Abstract
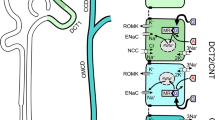
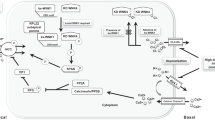
This review provides an overview of the molecular mechanisms of K transport in the mammalian connecting tubule (CNT) and cortical collecting duct (CCD), both nephron segments responsible for the regulation of renal K secretion. Aldosterone and dietary K intake are two of the most important factors regulating K secretion in the CNT and CCD. Recently, angiotensin II (AngII) has also been shown to play a role in the regulation of K secretion. In addition, genetic and molecular biological approaches have further identified new mechanisms by which aldosterone and dietary K intake regulate K transport. Thus, the interaction between serum-glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1 (SGK1) and with-no-lysine kinase 4 (WNK4) plays a significant role in mediating the effect of aldosterone on ROMK (Kir1.1), an important apical K channel modulating K secretion. Recent evidence suggests that WNK1, mitogen-activated protein kinases such as P38, ERK, and Src family protein tyrosine kinase are involved in mediating the effect of low K intake on apical K secretory channels.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Chen X, Lu M, Xu J-C, Lerea KM, Hebert SC, Wang W (1998) A kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) is required for mediating the effect of PKA on ROMK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:10274–10278
Amorim JB, Bailey MA, Musa-Aziz R, Giebisch G, Malnic G (2003) Role of luminal anion and pH in distal tubule potassium secretion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F381–F388
Amorim JBO, Malnic G (2000) V1 receptors in luminal action of vasopressin on distal K+ secretion. AJP–Renal Physiol 278:F809–F816
Amorim JBO, Musa-Aziz R, Mello-Aires M, Malnic G (2004) Signaling path of the action of AVP on distal K+ secretion. Kidney Int 66:696–704
Amorim JBO, Musa-Aziz R, Lessa LMA, Malnic G, Fonteles MC (2006) Effect of uroguanylin on potassium and bicarbonate transport in rat renal tubules. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 84:1003
Armitage FE, Wingo CS (1994) Luminal acidification in K-replete OMCDi: contributions of H-K-ATPase and bafilomycin-A1-sensitive H-ATPase. Am J Physiol 267:F450–F458
Babilonia E, Li D, Wang ZJ, Sun P, Lin DH, Wang WH (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibits ROMK-like small conductance K channels in the CCD of K-restricted rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2687–2696
Babilonia E, Lin D, Zhang Y, Wei Y, Yue P, Wang WH (2007) Role of gp91phox-containing NADPH oxidase in mediating the effect of K restriction on ROMK channels and renal K excretion. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2037–2045
Bailey MA, Cantone A, Yan QS, MacGregor GG, Leng Q, Amorim JB, Wang T, Hebert SC, Giebisch G, Malnic G (2006) Maxi-K channels contribute to urinary potassium excretion in the ROMK-deficient mouse model of type II Bartter’s syndrome and in adaptation to a high K diet. Kidney Int 70:51–59
Beck F-X, Dorge A, Giebisch G, Thurau K (1990) Effect of diuretics on cell potassium transport: an electron microprobe study. Kidney Int 37:1423–1428
Berger S, Bleich M, Schmid W, Cole TJ, Peters J, Watanabe H, Kriz W, Warth R, Greger R, Schutz G (1998) Mineralocorticoid receptor knockout mice: pathophysiology of Na+ metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:9424–9429
Buffin-Meyer B, Younes-Ibrahim M, Barlet-Bas C, Cheval L, Marsy S, Doucet A (1997) K depletion modifies the properties of Sch-28080-sensitive K-ATPase in rat collecting duct. Am J Physiol 272:F124–F131
Cassola AC, Giebisch G, Wang W (1993) Vasopressin increases density of apical low-conductance K+ channels in rat CCD. Am J Physiol 264:F502–F509
Choe H, Zhou H, Palmer LG, Sackin H (1997) A conserved cytoplasmic region of ROMK modulates pH sensitivity, conductance, and gating. Am J Physiol 273:F516–F529
Codina J, Wall SM, DuBose TD Jr. (1999) Contrasting functional and regulatory profiles of the renal H+,K+-ATPases. Sems Nephrol 19:399–404
