Abstract
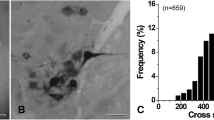
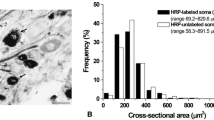
The intermediate subnucleus of the nucleus tractus solitarii (imNTS) receives somatosensory inputs from the soft palate and pharynx, and projects onto the nucleus ambiguus, thus serving as a relay nucleus for swallowing. The ultrastructure and synaptology of the rat imNTS, and its glossopharyngeal afferent terminals, have been examined with cholera toxin-conjugated horseradish peroxidase (CT-HRP) as an anterograde tracer. The imNTS contained oval or ellipsoid-shaped, small to medium-sized neurons (18.2×11.4 μm) with little cytoplasm, few cell organelles and an irregularly shaped nucleus. The cytoplasm often contained one or two nucleolus-like stigmoid bodies. The average number of axosomatic terminals was 1.8 per profile. About 83% of them contained round vesicles and formed asymmetric synaptic contacts (Gray’s type I), while about 17% contained pleomorphic vesicles and formed symmetric synaptic contacts (Gray’s type II). The neuropil contained small or large axodendritic terminals, and about 92% of them were Gray’s type I. When CT-HRP was injected into the nodose ganglion, many labeled terminals were found in the imNTS. All anterogradely labeled terminals contacted dendrites but not somata. The labeled terminals were usually large (2.69±0.09 μm) and exclusively of Gray’s type I. They often contacted more than two dendrites, were covered with glial processes, and formed synaptic glomeruli. A small unlabeled terminal occasionally made an asymmetric synaptic contact with a large labeled terminal. The large glossopharyngeal afferent terminals and the neurons containing stigmoid bodies characterized the imNTS neurons that received pharyngeal afferents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aicher SA, Sharma S, Pickel VM (1999) N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors are present in vagal afferents and their dendritic targets in the nucleus tractus solitarius. Neuroscience 91:119–132
Altschuler SM, Bao X, Bieger D, Hopkins DA, Miselis RR (1989) Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the rat: sensory ganglia and nuclei of the solitary and spinal trigeminal tracts. J Comp Neurol 283:248–268
Bao X, Wiedner EB, Altschuler SM (1995) Transsynaptic localization of pharyngeal premotor neurons in rat. Brain Res 696:246–249
Bieger D, Hopkins DA (1987) Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the medulla oblongata in the rat: the nucleus ambiguus. J Comp Neurol 262:546–562
Brining SK, Smith DV (1996) Distribution and synaptology of glossopharyngeal afferent nerve terminals in the nucleus of the solitary tract of the hamster. J Comp Neurol 365:556–574
Castro-Lopes JM, Coimbra A, Grant G, Arvidsson J (1990) Ultrastructural changes of the central scalloped (C1) primary afferent endings of synaptic glomeruli in the substantia gelatinosa Rolandi of the rat after peripheral neurotomy. J Neurocytol 19:329–337
Chazal G, Baude A, Barbe A, Puizillout JJ (1991) Ultrastructural organization of the interstitial subnucleus of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius in the cat: identification of vagal afferents. J Neurocytol 20:859–874
Contreras RJ, Beckestead RM, Norgren R (1982) The central projections of the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves: an autoradiographic study in the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst 6:303–322
Cruz F, Lima D, Zieglgansberger W, Coimbra A (1991) Fine structure and synaptic architecture of HRP-labelled primary afferent terminations in lamina IIi of the rat dorsal horn. J Comp Neurol 305:3–16
Cruz F, Lima D, Coimbra A (1993) Periterminal synaptic organization of primary afferents in laminae I and IIo of the rat spinal cord, as shown after anterograde HRP labelling. J Neurocytol 22:191–204
Cunningham ETJ, Sawchenko PE (1989) A circumscribed projection from the nucleus of the solitary tract to the nucleus ambiguus in the rat: anatomical evidence for somatostatin-28-immunoreactive interneurons subserving reflex control of esophageal motility. J Neurosci 9:1668–1682
Fujinaga R, Kawano J, Matsuzaki Y, Kamei K, Yanai A, Sheng Z, Tanaka M, Nakahama K, Nagano M, Shinoda K (2004) Neuroanatomical distribution of Huntingtin-associated protein 1-mRNA in the male mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 478:88–109
Gray EG (1959) Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex: an electron microscope study. J Anat 93:420–433
Groves PM, Wilson CJ (1980) Fine structure of rat locus coeruleus. J Comp Neurol 193:841–852
Gutekunst CA, Li SH, Yi H, Ferrante RJ, Li XJ, Hersch SM (1998) The cellular and subcellular localization of huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1): comparison with huntingtin in rat and human. J Neurosci 18:7674–7686
