Abstract
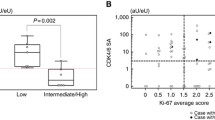
Progression through the mammalian cell cycle is regulated by cyclin—cyclin-dependent kinase (CDKs) complexes that are activated throughout the cell cycle. Alteration in cell cycle control could lead to proliferation and tumourogenesis. This study was designed to analyse, at messenger RNA (mRNA) level, cyclins and CDKs involved in the retinoblastoma pathway, as well as cell division cycle 25a phosphatase (CDC25a), which activates some of the CDKs that were analysed. The aim of the study was to determine the possible prognostic relevance of these molecules in 73 women with peri- and post-menopausal breast cancer. Cyclins A, D1 and E; CDKs 2, 4 and 6 and phosphatase CDC25a expression status were analysed in primary tumours at mRNA level, by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis in paraffin-embedded primary breast cancers. High expression levels of CDK2, CDK4 and CDC25a were related to tumour recurrence. Over-expression of CDK2 and CDC25a was also associated with reduced overall survival; moreover, the CDK2 expression level was able to define a short-living cohort of patients with tumour-positive lymph nodes. CDK2, CDK4 and CDC25a can be used as reliable biomarkers to predict prognosis in women with peri- and post-menopausal breast cancer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akli S, Keyomarsi K (2003) Cyclin E and its low molecular weight forms in human cancer and as targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther 2:S38–S47
Bonin S, Pascolo L, Croce LS, Stanta G, Tiribelli C (2002) Gene expression of ABC proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma, perineoplastic tissue, and liver diseases. Mol Med 8:318–325
Bukholm IR, Bukholm G, Nesland JM (2001) Over-expression of cyclin A is highly associated with early relapse and reduced survival in patients with primary breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer 93:283–287
Cangi MG, Cukor B, Soung P, Signoretti S, Moreira G Jr, Ranashinge M, Cady B, Pagano M, Loda M (2000) Role of the Cdc25A phosphatase in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest 106:753–761
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Esteva FJ, Hortobagyi GN (2004) Prognostic molecular markers in early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 6:109–118
Gillett CE, Lee AH, Millis RR, Barnes DM (1998) Cyclin D1 and associated proteins in mammary ductal carcinoma in situ and atypical ductal hyperplasia. J Pathol 184:396–400
Grambsch PM, Therneau TM (1994) Proportional hazards test and diagnostic based on weighted residuals. Biometrika 81:515–526
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch MC, Haller DG, Morrow M (eds) (2002) AJCC cancer staging manual, 6th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL (1980) The statistical analysis of failure time data. Wiley, New York
Parkin DM, Whelan SL, Ferlay J, Raymond L, Young J (1997) Cancer incidence in five continents—Vol VII, vol 153. IARC Scientific Publications, Lyon, pp 562–565
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2001) Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 94:153–156
Sherr CJ (1996) Cancer cell cycles. Science 274:1672–1677
Sherr CJ, McCormick F (2002) The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell 2:103–112
Simin K, Wu H, Lu L, Pinkel D, Albertson D, Cardiff RD, Dyke TV (2004) pRb Inactivation in mammary cells reveals common mechanisms for tumor initiation and progression in divergent epithelia. PLoS Biol 2:E22
Stanta G, Bonin S (1998) RNA quantitative analysis from fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues: membrane hybridization and capillary electrophoresis. Biotechniques 24:271–276
Stanta G, Schneider C (1991) RNA extracted from paraffin-embedded human tissues is amenable to analysis by PCR amplification. Biotechniques 11:304–308
Stanta G, Bonin S, Losi L, Eusebi V (1998) Molecular characterization of intraductal breast carcinomas. Virchows Arch 432:107–111
Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA (2002) Cyclin E and prognosis in patients with breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1546–1547
van’ tVeer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ, Witteveen AT, Schreiber GJ, Kerkhoven RM, Roberts C, Linsley PS, Bernards R, Friend SH (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415:530–536
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, Schreiber GJ, Peterse JL, Roberts C, Marton MJ, Parrish M, Atsma D, Witteveen A, Glas A, Delahaye L, van der Velde T, Bartelink H, Rodenhuis S, Rutgers ET, Friend SH, Bernards R (2002) A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1999–2009
Yazidi-Belkoura IE, Adriaenssens E, Vercoutter-Edouart AS, Lemoine J, Nurcombe V, Hondermarck H (2002) Proteomics of breast cancer: outcomes and prospects. Technol Cancer Res Treat 1:287–296
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Dr. Georgine Faulkner for the English revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonin, S., Brunetti, D., Benedetti, E. et al. Expression of cyclin-dependent kinases and CDC25a phosphatase is related with recurrences and survival in women with peri- and post-menopausal breast cancer. Virchows Arch 448, 539–544 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0146-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0146-5