Cope G, Murthy M, Golbang AP, Hamad A, Liu CH, Cuthbert AW, O’Shaughnessy KM (2006) WNK1 affects surface expression of the ROMK potassium channel independent of WNK4. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1867–1874
Dherbecourt O, Cheval L, Bloch-Faure M, Meneton P, Doucet A (2006) Molecular identification of Sch28080-sensitive K-ATPase activities in the mouse kidney. Pflugers Arch 451:769–775
Dong K, Xu J, Vanoye CG, Welch R, MacGregor GG, Giebisch G, Hebert SC (2001) An amino acid triplet in the NH2 terminus of rat ROMK1 determines interation with SUR2B. J Biol Chem 276:44347–44353
Doucet A, Marsy S (1987) Characterization of K-ATPase activity in distal nephron: stimulation by potassium depletion. Am J Physiol 253:F418–F423
Doyle DA, Cabral JM, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 280:69–77
DuBose TD Jr, Gitomer J, Codina J (1999) H+,K+-ATPase. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 8:597–602
Ellison DH, Velazquez H, Wright FS (1985) Stimulation of distal potassium secretion by low lumen chloride in the presence of barium. Am J Physiol 248:638–649
Estilo G, Liu W, Pastor-Soler N, Mitchell P, Carattino MD, Kleyman TR, Satlin LM (2008) Effect of aldosterone on BK channel expression in mammalian cortical collecting duct. AJP–Renal Physiol 295:F780–F788
Eric F, Davi M, Sand G, Geor D, Manl V, Alai D, Alai V, Vane S, Fran V, Martin PY (2003) Mechanism of control of Na,K-ATPase in principal cells of the mammalian collecting duct. Ann NY Acad Sci 986:570–578
Frindt G, Palmer LG (1987) Ca-activated K channels in apical membrane of mammalian CCT, and their role in K secretion. Am J Physiol (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol) 252–221:F458–F467
Frindt G, Palmer LG (1989) Low-conductance K channels in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol) 256–225:F143–F151
Frindt G, Palmer LG (2004) Apical potassium channels in the rat connecting tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F1030–F1037
Garg LC (1991) Respective role of H-ATPase and H–K-ATPase in ion transport in the kidney. JASN 2(5):949–960
Giebisch G (1998) Renal potassium transport: mechanisms and regulation. Am J Physiol 274:F817–F833
Giebisch G, Hebert SC, Wang WH (2003) New aspects of renal potassium transport. Pflugers Arch 446:289–297
Gray DA, Frindt G, Palmer LG (2005) Quantification of K+ secretion through apical low-conductance K channels in the CCD. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F117–F126
Gray DA, Frindt G, Zhang YY, Palmer LG (2005) Basolateral K+ conductance in principal cells of rat CCD. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F493–F504
Guntupalli J, Onuigbo M, Wall S, Alpern RJ, DuBose TD Jr (1997) Adaptation to low-K+ media increases H(+)–K(+)-ATPase but not H(+)-ATPase-mediated pHi recovery in OMCD1 cells. Am J Physiol 273:C558–C571
He G, Wang HR, Huang SK, Huang C-L (2007) Intersectin links WNK kinase to endocytosis of ROMK1. J Clin Invest 117:1078–1087
Hebert SC, Desir G, Giebisch G, Wang W (2005) Molecular diversity and regulation of renal potassium channels. Physiol Rev 85:319–371
Hebert SC, Wang W-H (1997) Structure and function of the low conductance KATP channel, ROMK. Wien Klin Wochenschr 109:471–476
Hirsch J, Schlatter E (1995) K+ channels in the basolateral membrane of rat cortical collecting duct. Kidney Int 48:1036–1046
Ho K (1998) The ROMK-cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator connection: new insights into the relationship between ROMK and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator channels. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 7:49–58
Horisberger J-D, Doucet A (2008) Renal ion-translocating ATPase: the P-type family. In: Alpern RJ, Hebert SC (eds) The kidney: physiology and pathophysiology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 57–90
Huang C-L, Feng S, Hilgemann DW (1998) Direct activation of inward rectifier potassium channels by PIP2 and its stabilization by Gbg. Nature 391:803–806
Huang DY, Wulff P, Volkl H, Loffing J, Richter K, Kuhl D, Lang F, Vallon V (2004) Impaired regulation of renal K+ elimination in the sgk1-knockout mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:885–891