Hadziefendic S, Haxhiu MA (1999) CNS innervation of vagal preganglionic neurons controlling peripheral airways: a transneuronal labeling study using pseudorabies virus. J Auton Nerv Syst 76:135–145
Hamilton RB, Norgren R (1984) Central projections of gustatory nerves in the rat. J Comp Neurol 222:560–577
Hay M, McKenzie H, Lindsley K, Dietz N, Bradley SR, Conn PJ, Hasser EM (1999) Heterogeneity of metabotropic glutamate receptors in autonomic cell groups of the medulla oblongata of the rat. J Comp Neurol 403:486–501
Hayakawa T, Zyo K (1992) Ultrastructural study of ascending projections to the lateral mammillary nucleus of the rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 185:547–557
Hayakawa T, Zheng JQ, Seki M, Yajima Y (1998) Synaptology of the direct projections from the nucleus of the solitary tract to pharyngeal motoneurons in the nucleus ambiguus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 393:391–401
Hayakawa T, Takanaga A, Maeda S, Seki M, Yajima Y (2001) Subnuclear distribution of afferents from the oral, pharyngeal and laryngeal regions in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat: a study using transganglionic transport of cholera toxin. Neurosci Res 39:221–232
Hayakawa T, Takanaga A, Tanaka K, Maeda S, Seki M (2003) Ultrastructure of the central subnucleus of the nucleus tractus solitarii and the esophageal afferent terminals in the rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 206:273–281
Hayakawa T, Takanaga A, Tanaka K, Maeda S, Seki M (2004) Distribution and ultrastructure of dopaminergic neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus projecting to the stomach of the rat. Brain Res 1006:66–73
Houpt TA, Philopena JM, Wessel TC, Joh TH, Smith GP (1994) Increased c-Fos expression in nucleus of the solitary tract correlated with conditioned taste aversion to sucrose in rats. Neurosci Lett 172:1–5
Houpt TA, Philopena JM, Joh TH, Smith GP (1996) c-Fos induction in the rat nucleus of the solitary tract by intraoral quinine infusion depends on prior contingent pairing of quinine and lithium chloride. Physiol Behav 60:1535–1541
Hurley KM, Herbert H, Moga MM, Saper CB (1991) Efferent projections of the infralimbic cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 308:249–276
Kalia M, Mesulam MM (1980a) Brain stem projections of sensory and motor components of the vagus complex in the cat: I. The cervical vagus and nodose ganglion. J Comp Neurol 193:435–465
Kalia M, Mesulam MM (1980b) Brain stem projections of sensory and motor components of the vagus complex in the cat: II. Laryngeal, tracheobronchial, pulmonary, cardiac, and gastrointestinal branches. J Comp Neurol 193:467–508
Kalia M, Sullivan JM (1982) Brainstem projections of sensory and motor components of the vagus nerve in the rat. J Comp Neurol 211:248–265
Kalia M, Fuxe K, Goldstein M (1985) Rat medulla oblongata. III. Adrenergic (C1 and C2) neurons, nerve fibers and presumptive terminal processes. J Comp Neurol 233:333–349
Kessler JP, Cherkaoui N, Catalin D, Jean A (1990) Swallowing responses induced by microinjection of glutamate and glutamate agonists into the nucleus tractus solitarius of ketamine-anesthetized rats. Exp Brain Res 83:151–158
Kishi K (1972) Fine structural and cytochemical observations on cytoplasmic nucleoluslike bodies in nerve cells of rat medulla oblongata. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 132:523–532
van der Kooy D, Koda LY, McGinty JF, Gerfen CR, Bloom FE (1984) The organization of projections from the cortex, amygdala, and hypothalamus to the nucleus of the solitary tract in rat. J Comp Neurol 224:1–24
Le Beux YJ, Langelier P, Poirier LJ (1971) Further ultrastructural data on the cytoplasmic nucleolus resembling bodies or nematosomes. Their relationship with the subsynaptic web and a cytoplasmic filamentous network. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 118:147–155
Lee Y, Takami K, Kawai Y, Girgis S, Hillyard CJ, MacIntyre I, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat peripheral nervous system with reference to its coexistence with substance P. Neuroscience 15:1227–1237
Leslie RA, Gwyn DG, Hopkins DA (1982) The ultrastructure of the subnucleus gelatinosus of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius in the cat. J Comp Neurol 206:109–118
Luiten PG, ter Horst GJ, Karst H, Steffens AB (1985) The course of paraventricular hypothalamic efferents to autonomic structures in medulla and spinal cord. Brain Res 329:374–378
McLean JH, Hopkins DA (1982) Ultrastructural identification of labeled neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve following injections of horseradish peroxidase into the vagus nerve and brainstem. J Comp Neurol 206:243–252
