Abstract
Background
Elevated donor serum creatinine has been associated with inferior graft survival in kidney transplantation (KT). The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of elevated donor serum creatinine on short and long-term outcomes and to determine possible ways to optimize the use of these organs.
Methods
All kidney transplants from 01–2000 to 12–2012 with donor creatinine ≥ 2 mg/dl were considered. Risk factors for delayed graft function (DGF) were explored with uni- and multivariate regression analyses. Donor and recipient data were analyzed with uni- and multivariate cox proportional hazard analyses. Graft and patient survival were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
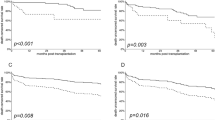
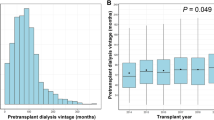
Seventy-eight patients were considered. Median recipient age and waiting time on dialysis were 53 years and 5.1 years, respectively. After a median follow-up of 6.2 years, 63 patients are alive. 1, 3, and 5-year graft and patient survival rates were 92, 89, and 89 % and 96, 93, and 89 %, respectively. Serum creatinine level at procurement and recipient’s dialysis time prior to KT were predictors of DGF in multivariate analysis (p = 0.0164 and p = 0.0101, respectively). Charlson comorbidity score retained statistical significance by multivariate regression analysis for graft survival (p = 0.0321). Recipient age (p = 0.0035) was predictive of patient survival by multivariate analysis.
Conclusions
Satisfactory long-term kidney transplant outcomes in the setting of elevated donor serum creatinine ≥2 mg/dl can be achieved when donor creatinine is <3.5 mg/dl, and the recipient has low comorbidities, is under 56 years of age, and remains in dialysis prior to KT for <6.8 years.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
acute kidney injury
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- CIT:
-
cold ischemic time
- CMV:
-
cytomegalovirus
- CPR:
-
cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- DGF:
-
delayed graft function
- DCD:
-
donor after cardiac death
- ECD:
-
extended criteria donor
- HLA:
-
human leukocyte antigen
- HTK:
-
histidine-tryptophane-ketoglutarate
- ICU:
-
intensive care unit
- IGF:
-
immediate graft function
- KT:
-
kidney transplantation
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristic
- UW:
-
University of Wisconsin
- WIT:
-
warm ischemia time
References
Mayer G, Persijn GG (2006) Eurotransplant kidney allocation system (ETKAS): rationale and implementation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2–3
Ahlert M, Kliemt H (2013) Problems of priority change in kidney allocation and beyond. Eur J Health Econ 14:383–390
Glander P, Budde K, Schmidt D, Fuller TF, Giessing M, Neumayer HH, Liefeldt L (2010) The “blood group O problem” in kidney transplantation—time to change? Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:1998–2004
Palmes D, Wolters HH, Brockmann J, Senninger N, Spiegel HU, Dietl KH (2004) Strategies for compensating for the declining numbers of cadaver donor kidney transplants. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:952–962
Gallinat A, Feldkamp T, Schaffer R, Radünz S, Treckmann JW, Minor T, Witzke O, Paul A, Sotiropoulos GC (2011) Single-center experience with kidney transplantation using deceased donors older than 75 years. Transplantation 92:76–81
Gallinat A, Paul A, Minor T, Treckmann JW, Molmenti EP, Witzke O, Sotiropoulos GC (2012) Optimized outcomes for renal allografts with cold ischemic times of 20 h or greater. Int Urol Nephrol 44:1417–1423
Gallinat A, Sotiropoulos GC, Witzke O, Treckmann JW, Molmenti EP, Paul A, Vester U (2013) Kidney grafts from donors ≤ 5 yr of age: single kidney transplantation for pediatric recipients or en bloc transplantation for adults? Pediatr Transplant 17:179–184
Gallinat A, Moers C, Treckmann J, Smits JM, Leuvenink HG, Lefering R, van Heurn E, Kirste GR, Squifflet JP, Rahmel A, Pirenne J, Ploeg RJ, Paul A (2012) Machine perfusion versus cold storage for the preservation of kidneys from donors ≥ 65 years allocated in the Eurotransplant Senior Programme. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:4458–4463
Gallinat A, Paul A, Efferz P, Lüer B, Swoboda S, Hoyer D, Minor T (2012) Role of oxygenation in hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys from heart beating donors. Transplantation 94:809–813
Gallinat A, Lüer B, Swoboda S, Rauen U, Paul A, Minor T (2013) Use of the new preservation solution Custodiol-N supplemented with dextran for hypothermic machine perfusion of the kidney. Cryobiology 66:131–135