Hunter M, Lopes AG, Boulpaep EL, Giebisch G (1984) Single channel recordings of calcium-activated potassium channels in the apical membrane of rabbit cortical collecting tubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81:4237–4239
Jin Y, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Yang B, Wang WH (2007) PGE2 inhibits apical K channels in the CCD through activation of the MAPK pathway. AJP–Renal Physiol 293:F1299–F1307
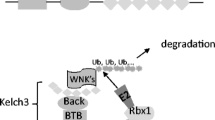
Kahle KT, Wilson FH, Leng Q, Lalioti MD, O’Connell AD, Dong K, Rapson AK, MacGregor GG, Giebisch G, Hebert SC, Lifton RP (2003) WNK4 regulates the balance between renal NaCl reabsorption and K+ secretion. Nat Genet 35:372–376
Kahle KT, Gimenez I, Hassan H, Wilson FH, Wong RD, Forbush B, Aronson PS, Lifton RP (2004) WNK4 regulates apical and basolateral Cl-flux in extrarenal epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:2064–2069
Kahle KT, Ring AM, Lifton RP (2008) Molecular physiology of the WNK kinases. Annu Rev Physiol 70:329–355
Kone BC (1996) Renal H,K-ATPase: structure, function and regulation. Miner Electrolyte Metab 22:349–365
Lazrak A, Liu Z, Huang CL (2006) Antagonistic regulation of ROMK by long and kidney-specific WNK1 isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:1615–1620
Lee FN, Oh G, McDonough AA, Youn JH (2007) Evidence for gut factor in K+ homeostasis. AJP–Renal Physiol 293:F541–F547
Leng Q, Kahle KT, Rinehart J, MacGregor GG, Wilson FH, Canessa CM, Lifton RP, Hebert SC (2006) WNK3, a kinase related to genes mutated in hereditary hypertension with hyperkaelemia, regulates the K+ channel ROMK1 (Kir1.1). J Physiol 571:275–286
Li DM, Wang ZJ, Sun P, Jin Y, Lin DH, Hebert SC, Giebisch G, Wang WH (2006) Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase stimulates the Ca2+-dependent big conductance K channels (BK) in cortical collecting duct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:19569–19574
Liapis H, Nag M, Kaji DM (1998) K–Cl cotransporter expression in the human kidney. AJP–Cell Physiol 275:C1432–C1437
Lin DH, Sterling H, Lerea KM, Giebisch G, Wang WH (2002) Protein kinase C (PKC)-induced phosphorylation of ROMK1 is essential for the surface expression of ROMK1 channels. J Biol Chem 277:44332–44338
Lin DH, Sterling H, Lerea KM, Welling P, Jin L, Giebisch G, Wang WH (2002) K depletion increases the protein tyrosine-mediated phosphorylation of ROMK. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F671–F677
Lin DH, Sterling H, Yang B, Hebert SC, Giebisch G, Wang WH (2004) Protein tyrosine kinase is expressed and regulates ROMK1 location in the cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F881–F892
Ling BN, Hinton CF, Eaton DC (1991) Potassium permeable channels in primary cultures of rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Kidney Int 40:441–452
Liou HH, Zhou SS, Huang CL (1999) Regulation of ROMK1 channel by protein kinase A via a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:5820–5825
Lu M, Hebert SC, Giebisch G (2002) Hydrolyzable ATP and PIP2 modulate the small-conductance K channel in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting duct. J Gen Physiol 120:603–615
Lu M, Leng Q, Egan ME, Caplan MJ, Boulpaep E, Giebisch G, Hebert SC (2006) CFTR is required for PKA-regulated ATP sensitivity of Kir1.1 potassium channels in mouse kidney. J Clin Invest 116:797–806
Lu R, Alioua A, Kumar Y, Eghbali M, Stefani E, Toro L (2006) MaxiK channel partners: physiological impact. J Physiol 570:65–72
Ma J, Qu W, Scarborough PE, Tomer KB, Moomaw CR, Maronpot R, Davis LS, Breyer MD, Zeldin DC (1999) Molecular cloning, enzymatic characterization, developmental expression, and cellular localization of a mouse cytochrome P450 highly expressed in kidney. J Biol Chem 274:17777–17788
Marsy S, Elalouf J-M, Doucet A (1996) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA encoding a colonic H,K-ATPase alpha subunit along the rat nephron: effect of K+ depletion. Pflugers Arch 432:494–500
McNicholas CM, Nason MW, Guggino WB, Schwiebert EM, Hebert S, Giebisch G, Egan ME (1997) The functional CFTR-NBF1 is required for ROMK2-CFTR interaction. Am J Physiol 273:F843–F848
