Abstract
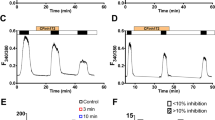
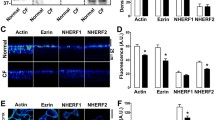
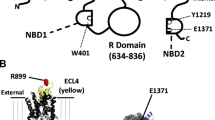
It has been reported that the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) can be activated through cAMP- and protein kinase A-independent pathways involving GTP-binding proteins and an unknown kinase. In this study, we further examined how G protein-coupled pathways regulate CFTR. We demonstrate that stimulation of purinergic P2Y2 receptors in CFTR-expressing oocytes and in airway epithelial cells activates CFTR Cl− currents. Activation of CFTR Cl− currents via P2Y2 was inhibited by CFTRinh-172 and was independent of intracellular Ca2+, protein kinase C, or calmodulin-dependent kinase (CAMK). However, activation of CFTR was suppressed by inhibition of phospholipase C and by the nonselective protein kinase inhibitor staurosporine. Activation of CFTR through P2Y2 receptors was enhanced when Gi proteins were inhibited by pertussis toxin. Inhibition of protein kinase A and of protein kinases downstream of P2Y2 receptors such as mitogen-activated protein kinases, tyrosine kinase, or c-src kinase did not interfere with activation of CFTR. The present results demonstrate an antagonistic regulation of CFTR by P2Y2 receptors: CFTR is inhibited by stimulation of Gi proteins and is activated by stimulation of Gq/11/PLC and an unknown downstream protein kinase.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barro Soria R, Spitzner M, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (2006) Bestrophin 1 enables Ca2+ activated Cl− conductance in epithelia. J Biol Chem 281:17460–17467
Chang X-B, Tabcharani JA, Hou Y-X, Jensen TJ, Kartner N, Alon N, Hanrahan JW, Riordan JR (1993) Protein kinase A (PKA) still activates CFTR chloride channels after mutagenesis of all 10 PKA consensus phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem 268:11304–11311
Dinudom A, Fotia AB, Lefkowitz RJ, Young JA, Kumar S, Cook DI (2004) The kinase Grk2 regulates Nedd4/Nedd4-2-dependent control of epithelial Na+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:11886–11890
Fischer H, Machen TE (1996) The tyrosine kinase p60c-src regulates the fast gate of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channel. Biophys J 71:3073–3082
Fredholm BB, Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Daly JW, Harden TK, Jacobson KA, Leff P, Williams M (1994) Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol Rev 46:143–156
Hartzell HC, Putzier I, Arreola J (2005) Calcium-activated chloride channels. Annu Rev Physiol 67:719–758
Homolya L, Watt WC, Lazarowski ER, Koller BH, Boucher RC (1999) Nucleotide-regulated calcium signaling in lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells from normal and P2Y2 receptor (−/−) mice. J Biol Chem 274:26454–26460
Huang P, Lazarowski ER, Tarran R, Milgram SL, Boucher RC, Stutts MJ (2001) From the Cover: compartmentalized autocrine signaling to cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator at the apical membrane of airway epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:14120–14125
Hwang TH, Schwiebert EM, Guggino WB (1996) Apical and basolateral ATP stimulates tracheal epithelial chloride secretion via multiple purinergic receptors. Am J Physiol 270:C1611–C1623
Ishibashi K, Okamura K, Yamazaki J (2008) Involvement of apical P2Y2 receptor-regulated CFTR activity in muscarinic stimulation of Cl(−) reabsorption in rat submandibular gland. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R1729–R1736
Jiang X, Ingbar DH, O’Grady SM (1998) Adrenergic stimulation of Na+ transport across alveolar epithelial cells involves activation of apical Cl− channels. Am J Physiol. 275:C1610–C1620
Kaulich M, Streicher F, Mayer R, Müller CE (2003) Flavonoids—novel lead compounds for the development of P2Y2 receptor antagonists. Drug Dev Res 59:72–81
Kulaksiz H, Schmid A, Honscheid M, Ramaswamy A, Cetin Y (2002) Clara cell impact in air-side activation of CFTR in small pulmonary airways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:6796–6801
Kunzelmann K, Mall M (2002) Electrolyte transport in the colon: mechanisms and implications for disease. Physiol Rev 82:245–289
Kunzelmann K, Mall M (2003) Pharmacotherapy of the ion transport defect in cystic fibrosis: role of purinergic receptor agonists and other potential therapeutics. Am J Respir Med 2:299–309
Kunzelmann K, Schreiber R, Cook DI (2002) Mechanisms for inhibition of amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption by extracellular nucleotides in mouse trachea. Pflügers Arch 444:220–226
Lakshmi S, Joshi PG (2006) Activation of Src/kinase/phospholipase C/mitogen-activated protein kinase and induction of neurite expression by ATP, independent of nerve growth factor. Neuroscience 141:179–189
Lazrak A, Matalon S (2003) cAMP-induced changes of apical membrane potentials of confluent H441 monolayers. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285:L443–L450
