Abstract
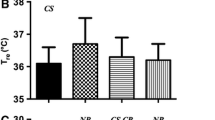
Many drowning victims have alcohol in their blood, but it is not clear whether there is a causal relationship. This study examined the effect of moderate alcohol consumption on the initial responses to cold water immersion. Sixteen subjects wearing swimming costumes undertook two, 3-min head-out seated immersions in water at 15 °C. One hour before immersion, subjects drank either 3.7 ml · kg body water–1 of 40% v:v alcohol as vodka, or an equivalent volume of water (control) mixed with squash. On immersion, the average blood alcohol concentration was 23 mmol · l–1 (105 mg · 100 ml–1) after alcohol consumption and zero in the control condition. Respiratory frequency in the first 20 s of immersion was found to be reduced (P < 0.05) by 10% (a total of 2–3 breaths) after alcohol consumption compared to the control immersion. Tidal volume, heart rate, rectal temperature and skin temperatures did not differ significantly between immersions. It is concluded that moderate alcohol consumption does not attenuate the initial "cold shock" responses to a practically significant extent and is thus unlikely to reduce the risk of drowning on immersion in cold water.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 28 November 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franks, C., Golden, F., Hampton, I. et al. The effect of blood alcohol on the initial responses to cold water immersion in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 75, 279–281 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050161
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050161