McNicholas CM, Wang W, Ho K, Hebert SC, Giebisch G (1994) Regulation of ROMK1 K+ channel activity involves phosphorylation processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:8077–8081
Meneton P, Schultheis PJ, Greeb J, Nieman ML, Liu LH, Clarke LL, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T, Lorenz JN, Shull GE (1998) Increased sensitivity to K+ deprivation in colonic H,K-ATPase-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 101:536–542
Minor DL, Masseling SJ, Jan YN, Jan LY (1999) Transmembrane structure of an inwardly rectifying potassium channel. Cell 97:879–891
Moral Z, Deng K, Wei Y, Sterling H, Deng H, Ali S, Gu RM, Huang XY, Hebert SC, Giebisch G, Wang WH (2001) Regulation of ROMK1 channels by protein tyrosine kinase and tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem 276:7156–7163
Muto S, Sansom S, Giebisch G (1988) Effects of a high potassium diet on electrical properties of cortical collecting duct from adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest 81:376–380
Muto S, Tsuruoka S, Miyata Y, Fujimura A, Kusano E, Wang WH, Seldin D, Giebing G (2008) Basolateral Na+/H+ exchange is involved in maintaining K+ secretion during diminished Na+ transport in rabbit CCD. Kid Int. doi:10.1038/ki.2008.447
Najjar F, Zhou H, Morimoto T, Bruns JB, Li HS, Liu W, Kleyman TR, Satlin LM (2005) Dietary K+ regulates apical membrane expression of maxi-K channels in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F922–F932
Nakagawa K, Holla VR, Wei Y, Wang WH, Gatica A, Wei S, Mei S, Miller CM, Cha DR, Price EJ, Zent R, Pozzi A, Breyer MD, Guan Y, Falck JR, Waterman MR, Capdevila JH (2006) Salt sensitive hypertension is associated with a dysfunctional Cyp4a10 gene and kidney epithelial sodium channel. J Clin Invest 116:1696–1702
Nichols CG, Lopatin AN (1997) Inward rectifier potassium channels. Ann Rev Physiol 59:171–191
O’Connell AD, Leng Q, Dong K, MacGregor GG, Giebisch G, Hebert SC (2005) Phosphorylation-regulated endoplasmic reticulum retention signal in the renal outer-medullary K+ channel (ROMK). Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:9954–9959
O’Neil RG (1981) Potassium secretion by the cortical collecting tubule. Federation Proc 40:2403–2407
O’Neil RG, Hayhurst AR (1985) Functional differentiation of cell types of cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol 248:449–453
O’Neil RG, Sansom SC (1984) Characterization of apical cell membrane Na+ and K+ conductances of cortical collecting duct using microelectrode techniques. Am J Physiol 247(Renal 16):F14–F24
O’Reilly M, Marshall E, Speirs HJL, Brown RW (2003) WNK1, a gene within a novel blood pressure control pathway, tissue-specifically generates radically different isoforms with and without a kinase domain. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2447–2456
Orias M, Velazquez H, Tung F, Lee G, Desir GV (1997) Cloning and localization of a double-pore K channel, KCNK1: exclusive expression in distal nephron segments. AJP–Renal Physiol 273:F663–F666
Palmer LG (1999) Potassium secretion and the regulation of distal nephron K channels. Am J Physiol 277:F821–F825
Palmer LG, Antonian L, Frindt G (1993) Regulation of the Na–K pump of the rat cortical collecting tubule by aldosterone. J Gen Physiol 102:43–57
Palmer LG, Antonian L, Frindt G (1994) Regulation of apical K and Na channels and Na/K pumps in rat cortical collecting tubule by dietary K. J Gen Physiol 104:693–710
Palmer LG, Frindt G (1992) Regulation of apical membrane Na and K channels in rat renal collecting tubules by aldosterone. Sems Nephrol 12:37–43
Palmer LG, Frindt G (1999) Regulation of apical K channels in rat cortical collecting tubule during changes in dietary K intake. Am J Physiol 277:F805–F812
Palmer LG, Frindt G (2007) High-conductance K channels in intercalated cells of the rat distal nephron. AJP–Renal Physiol 292:F966–F973
Rapedius M, Haider S, Browner KF, Shang L, Sanson MSP, Baukroitz T, Tucker SJ (2006) Structural and functional analysis of the putative pH sensor in the Kir1.1 (ROMK) potassium channel. EMBO Rep 7:611–616