Lepple-Wienhues A, Wieland U, Laun T, Heil L, Stern M, Lang F (2001) A src-like kinase activates outwardly rectifying chloride channels in CFTR-defective lymphocytes. FASEB J 15:927–931
Liu J, Liao Z, Camden J, Griffin KD, Garrad RC, Santiago-Perez LI, Gonzalez FA, Seye CI, Weisman GA, Erb L (2004) Src homology 3 binding sites in the P2Y2 nucleotide receptor interact with Src and regulate activities of Src, proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2, and growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 279:8212–8218
Mall M, Wissner A, Hübner M, Kühr J, Brandis M, Greger R, Kunzelmann K (2000) Effect of genistein on native epithelial tissues from normal individuals and CF patients and on CFTR expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Br J Pharmacol 130:1884–1892
Marcet B, Chappe V, Delmas P, Verrier B (2004) Pharmacological and signaling properties of endogenous P2Y1 receptors in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-expressing Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:533–539
Mense M, Vergani P, White DM, Altberg G, Nairn AC, Gadsby DC (2006) In vivo phosphorylation of CFTR promotes formation of a nucleotide-binding domain heterodimer. EMBO J 25:4728–4739
Mohler PJ, Kreda SM, Boucher RC, Sudol M, Stutts MJ, Milgram SL (1999) Yes-associated protein 65 localizes p62(c-Yes) to the apical compartment of airway epithelia by association with EBP50. J Cell Biol 147:879–890
O’Reilly MA, Weaver TE, Pilot-Matias TJ, Sarin VK, Gazdar AF, Whitsett JA (1989) In vitro translation, post-translational processing and secretion of pulmonary surfactant protein B precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1011:140–148
Palmer ML, Lee SY, Carlson D, Fahrenkrug S, O’Grady SM (2006) Stable knockdown of CFTR establishes a role for the channel in P2Y receptor-stimulated anion secretion. J Cell Physiol 206:759–770
Poronnik P, O’Mullane LM, Harding EA, Greger R, Cook DI (1998) Use of replication deficient adenoviruses to investigate the role of G proteins in Ca2+ signalling in epithelial cells. Cell Calcium 24:97–103
Reddy MM, Quinton PM (2001) cAMP-independent phosphorylation activation of CFTR by G proteins in native human sweat duct. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C604–C613
Reddy MM, Sun D, Quinton PM (2001) Apical heterotrimeric G-proteins activate CFTR in the native sweat duct. J Membr Biol 179:51–61
Schreiber R, Kindle P, Benzing T, Walz G, Kunzelmann K (2001) Control of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator by alphaGi and RGS proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:917–923
Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (2005) Purinergic P2Y6 receptors induce Ca2+ and CFTR dependent Cl− secretion in mouse trachea. Cell Physiol Biochem 16:99–108
Schwiebert EM, Gesek F, Ercolani L, Wjasow C, Gruenert DC, Karlson K, Stanton BA (1994) Heterotrimeric G proteins, vesicle trafficking, and CFTR Cl− channels. Am J Physiol 267:C272–C281
Schwiebert EM, Gruenert DC, Guggino WB, Stanton BA (1995) G protein G alpha i-2 inhibits outwardly rectifying chloride channels in human airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 269:C451–C456
Schwiebert EM, Kizer N, Gruenert DC, Stanton BA (1992) GTP-binding proteins inhibit cAMP activation of chloride channels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:10623–10627
Sheppard DN, Welsh MJ (1999) Structure and function of the CFTR chloride channel. Physiol Rev 79:S23–S45
van der Merwe JQ, Hollenberg MD, Macnaughton WK (2008) EGF receptor transactivation and MAP kinase mediate proteinase-activated receptor-2-induced chloride secretion in intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G441–G451
Vank C, Fromter E, Kottra G (1999) The activation of an apical Cl− conductance by extracellular ATP is potentiated by genistein in Necturus gallbladder epithelium. Pflugers Arch 438:497–501
Wilson SM, Brown SG, McTavish N, McNeill RP, Husband EM, Inglis SK, Olver RE, Clunes MT (2006) Expression of intermediate-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel (KCNN4) in H441 human distal airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291:L957–L965
Winter MC, Welsh MJ (1997) Stimulation of CFTR activity by its phosphorylated R domain. Nature 389:294–296
Yamamoto S, Ichishima K, Ehara T (2007) Regulation of extracellular UTP-activated Cl− current by P2Y-PLC-PKC signaling and ATP hydrolysis in mouse ventricular myocytes. J Physiol Sci 57:85–94
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by DFG SFB699 A6, DFG KU 756/8-2. We acknowledge the generous supply of Grk-2 cDNA by Prof. Dr. D. I. Cook, University of Sydney. We acknowledge the expert technical assistance by Ms. E. Tartler and Ms. A. Paech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faria, D., Schreiber, R. & Kunzelmann, K. CFTR is activated through stimulation of purinergic P2Y2 receptors. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 457, 1373–1380 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0606-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0606-2