Mesulam M-M (1978) Tetramethyl benzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferent and efferents. J Histochem Cytochem 26:106–117
Mrini A, Jean A (1995) Synaptic organization of the interstitial subdivision of the nucleus tractus solitarii and of its laryngeal afferents in the rat. J Comp Neurol 355:221–236
Nakamura Y (1975) An electron microscope study of the red nucleus in the cat with special reference to the quantitative analysis of the axosomatic synapses. Brain Res 94:1–17
Nomura S, Mizuno N (1983a) Central distribution of efferent and afferent components of the cervical branches of the vagus nerve. A HRP study in the cat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 166:1–18
Nomura S, Mizuno N (1983b) Central distribution of afferent fibers in the intermediate nerve: a transganglionic HRP study in the cat. Neurosci Lett 41:227–231
Norgren R (1995) Gustatory system. In: Paxions G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 751–771
Rinaman L, Card JP, Schwaber JS, Miselis RR (1989) Ultrastructural demonstration of a gastric monosynaptic vagal circuit in the nucleus of the solitary tract in rat. J Neurosci 9:1985–1996
Ross CA, Ruggiero DA, Reis DJ (1985) Projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii to the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol 242:511–534
Saha S, Batten TF, McWilliam PN (1995) Glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid and tachykinin-immunoreactive synapses in the cat nucleus tractus solitarii. J Neurocytol 24:55–74
Saha S, Batten TF, Henderson Z (2000) A GABAergic projection from the central nucleus of the amygdala to the nucleus of the solitary tract: a combined anterograde tracing and electron microscopic immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience 99:613–626
Saper CB (1982) Convergence of autonomic and limbic connections in the insular cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 210:163–173
Shimizu N, Ishii S (1965) Electron-microscopic observations on nucleolar extrusion in nerve cells of the rat hypothalamus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 67:367–372
Shinoda K, Mori S, Ohtsuki T, Osawa Y (1992) An aromatase-associated cytoplasmic inclusion, the “stigmoid body,” in the rat brain: I. Distribution in the forebrain. J Comp Neurol 322:360–376
Shinoda K, Nagano M, Osawa Y (1993) An aromatase-associated cytoplasmic inclusion, the “stigmoid body,” in the rat brain: II. Ultrastructure (with a review of its history and nomenclature). J Comp Neurol 329:1–19
Sofroniew MV (1983) Direct reciprocal connections between the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and dorsomedial medulla oblongata: evidence from immunohistochemical detection of tracer proteins. J Comp Neurol 213:399–405
Spray KJ, Bernstein IL (2004) Afferent and efferent connections of the parvicellular subdivision of iNTS: defining a circuit involved in taste aversion learning. Behav Brain Res 154:85–97
Spray KJ, Halsell CB, Bernstein IL (2000) c-Fos induction in response to saccharin after taste aversion learning depends on conditioning method. Brain Res 852:225–227
Taxi E (1961) Etude de l‘ultrastructure des zones synaptiques dans les ganglions sympathiques de la grenouille. CR Acad Sci [lll] (Paris) 252:174–176
Torrealba F, Muller C (1999) Ultrastructure of glutamate and GABA immunoreactive axon terminals of the rat nucleus tractus solitarius, with a note on infralimbic cortex afferents. Brain Res 820:20–30
Whitehead MC (1986) Anatomy of the gustatory system in the hamster: synaptology of facial afferent terminals in the solitary nucleus. J Comp Neurol 244:72–85
Yamazoe M, Shiosaka S, Shibasaki T, Ling N, Tateishi K, Hashimura E, Hamaoka T, Kimmel JR, Matsuo H, Tohyama M (1984) Distribution of six neuropeptides in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat: an immunohistochemical analysis. Neuroscience 13:1243–1266
Yamazoe M, Shiosaka S, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Distribution of neuropeptide Y in the lower brainstem: an immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res 335:109–120
Zheng JQ, Seki M, Hayakawa T, Ito H, Zyo K (1995) Descending projections from the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus to the spinal cord: anterograde tracing study in the rat. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 72:119–135
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. M. Hatta and Mr. K. Gion for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayakawa, T., Maeda, S., Tanaka, K. et al. Fine structural survey of the intermediate subnucleus of the nucleus tractus solitarii and its glossopharyngeal afferent terminals. Anat Embryol 210, 235–244 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-005-0021-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-005-0021-9