Ray PE, Suga SI, Liu XH, Huang X, Johnson RJ (2001) Chronic potassium depletion induces renal injury, salt sensitivity, and hypertension in young rats. Kidney Int 59:1850–1858
Rieg T, Vallon V, Sausbier M, Sausbier U, Kaissling B, Ruth P, Osswald H (2007) The role of the BK channel in potassium homeostasis and flow-induced renal potassium excretion. Kidney Int 72:566–573
Ring AM, Leng Q, Rinehart J, Wilson FH, Kahle KT, Hebert SC, Lifton RP (2007) An SGK1 site in WNK4 regulates Na+ channel and K+ channel activity and has implications for aldosterone signaling and K+ homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:4025–4029
Rossier BC, Canessa CM, Schild L, Horisberger J-D (1994) Epithelial sodium channels. Curr Opin Nephrol Hyperten 3:487–496
Saikaley A, Bichet D, Kucharczyk J, Peterson LN (1986) Neuroendocrine factors mediating polydipsia induced by dietary Na, Cl, and K depletion. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 251:R1071–R1077
Salkoff L, Butler A, Ferreira G, Santi C, Wei A (2006) High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:921–931
Sansom SC, O’Neil RG (1986) Effects of mineralocorticoids on transport properties of the cortical collecting duct basolateral membrane. Am J Physiol 251:743–757
Satlin LM (1994) Postnatal maturation of potassium transport in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol 266:F57–F65
Satlin LM (2004) Developmental regulation of expression of renal potassium secretory channels. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13:445–450
Satlin LM, Palmer LG (1997) Apical K+ conductance in maturing rabbit principal cell. Am J Physiol 272:F397–F404
Schafer JA, Troutman SL (1987) Potassium transport in cortical collecting tubules from mineralocorticoid-treated rat. Am J Physiol (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol) 253:F76–F88
Schafer JA, Troutman SL, Schlatter E (1990) Vasopressin and mineralocorticoid increase apical membrane driving force for K+ secretion in rat CCD. Am J Physiol 258:F199–F210
Schlatter E (1993) Regulation of ion channels in the cortical collecting duct. Renal Physiol Biochem 16:21–36
Schlatter E, Haxelmans S, Hirsch J, Leipziger J (1994) pH dependence of K+ conductances of rat cortical collecting duct principal cells. Pflugers Archiv 428:631–640
Schlatter E, Lohrmann E, Greger R (1992) Properties of the potassium conductances of principal cells of rat cortical collecting ducts. Pflugers Arch 420:39–45
Schlatter E, Schafer JA (1987) Electrophysiological studies in principal cells of rat cortical collecting tubules. Pflugers Arch 409:81–92
Sealey JE, Clark I, Bull MB, Laragh JH (1970) Potassium balance and the control of renin secretion. J Clin Invest 49:2119–2127
Silver RB, Soleimani M (1999) H–K-ATPase regulation and role in pathophysiological states. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 276:F799–F811
Sindic A, Hirsch JR, Velic A, Piechota H, Schlatter E (2005) Guanylin and uroguanylin regulate electrolyte transport in isolated human cortical collecting ducts. Kidney Int 67:1420–1427
Sindic A, Velic A, Basoglu C, Hirsch JR, Edemir B, Kuhn M, Schlatter E (2005) Uroguanylin and guanylin regulate transport of mouse cortical collecting duct independent of guanylate cyclase C. Kidney Int 68:1008–1017
Soundararajan R, Zhang TT, Wang J, Vandewalle A, Pearce D (2005) A novel role for glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper protein in epithelial sodium channel-mediated sodium transport. J Biol Chem 280:39970–39981
Sterling H, Lin DH, Gu RM, Dong K, Hebert SC, Wang WH (2002) Inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatase stimulates the dynamin-dependent endocytosis of ROMK1. J Biol Chem 277:4317–4323
Sterling H, Lin DH, Wei Y, Wang WH (2003) Tetanus toxin abolishes exocytosis of ROMK1 induced by inhibition of protein tyrosine kinase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F510–F517
Summa V, Camargo SMR, Bauch C, Zecevic M, Verrey F (2004) Isoform specificity of human Na+,K+-ATPase localization and aldosterone regulation in mouse kidney cells. J Physiol 555:355–364
