Abstract
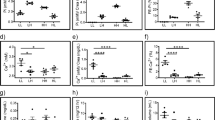
Proximal solute and fluid absorption is greatly reduced in mice in which the gene encoding the Na/H exchanger isoform 3 has been ablated (NHE3−/−). To obtain information on the intracellular functional consequences of such selective NHE3 deficiency, Na, Cl and K concentrations and cell Rb uptake were measured using electron microprobe analysis after a 30-s infusion of Rb (an index of basolateral Na/K-ATPase activity) in proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) cells of NHE3−/− and wild-type (NHE3+/+) mice. In addition, the relative abundance of the α1-subunit of the Na/K-ATPase in the outer cortex was determined by Western blot analysis. PCT cell Na concentration in NHE3−/− mice was slightly but significantly lower than in NHE3+/+ [13.1±0.6 (n=64) vs. 14.9±0.6 (n=62) mmol/kg wet wt.; means ±SEM]. The lower intracellular Na concentration was associated with significantly reduced Rb uptake rates [9.7±0.6 (n=59) vs. 14.8±0.8 (n=50) mmol/kg wet wt./30 s], but the abundance of the α1-subunit of the Na/K-ATPase was not different between NHE3−/− and NHE3+/+ mice. Intracellular Cl concentration was higher (14.2±0.4 vs. 12.8±0.4 mmol/kg wet wt.) and K concentration unchanged (122.7±2.7 vs. 121.6±2.5 mmol/kg wet wt.) in PCT cells in NHE3−/− compared with NHE3+/+ mice. These findings suggest that the elimination of apical NHE3 in PCT cells of NHE3−/− mice reduces apical Na entry and, due to lower cell Na concentrations, Na/K-ATPase activity. The observed changes in intracellular Na concentration did not affect the expression of Na/K-ATPase in the renal cortex of NHE3−/− mice. There were no significant changes of cell Na concentration and Rb uptake in distal convoluted tubule, connecting tubule, principal and intercalated cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Type-I IC cells are thought to be type-A IC cells [4]. In rabbits, IC cells of the cortical collecting duct have a low membrane potential (−35 mV) and a high basolateral Cl conductance [24]. Comparatively high intracellular Cl concentrations would thus be expected. This type of IC cell is the predominant cell type in the outer medulla and mimics the intrarenal distribution of type-A IC cells [8, 34]. It should be noted that such high intracellular Cl concentrations would compromise the activity of the apical Cl/HCO3 exchanger in type-B IC cells because the concentrations of Cl in the distal tubule fluid may be below 40 mM in this tubule segment [6]. Thus, Cl concentrations in the range of those observed in type-I IC cells would diminish the chemical driving force for apical entry of Cl via electroneutral Cl/HCO3 exchange in type-B IC cells.
References
Aronson PS, Giebisch G (1997) Mechanisms of chloride transport in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol 273:F179–F192
Barlet-Bas C, Khadouri C, Marsy S, Doucet A (1990) Enhanced intracellular sodium concentration in kidney cells recruits a latent pool of Na-K-ATPase whose size is modulated by corticosteroids. J Biol Chem 265:7799–7803
Beck FX, Dörge A, Blümner E, Giebisch G, Thurau K (1988) Cell rubidium uptake: a method for studying functional heterogeneity in the nephron. Kidney Int 33:642–651
Beck FX, Dörge A, Giebisch G, Thurau K (1988) Renal excretion of rubidium and potassium: an electron microprobe and clearance study. Kidney Int 34:455–462
Beck FX, Dörge A, Giebisch G, Thurau K (1990) Effect of diuretics on cell potassium transport: an electron microprobe study. Kidney Int 37:1423–1428
Beck FX, Dörge A, Rick R, Schramm M, Thurau K (1987) Effect of potassium adaptation on the distribution of potassium, sodium and chloride across the apical membrane of renal tubular cells. Pflugers Arch 409:477–485
Beck FX, Ohno A, Dörge A, Thurau K (1994) Loop diuretics affect transcellular electrolyte transport in cells of the distal convoluted tubule. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:403–407
Beck FX, Ohno A, Dörge A, Thurau K (1995) Ischemia-induced changes in cell element composition and osmolyte contents of outer medulla. Kidney Int 48:449–457
Beck FX, Schramm M, Dörge A, Rick R, Thurau K (1988) Effect of acute metabolic acidosis on transmembrane electrolyte gradients in individual renal tubule cells. Pflugers Arch 412:427–433
Berger UV, Peng JB, Hediger MA (2000) The membrane transporter families in mammals. In: Seldin DW, Giebisch G (eds) The kidney: physiology and pathophysiology, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 107–138
Brooks HL, Sorensen AM, Terris J, Schultheis PJ, Lorenz JN, Shull GE, Knepper MA (2001) Profiling of renal tubule Na+ transporter abundance in NHE3 and NCC null mice using targeted proteomics. J Physiol (Lond) 530:359–366
Doucet A, Katz AI (1980) Renal potassium adaptation: Na-K-ATPase activity along the nephron after chronic potassium loading. Am J Physiol 238:F380–F386
Eaton DC, Hamilton KL, Johnson KE (1984) Intracellular acidosis blocks the basolateral Na-K-pump in rabbit urinary bladder. Am J Physiol 247:F946–F954
