Abstract
Purpose
β2-Agonists have been proposed as weight-loss treatment, because they elevate energy expenditure. However, it is unknown what effect β2-agonists have on energy expenditure in overweight individuals. Furthermore, the influence of β2-agonist R- and S-enantiomer ratio for the increased energy expenditure is insufficiently explored.
Methods
Nineteen males were included in the study of which 14 completed. Subjects were 31.6 (±3.5) years [mean (±95% CI)] and had a fat percentage of 22.7 (±2.1)%. On separate days, subjects received either placebo or inhaled racemic (rac-) formoterol (2 × 27 µg). After an overnight fast, energy expenditure and substrate oxidation were estimated by indirect calorimetry at rest and during submaximal exercise. Plasma (R,R)- and (S,S)-formoterol enantiomer levels were measured by ultra-performance liquid chromatograph–mass spectrometry.
Results
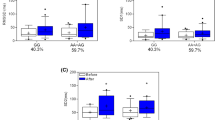
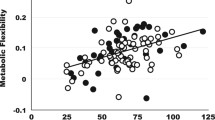
At rest, energy expenditure and fat oxidation were 12% (P ≤ 0.001) and 38% (P = 0.006) higher for rac-formoterol than placebo. Systemic (R,R):(S,S) formoterol ratio was correlated with change in energy expenditure at rest in response to rac-formoterol (r = 0.63, P = 0.028), whereas no association was observed between fat percentage and rac-formoterol-induced change in energy expenditure. During exercise, energy expenditure was not different between treatments, although carbohydrate oxidation was 15% higher (P = 0.021) for rac-formoterol than placebo. Rac-formoterol-induced shift in substrate choice from rest to exercise was related to plasma ln-rac-formoterol concentrations (r = 0.75, P = 0.005).
Conclusion
Selective β2-adrenoceptor agonism effectively increases metabolic rate and fat oxidation in overweight individuals. The potential for weight loss induced by β2-agonists may be greater for R-enantiopure formulations.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BW:
-
Body weight
- β2-agonist:
-
Beta2-adrenoceptor agonist
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- DXA:
-
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
- EE:
-
Energy expenditure
- \({\dot{\text{V}}\text{O}}_{{2{ \hbox{max} }}}\) :
-
Maximal oxygen uptake
- RER:
-
Respiratory exchange ratio
- MDL:
-
Method detection limit
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- SD:
-
Standardized mean difference
- UPLC–MS/MS:
-
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometer
References
Astrup A (1995) The sympathetic nervous system as a target for intervention in obesity. Int J Obes Rat Metab Disord 19:S24–S28
Baker JG (2010) The selectivity of beta-adrenoceptor agonists at human beta1-, beta2- and beta3-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol 160:1048–1061
Bakker LE, Boon MR, van der Linden RA, Arias-Bouda LP, van Klinken JB, Smit F, Verberne HJ, Jukema JW, Tamsma JT, Havekes LM, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Jazet IM, Rensen PC (2014) Brown adipose tissue volume in healthy lean south Asian adults compared with white Caucasians: a prospective, case-controlled observational study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2:210–217
Blaak EE, Schiffelers SL, Saris WH, Mensink M, Kooi ME (2004) Impaired beta-adrenergically mediated lipolysis in skeletal muscle of obese subjects. Diabetologia 47:1462–1468
Burniston JG, Tan LB, Goldspink DF (2006) Relative myotoxic and haemodynamic effects of the beta-agonists fenoterol and clenbuterol measured in conscious unrestrained rats. Exp Physiol 91:1041–1049
Cao W, Medvedev AV, Daniel KW, Collins S (2001) β-Adrenergic activation of p38 MAP kinase in adipocytes: cAMP induction of the uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) gene requires p38 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem 276:27077–27082
Cheymol G (2000) Effects of obesity on pharmacokinetics implications for drug therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet 39:215–231
Clausen T, Flatman JA (1980) Beta 2-adrenoceptors mediate the stimulating effect of adrenaline on active electrogenic Na-K-transport in rat soleus muscle. Br J Pharmacol 68:749–755
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Derks MG, van den Berg BT, van der Zee JS, Braat MC, van Boxtel CJ (1997) Biphasic effect-time courses in man after formoterol inhalation: eosinopenic and hypokalemic effects and inhibition of allergic skin reactions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:824–832
Dyreborg A, Krogh N, Backer V, Rzeppa S, Hemmersbach P, Hostrup M (2016) Pharmacokinetics of oral and inhaled terbutaline after exercise in trained men. Front Pharmacol 7:150
Elers J, Hostrup M, Pedersen L, Henninge J, Hemmersbach P, Dalhoff K, Backer V (2012) Urine and serum concentrations of inhaled and oral terbutaline. Int J Sports Med 33:1026–1033
