Wright M, Roy N, Frosch MP, McKee AC, Wald LL (2015) A computational atlas of the hippocampal formation using ex vivo, ultra-high resolution MRI: application to adaptive segmentation of in vivo MRI. Neuroimage 115:117–137
Kotkowski E, Price LR, Fox PM, Vanasse TJ, Fox PT (2018) The hippocampal network model: A transdiagnostic metaconnectomic approach. Neuroimage Clin 18:115–129
Lin X, Amalraj M, Blanton C, Avila B, Holmes TC, Nitz DA, Xu X (2021) Noncanonical projections to the hippocampal CA3 regulate spatial learning and memory by modulating the feedforward hippocampal trisynaptic pathway. PLoS Biol 19(12):e3001127
Lindenberger U (2014) Human cognitive aging: corriger la fortune? Science 346(6209):572–578. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254403
Luo X, Li K, Zeng Q, Huang P, Jiaerken Y, Wang S, Shen Z, Xu X, Xu J, Wang C (2019) Application of T1-/T2-weighted ratio mapping to elucidate intracortical demyelination process in the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Front Neurosci 13:904
Ma Z, Zhang N (2017) Cross-population myelination covariance of human cerebral cortex. Hum Brain Mapp 38(9):4730–4743
Maingret N, Girardeau G, Todorova R, Goutierre M, Zugaro M (2016) Hippocampo-cortical coupling mediates memory consolidation during sleep. Nat Neurosci 19(7):959–964
Margoni M, Pagani E, Meani A, Storelli L, Mesaros S, Drulovic J, Barkhof F, Vrenken H, Strijbis E, Gallo A (2022) Exploring in vivo multiple sclerosis brain microstructural damage through T1w/T2w ratio: a multicentre study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry
McCormick C, Dalton MA, Zeidman P, Maguire EA (2021) Characterising the hippocampal response to perception, construction and complexity. Cortex 137:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2020.12.018
Pelkmans W, Dicks E, Barkhof F, Vrenken H, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM, Tijms BM (2019) Gray matter T1-w/T2-w ratios are higher in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 40(13):3900–3909
Pini L, Pievani M, Bocchetta M, Altomare D, Bosco P, Cavedo E, Galluzzi S, Marizzoni M, Frisoni GB (2016) Brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Ageing Res Rev 30:25–48
Qing Z, Chen F, Lu J, Lv P, Li W, Liang X, Wang M, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhang B (2021) Causal structural covariance network revealing atrophy progression in Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Hum Brain Mapp 42(12):3950–3962
Sämann PG, Iglesias JE, Gutman B, Grotegerd D, Leenings R, Flint C, Dannlowski U, Clarke-Rubright EK, Morey RA, van Erp TG (2022) FreeSurfer-based segmentation of hippocampal subfields: a review of methods and applications, with a novel quality control procedure for ENIGMA studies and other collaborative efforts. Hum Brain Mapp 43(1):207–233
Seidlitz J, Váša F, Shinn M, Romero-Garcia R, Whitaker KJ, Vértes PE, Wagstyl K, Reardon PK, Clasen L, Liu S (2018) Morphometric similarity networks detect microscale cortical organization and predict inter-individual cognitive variation. Neuron 97(1):231–247
Shams Z, Norris DG, Marques JP (2019) A comparison of in vivo MRI based cortical myelin mapping using T1w/T2w and R1 mapping at 3T. PLoS ONE 14(7):e0218089. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0218089
Song D, Wang D, Yang Q, Yan T, Wang Z, Yan Y, Zhao J, Xie Z, Liu Y, Ke Z (2020) The lateralization of left hippocampal CA3 during the retrieval of spatial working memory. Nat Commun 11(1):1–13
Sorensen TA (1948) A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species content and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Biol Skar 5:1–34
Stepan J, Dine J, Fenzl T, Polta SA, von Wolff G, Wotjak CT, Eder M (2012) Entorhinal theta-frequency input to the dentate gyrus trisynaptically evokes hippocampal CA1 LTP. Front Neural Circuits 6:64
Suárez LE, Markello RD, Betzel RF, Misic B (2020) Linking structure and function in macroscale brain networks. Trends Cogn Sci 24(4):302–315
Vandewouw MM, Hunt BA, Ziolkowski J, Taylor MJ (2021) The developing relations between networks of cortical myelin and neurophysiological connectivity. Neuroimage 237:118142
Vidal-Piñeiro D, Walhovd KB, Storsve AB, Grydeland H, Rohani DA, Fjell AM (2016) Accelerated longitudinal gray/white matter contrast decline in aging in lightly myelinated cortical regions. Hum Brain Mapp 37(10):3669–3684
Yu M, Sporns O, Saykin AJ (2021) The human connectome in Alzheimer disease—relationship to biomarkers and genetics. Nat Rev Neurol 17(9):545–563
Zhao K, Ding Y, Han Y, Fan Y, Alexander-Bloch AF, Han T, Jin D, Liu B, Lu J, Song C (2020) Independent and reproducible hippocampal radiomic biomarkers for multisite Alzheimer’s disease: diagnosis, longitudinal progress and biological basis. Sci Bull 65(13):1103–1113
Zhou C, Gao T, Guo T, Wu J, Guan X, Zhou W, Huang P, Xuan M, Gu Q, Xu X (2020) Structural covariance network disruption and functional compensation in Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 12:199
Zielinski BA, Gennatas ED, Zhou J, Seeley WW (2010) Network-level structural covariance in the developing brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(42):18191–18196
Funding
This study was supported in part by STI2030–Major Projects (2022ZD0213400); National Natural Science Foundation of China (82201720); Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (Grant No. 202040086); and Shanghai Special Research Project on Aging and Maternal and Child Health (Grant No. 2020YJZX0121). Dr. Wu played a pivotal role in securing the funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: C-CH, MF; Formal Analysis: C-CH, MF; Data Collection: MF, H-HH, S-YZ; Writing-Original Draft: C-CH, MF; Writing Review & Editing: C-CH, MF, H-HH, JY, S-YZ; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the regional ethics committee.
Consent to participant
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, M., Huang, H., Yang, J. et al. Changes in microstructural similarity of hippocampal subfield circuits in pathological cognitive aging. Brain Struct Funct 229, 311–321 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02721-z