Flemmer A, Dörge A, Thurau K, Beck FX (1993) Transcellular sodium transport and basolateral rubidium uptake in the isolated perfused cortical collecting duct. Pflugers Arch 424:250–254
Giebisch G, Wang W (2000) Renal tubule potassium channels: function, regulation and structure. Acta Physiol Scand 170:153–173
Gmaj P, Murer H, Kinne R (1979) Calcium ion transport across plasma membranes isolated from rat kidney cortex. Biochem J 15:549–557
Hurst AM, Beck JS, Laprade R, Lapointe JY (1993) Na+ pump inhibition downregulates an ATP-sensitive K+ channel in rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol 264:F760–F764
Ibarra FR, Jun Cheng SX, Agren M, Svensson LB, Aizman O, Aperia A (2002) Intracellular sodium modulates the state of protein kinase C phosphorylation of rat proximal tubule Na+,K+-ATPase. Acta Physiol Scand 175:165–171
Jörgensen PL (1980) Sodium and potassium ion pump in the kidney tubules. Physiol Rev 60:864–917
Katz AI, Doucet A, Morel F (1979) Na-K-ATPase activity along the rabbit, rat, and mouse nephron. Am J Physiol 237:F114–F120
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee YC, Lin HH, Tang MJ (1995) Glucocorticoid upregulates Na-K-ATPase alpha- and beta-mRNA via an indirect mechanism in proximal tubule cell primary cultures. Am J Physiol 268:F862–F867
Lorenz JN, Schultheis PJ, Traynor T, Shull GE, Schnermann J (1999) Micropuncture analysis of single-nephron function in NHE3-deficient mice. Am J Physiol 277:F447–F453
Muto S, Giebisch G, Sansom S (1987) Effects of adrenalectomy on CCD: evidence for differential response of two cell types. Am J Physiol 253:F742–F752
Muto S, Nemoto J, Okada K, Miyata Y, Kawakami K, Saito T, Asano Y (2000) Intracellular Na+ directly modulates Na+,K+-ATPase gene expression in normal rat kidney epithelial cells. Kidney Int 57:1617–1635
Neuhofer W, Lugmayr K, Fraek ML, Beck FX (2001) Regulated overexpression of heat shock protein 72 protects Madin-Darby canine kidney cells from the detrimental effects of high urea concentrations. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2565–2571
O'Neil RG, Hayhurst RA (1985) Sodium-dependent modulation of the renal Na-K-ATPase: influence of mineralocorticoids on the cortical collecting duct. J Membr Biol 85:169–179
Ohno A, Beck FX, Pfaller W, Giebisch G, Wang T (1995) Effects of chronic hyperfiltration on proximal tubule bicarbonate transport and cell electrolytes. Kidney Int 48:712–721
Pfaller W (1982) Structure function correlation on rat kidney. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 70:1–106
Pietrini G, Matteoli M, Banker G, Caplan MJ (1992) Isoforms of the Na,K-ATPase are present in both axons and dendrites of hippocampal neurons in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8414–8418
Schultheis PJ, Clarke LL, Meneton P, Miller ML, Soleimani M, Gawenis LR, Riddle TM, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T, Wang T, Giebisch G, Aronson PS, Lorenz JN, Shull GE (1998) Renal and intestinal absorptive defects in mice lacking the NHE3 Na+/H+ exchanger. Nature Genet 19:282–285
Shyjan AW, Levenson R (1989) Antisera specific for the α1, α2, α 3 and β subunits of the Na,K-ATPase: differential expression of α and β subunits in rat tissue membranes. Biochemistry 28:4531–4535
Therien AG, Blostein R (2000) Mechanisms of sodium pump regulation. Am J Physiol 279:C541–C566
Tisher CC, Madsen KM (2000) Anatomy of the kidney. In: Brenner BM (ed) The kidney, 6th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 3–67
Tsuchiya K, Wang W, Giebisch G, Welling PA (1992) ATP is a coupling modulator of parallel Na,K-ATPase-K-channel activity in the renal proximal tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6418–6422
Wang T, Yang CL, Abbiati T, Schultheis PJ, Shull GE, Giebisch G, Aronson PS (1999) Mechanism of proximal tubule bicarbonate absorption in NHE3 null mice. Am J Physiol 277:F298–F302
Wang W, Hebert SC, Giebisch G (1997) Renal K+ channels: structure and function. Annu Rev Physiol 59:413–436
Weinstein AM (2000) Sodium and chloride transport: proximal nephron. In: Seldin DW, Giebisch G (eds) The kidney: physiology and pathophysiology, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1287–1331
Willmann JK, Bleich M, Rizzo M, Schmidt-Hieber M, Ullrich KJ, Greger R (1997) Amiloride-inhibitable Na+ conductance in rat proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch 434:173–178
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (BE 963/10–1) and NIH grant DK 17433. Collaboration between the authors' laboratories was supported by a NATO collaborative research grant. The authors are indebted to Dr. M. Caplan for the gift of the Na/K-ATPase-specific antibody, to Dr. G. Shull for providing the NHE3+/+ and NHE3−/− mice (NIH grant DK 50594) and to M.L. Fraek and I. Öztürk for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, FX., Neuhofer, W., Dörge, A. et al. Intracellular Na concentration and Rb uptake in proximal convoluted tubule cells and abundance of Na/K-ATPase α1-subunit in NHE3−/− mice. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 446, 100–105 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-1001-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-1001-z