Sun P, Lin DH, Wang T, Babilonia E, Wang ZJ, Jin Y, Kemp R, Nasjletti A, Wang WH (2006) Low Na intake suppresses the expression of CYP2C23 and the arachidonic acid-induced inhibition of ENaC. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:1192–1200
Sun P, Liu W, Lin DH, Yue P, Kemp R, Satlin LM, Wang WH (2008) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET) activates the Ca2+-dependent bid conductance K channel in the cortical collecting duct. J Am Soc Nephrol (in press)
Taniguchi J, Imai M (1998) Flow-dependent activation of maxi K+ channels in apical membrane of rabbit connecting tubule. J Membr Biol 164:35–45
Vallon V, Wulff P, Huang DY, Loffing J, Volkl H, Kuhl D, Lang F (2005) Role of Sgk1 in salt and potassium homeostasis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R4–R10
Velazquez H, Ellison DH, Wright FS (1992) Luminal influences on potassium secretion: chloride, sodium, and thiazide diuretics. Am J Physiol (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol) 262–231:F1076–F1082
Verlander JW, Moudy RM, Campbell WG, Cain BD, Wingo CS (2001) Immunohistochemical localization of H–K-ATPase alpha 2c-subunit in rabbit kidney. AJP–Renal Physiology 281:F357–F365
Fran V, Vane S, Dirk H, Davi M, Alai V, Eric F, Mari Z (2003) Short-term aldosterone action on Na,K-ATPase surface expression: role of aldosterone-induced SGK1? Ann NY Acad Sci 986:554–561
Wade JB, Fang L, Liu J, Li D, Yang CL, Subramanya AR, Maouyo D, Mason A, Ellison DH, Welling PA (2006) WNK1 kinase isoform switch regulates renal potassium excretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:8558–8563
Wang T, Giebisch G (1996) Effects of angiotensin II on electrolyte transport in the early and late distal tubule in rat kidney. Am J Physiol 271:F143–F149
Wang W, Schwab A, Giebisch G (1990) Regulation of small-conductance K channel in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol 259:F494–F502
Wang WH (2000) The cGMP-dependent protein kinase stimulates the basolateral 18 pS K channel of the rat CCD. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278:C1212–C1217
Wang WH (2004) Regulation of Renal K transport by dietary K intake. Annu Rev Physiol 66:547–569
Wang WH, Lerea KM, Chan M, Giebisch G (2000) Protein tyrosine kinase regulates the number of renal secretory K channel. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278:F165–F171
Wang WH, McNicholas CM, Segal AS, Giebisch G (1994) A novel approach allows identification of K channels in the lateral membrane of rat CCD. Am J Physiol 266:F813–F822
Wei Y, Bloom P, Gu R, Wang W (2000) Protein-tyrosine phosphatase reduces the number of apical small conductance K+ channels in the rat cortical collecting duct. J Biol Chem 275:20502–20507
Wei Y, Bloom P, Gu RM, Wang WH (2000) Protein-tyrosine phosphatase reduces the number of apical small conductance K channels in the rat cortical collecting duct. J Biol Chem 275:20502–20507
Wei Y, Bloom P, Lin DH, Gu RM, Wang WH (2001) Effect of dietary K intake on the apical small-conductance K channel in the CCD: Role of protein tyrosine kinase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F206–F212
Wei Y, Bloom P, Lin DH, Gu RM, Wang WH (2001) Effect of dietary K intake on the apical small-conductance K channel in the CCD: Role of protein tyrosine kinase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F206–F212
Wei Y, Wang WH (2001) The role of cytoskeleton in mediating the effect of vasopressin and herbimycin A on the secretory K channels in the CCD. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F680–F686
Wei Y, Wang ZJ, Babilonia E, Sterling H, Sun P, Wang WH (2006) Effect of hydrogen peroxide on ROMK channels in the cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 0:0
Wei Y, Zavilowitz B, Satlin LM, Wang WH (2007) Angiotensin II inhibits the ROMK-like small-conductance K channel in renal cortical collecting duct during dietary K restriction. J Biol Chem 0:0
Welling PA, Caplan M, Sutters M, Giebisch G (1993) Aldosterone-mediated Na/K-ATPase expression is alpha 1 isoform specific in the renal cortical collecting duct. J Biol Chem 268:23469–23476