Emery PW, Rothwell NJ, Stock MJ, Winter PD (1984) Chronic effects of beta 2-adrenergic agonists on body composition and protein synthesis in the rat. Biosci Rep 4:83–91
Ernande L, Stanford KI, Thoonen R, Zhang H, Clerte M, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ, Bloch KD, Buys ES, Scherrer-Crosbie M (2016) Relationship of brown adipose tissue perfusion and function: a study through β2-adrenoreceptor stimulation. J Appl Physiol 120:825–832
Ferrannini E (1988) The theoretical bases of indirect calorimetry: a review. Metabolism 37:287–301
Gregorevic P, Ryall JG, Plant DR, Sillence MN, Lynch GS (2005) Chronic beta-agonist administration affects cardiac function of adult but not old rats, independent of beta-adrenoceptor density. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:344–349
Gross NJ, Kerwin E, Levine B, Kim KT, Denis-Mize K, Hamzavi M, Carpenter M, Rinehart M (2008) Nebulized formoterol fumarate: dose selection and pharmacokinetics. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 21:818–823
Haman F, Peronnet F, Kenny GP, Massicotte D, Lavoie C, Scott C, Weber JM (2002) Effect of cold exposure on fuel utilization in humans: plasma glucose, muscle glycogen, and lipids. J Appl Physiol 93:77–84
Hoeks J, van Baak MA, Hesselink MK, Hul GB, Vidal H, Saris WH, Schrauwen P (2003) Effect of beta1- and beta2-adrenergic stimulation on energy expenditure, substrate oxidation, and UCP3 expression in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:775–782
Hostrup M, Kalsen A, Ortenblad N, Juel C, Mørch K, Rzeppa S, Karlsson S, Backer V, Bangsbo J (2014) β2-Adrenergic stimulation enhances Ca2+ release and contractile properties of skeletal muscles, and counteracts exercise-induced reductions in Na+–K+–ATPase Vmax in trained men. J Physiol 592:5445–5459
Hostrup M, Kalsen A, Onslev J, Jessen S, Haase C, Habib S, Ørtenblad N, Backer V, Bangsbo J (2015) Mechanisms underlying enhancements in muscle force and power output during maximal cycle ergometer exercise induced by chronic β2-adrenergic stimulation in men. J Appl Physiol 119:475–486
Hue L, Maisin L, Rider MH (1988) Palmitate inhibits liver glycolysis. Involvement of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the glucose/fatty acid cycle. Biochem J 251:541–545
Hulot F, Ouhayoun J, Manoucheri M (1996) Effect of clenbuterol on productive performance, body composition and muscle biochemistry in the rabbit. Meat Sci 42:457–464
Jacobson GA, Yee KC, Premilovac D, Rattigan S (2014) Enantioselective disposition of (R/S)-albuterol in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Drug Test Anal 6:563–567
Jacobson GA, Yee KC, Wood-Baker R, Walters EH (2015) SULT 1A3 single-nucleotide polymorphism and the single dose pharmacokinetics of inhaled salbutamol enantiomers: are some athletes at risk of higher urine levels? Drug Test Anal 7:109–113
Jacobson GA, Hostrup M, Narkowicz CK, Nichols DS, Haydn Walters E (2016) Enantioselective disposition of (R)-salmeterol and (S)-salmeterol in urine following inhaled dosing and application to doping control. Drug Test Anal. doi:10.1002/dta.2131 (Epub ahead of print)
Jensen J, Dahl HA (1995) Adrenaline stimulated glycogen breakdown in rat epitrochlearis muscles: fibre type specificity and relation to phosphorylase transformation. Biochem Mol Biol Int 35:145–154
Jeppsson AB, Waldeck B, Widmark E (1986) Further studies on the cardiomegaly induced by beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 58:121–125
Jocken JW, Roepstorff C, Goossens GH, van der Baan P, van Baak M, Saris WH, Kiens B, Blaak EE (2008) Hormone-sensitive lipase serine phosphorylation and glycerol exchange across skeletal muscle in lean and obese subjects: effect of beta-adrenergic stimulation. Diabetes 57:1834–1841
Källström BL, Sjöberg J, Waldeck B (1996) Steric aspects of formoterol and terbutaline: is there an adverse effect of the distomer on airway smooth muscle function? Chirality 8:567–573
Kalsen A, Hostrup M, Karlsson S, Hemmersbach P, Bangsbo J, Backer V (2014) Effect of inhaled terbutaline on substrate utilization and 300-kcal time trial performance. J Appl Physiol 117:1180–1187
Kalsen A, Hostrup M, Backer V, Bangsbo J (2016) Effect of formoterol, a long-acting β2-adrenergic agonist, on muscle strength and power output, metabolism, and fatigue during maximal sprinting in men. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 310:1312–1321
Lecaillon JB, Kaiser G, Palmisano M, Morgan J, Della Cioppa G (1999) Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of formoterol in healthy volunteers after a single high dose of Foradil dry powder inhalation via aerolizer. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 55:131–138