Gallinat A, Moers C, Smits JM, Strelniece A, Pirenne J, Ploeg RJ, Paul A, Treckmann J (2013) Machine perfusion versus static cold storage in expanded criteria donor kidney transplantation: 3-year follow-up data. Transpl Int 26:E52–53
Gallinat A, Paul A, Efferz P, Lüer B, Kaiser G, Wohlschlaeger J, Treckmann J, Minor T (2012) Hypothermic reconditioning of porcine kidney grafts by short-term preimplantation machine perfusion. Transplantation 93:787–793
Treckmann J, Moers C, Smits JM, Gallinat A, Maathuis MH, van Kasterop-Kutz M, Jochmans I, Homan van der Heide JJ, Squifflet JP, van Heurn E, Kirste GR, Rahmel A, Leuvenink HG, Pirenne J, Ploeg RJ, Paul A (2011) Machine perfusion versus cold storage for preservation of kidneys from expanded criteria donors after brain death. Transpl Int 24:548–554
Gallinat A, Fox M, Lüer B, Efferz P, Paul A, Minor T (2013) Role of pulsatility in hypothermic reconditioning of porcine kidney grafts by machine perfusion after cold storage. Transplantation 96:538–542
Nagelschmidt M, Minor T, Gallinat A, Moers C, Jochmans I, Pirenne J, Ploeg RJ, Paul A, Treckmann J (2013) Lipid peroxidation products in machine perfusion of older donor kidneys. J Surg Res 180:337–342
Lopes JA, Moreso F, Riera L, Carrera M, Ibernon M, Fulladosa X, Grinyó JM, Serón D (2005) Evaluation of pre-implantation kidney biopsies: comparison of Banff criteria to a morphometric approach. Kidney Int 67:1595–1600
Roodnat JI, Mulder PG, Van Riemsdijk IC, IJzermans JN, van Gelder T, Weimar W (2003) Ischemia times and donor serum creatinine in relation to renal graft failure. Transplantation 75:799–804
Parzanese I, Maccarone D, Caniglia L, Pisani F, Mazzotta C, Rizza V, Famulari A (2006) Risk factors that can influence kidney transplant outcome. Transplant Proc 38:1022–1023
Wu WK, Famure O, Li Y, Kim SJ (2015) Delayed graft function and the risk of acute rejection in the modern era of kidney transplantation. Kidney Int 88:851–858
Ugarte R, Kraus E, Montgomery RA, Burdick JF, Ratner L, Haas M, Hawxby AM, Karp SJ (2005) Excellent outcomes after transplantation of deceased donor kidneys with high terminal creatinine and mild pathologic lesions. Transplantation 80:794–800
Morgan C, Martin A, Shapiro R, Randhawa PS, Kayler LK (2007) Outcomes after transplantation of deceased-donor kidneys with rising serum creatinine. Am J Transplant 7:1288–1292
Lin NC, Yang AH, King KL, Wu TH, Yang WC, Loong CC (2010) Results of kidney transplantation from high-terminal creatinine donors and the role of time-zero biopsy. Transplant Proc 42:3382–3386
Kolonko A, Chudek J, Pawlik A, Wilk J, Jałowiecki P, Więcek A (2011) Acute kidney injury before organ procurement is associated with worse long-term kidney graft outcome. Transplant Proc 43:2871–2874
Zuckerman JM, Singh RP, Farney AC, Rogers J, Stratta RJ (2009) Single center experience transplanting kidneys from deceased donors with terminal acute renal failure. Surgery 146:686–694
Bacak-Kocman I, Peric M, Kastelan Z, Kes P, Mesar I, Basic-Jukic N (2013) First documented case of successful kidney transplantation from a donor with acute renal failure treated with dialysis. Int Urol Nephrol 45:1523–1526
Heilman RL, Smith ML, Kurian SM, Huskey J, Batra RK, Chakkera HA, Katariya NN, Khamash H, Moss A, Salomon DR, Reddy KS (2015) Transplanting kidneys from deceased donors with severe acute kidney injury. Am J Transplant 15:2143–2151
Riethmüller S, Ferrari-Lacraz S, Müller MK, Raptis DA, Hadaya K, Rüsi B, Laube G, Schneiter G, Fehr T, Villard J (2010) Donor-specific antibody levels and three generations of crossmatches to predict antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation. Transplantation 90:160–167
Tait BD, Süsal C, Gebel HM, Nickerson PW, Zachary AA, Claas FH, Reed EF, Bray RA, Campbell P, Chapman JR, Coates PT, Colvin RB, Cozzi E, Doxiadis II, Fuggle SV, Gill J, Glotz D, Lachmann N, Mohanakumar T, Suciu-Foca N, Sumitran-Holgersson S, Tanabe K, Taylor CJ, Tyan DB, Webster A, Zeevi A, Opelz G (2013) Consensus guidelines on the testing and clinical management issues associated with HLA and non-HLA antibodies in transplantation. Transplantation 95:19–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial support and no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that the results presented in this paper have not been published previously in whole or part except in abstract format.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallinat, A., Leerhoff, S., Paul, A. et al. Kidney transplantation from deceased donors with elevated serum creatinine. Langenbecks Arch Surg 401, 1211–1217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1445-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1445-9