Wingo CS, Cain BD (1993) The renal H–K-ATPase: physiological significance and role in potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol 55:323–347
Wingo CS (1987) Potassium transport by medullary collecting tubule of rabbit: effects of variation in K intake. Am J Physiol (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol) 253–22:F1136–F1141
Wingo CS (1989) Reversible chloride-dependent potassium transport in cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol 256:F697–F704
Wingo CS, Armitage FE (1992) Rubidium absorption and proton secretion by rabbit outer medullary collecting duct via H–K-ATPase. Am J Physiol (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol) 263:F849–F857
Woda CB, Bragin A, Kleyman TR, Satlin LM (2001) Flow-dependent K+ secretion in the cortical collecting duct is mediated by a maxi-K channel. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F786–F793
Xu B, Stippec S, Lazrak A, Huang CL, Cobb MH (2005) WNK1 Activates SGK1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and non-catalytic mechanism. J Biol Chem 280:34218–34223
Xu ZC, Yang Y, Hebert SC (1996) Phosphorylation of the ATP-sensitive, inwardly rectifying K+ channel, ROMK, by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 271:9313–9319
Yang T, Singh I, Pham H, Sun D, Smart A, Schnermann JB, Briggs JP (1998) Regulation of cyclooxygenase expression in the kidney by dietary salt intake. AJP–Renal Physiol 274:F481–F489
Yoo D, Kim BY, Campo C, Nance L, King A, Maouyo D, Welling PA (2003) Cell surface expression of the ROMK (Kir 1.1) channel is regulated by the aldosterone-induced kinase, SGK-1, and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem 278:23066–23075
Yoo D, Fang L, Mason A, Kim BY, Welling PA (2005) A phosphorylation-dependent export structure in ROMK (Kir 1.1) channel overrides an endoplasmic reticulum localization signal. J Biol Chem 280:35281–35289
Younes-Ibrahim M, Barlet-Bas C, Buffin-Meyer B, Cheval L, Rajerison R, Doucet A (1995) Ouabain-sensitive and -insensitive K-ATPases in rat nephron: effect of K depletion. Am J Physiol 268:F1141–F1147
Yun CC, Palmada M, Embark HM, Fedorenko O, feng Y, Henke G, Setiawan I, Boehmer C, Weinman EJ, Sandrasagra S, Korbmacher C, Cohen P, Pearce D, Lang F (2002) The serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase SGK1 and Na/H exchange regulating factor NHERF2 synergize to stimulate the renal outer medullary K channel ROMK1. JASN 13:2823–2830
Zhen WZ, Li XJ, Hilgemann DW, Huang CL (2003) Protein kinase C inhibits ROMK1 channel activity via phosphotidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphosphate-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 276:16852–16856
Zhou X, Lynch IJ, Xia SL, Wingo CS (2000) Activation of H-K-ATPase by CO2 requires a basolateral Ba2+-sensitive pathway during K restriction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F153–F160
Zhou X, Wingo CS (1992) H-K-ATPase enhancement of Rb efflux by cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol (Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol) 263:F43–F48
Zhou X, Wingo CS (1992) Mechanisms of rubidium permeability by rabbit cortical collecting duct during potassium restriction. Am J Physiol 263:F1134–F1141
Zhou X, Wingo CS (1994) Stimulation of total CO2 flux by 10% CO2 in rabbit CCD: role of an apical Sch-28080- and Ba-sensitive mechanism. Am J Physiol 267(Renal 36):F114–F120
Acknowledgment
We dedicate this manuscript to Dr. Steven H. Hebert, our friend and colleague who died quite unexpectedly on April 15th 2008. We lost with him a long-standing collaborator, friend, and an investigator who made major contributions in the field of potassium transport. The authors also thank Drs. D. Mount and R. B. Silver for their insightful comments. The work is supported by NIH grants DK 47402, DK54983 and HL34100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, WH., Giebisch, G. Regulation of potassium (K) handling in the renal collecting duct. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 458, 157–168 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0593-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0593-3