Lee P, Day RO, Greenfield JR, Ho KK (2013) Formoterol, a highly β2-selective agonist, increases energy expenditure and fat utilisation in men. Int J Obes (Lond) 37:593–597
Löfdahl CG, Svedmyr N (1989) Formoterol fumarate, a new beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Acute studies of selectivity and duration of effect after inhaled and oral administration. Allergy 44:264–271
Lund J, Gillum MP (2016) Towards leanness by ‘Feeding’ a novel thermogenic pathway? Trends Endocrinol Metab 27:529–530
Lynch GS, Ryall JG (2008) Role of beta-adrenoceptor signaling in skeletal muscle: implications for muscle wasting and disease. Physiol Rev 88:729–767
Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M et al (2014) Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 384:766–781
Randle PJ (1964) The interrelationships of hormones, fatty acid and glucose in the provision of energy. Postgrad Med J 40:457–463
Randle PJ (1995) Metabolic fuel selection: general integration at the whole-body level. Proc Nutr Soc 54:317–327
Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA (1963) The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1:785–789
Ryall JG, Sillence MN, Lynch GS (2006) Systemic administration of beta2-adrenoceptor agonists, formoterol and salmeterol, elicit skeletal muscle hypertrophy in rats at micromolar doses. Br J Pharmacol 147:587–595
Schiffelers SL, Saris WH, Boomsma F, van Baak MA (2001) Beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated thermogenesis and lipid utilization in obese and lean men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2191–2199
Schmidt D, Källström BL, Waldeck B, Branscheid D, Magnussen H, Rabe KF (2000) The effect of the enantiomers of formoterol on inherent and induced tone in guinea-pig trachea and human bronchus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 361:405–409
Simonsen S, Kjekshus JK (1978) The effect of free fatty acids on myocardial oxygen consumption during atrial pacing and catecholamine infusion in man. Circulation 58:484–491
Suko J, Maurer-Fogy I, Plank B, Bertel O, Wyskovsky W, Hohenegger M, Hellmann G (1993) Phosphorylation of serine 2843 in ryanodine receptor-calcium release channel of skeletal muscle by cAMP-, cGMP- and CaM-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1175:193–206
Vosselman MJ, van der Lans AA, Brans B, Wierts R, van Baak MA, Schrauwen P, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD (2012) Systemic β-adrenergic stimulation of thermogenesis is not accompanied by brown adipose tissue activity in humans. Diabetes 61:3106–3113
Whale CI, Sovani MP, Mortimer KJ, Harrison TW, Tattersfield AE (2008) Systemic and bronchodilator effects of inhaled rac-formoterol in subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a dose–response study. Br J Clin Pharmacol 65:841–847
White M, Roden R, Minobe W, Khan MF, Larrabee P, Wollmering M, Port JD, Anderson F, Campbell D, Feldman AM et al (1994) Age-related changes in beta-adrenergic neuroeffector systems in the human heart. Circulation 90:1225–1238
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Jens Lund for many fruitful scientific discussions during the writing process and Dr. David Nichols (Central Science Laboratory, University of Tasmania) for conducting the UPLC–MS/MS instrumental analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JO collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data, and drafted the manuscript. GJ developed and supervised the enantioselective UPLC–MS/MS analytical component of the study, including assay performance, analysis and reporting of results, as well as contributing to the final manuscript. CN undertook the UPLC–MS/MS sample preparation and method UPLC–MS/MS optimization, and reviewed the manuscript. VB was the responsible medical doctor of the study and performed medical examination of the subjects, and contributed to interpretation and review of the manuscript. AK, MK, and SJ conducted the human experiments and contributed to interpretation of the data and in drafting of the manuscript. JB and MH designed the study and contributed to data collection, analysis, interpretation, and in drafting of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The study was supported by the Danish Ministry of Culture. The funder had no role in the design of the study, the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data or the writing of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Jean-René Lacour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onslev, J., Jacobson, G., Narkowicz, C. et al. Beta2-adrenergic stimulation increases energy expenditure at rest, but not during submaximal exercise in active overweight men. Eur J Appl Physiol 117, 1907–1915 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3679-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3679-9